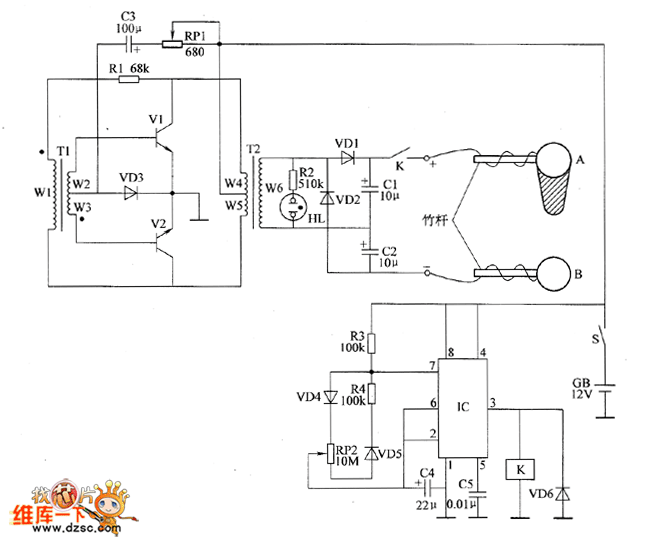
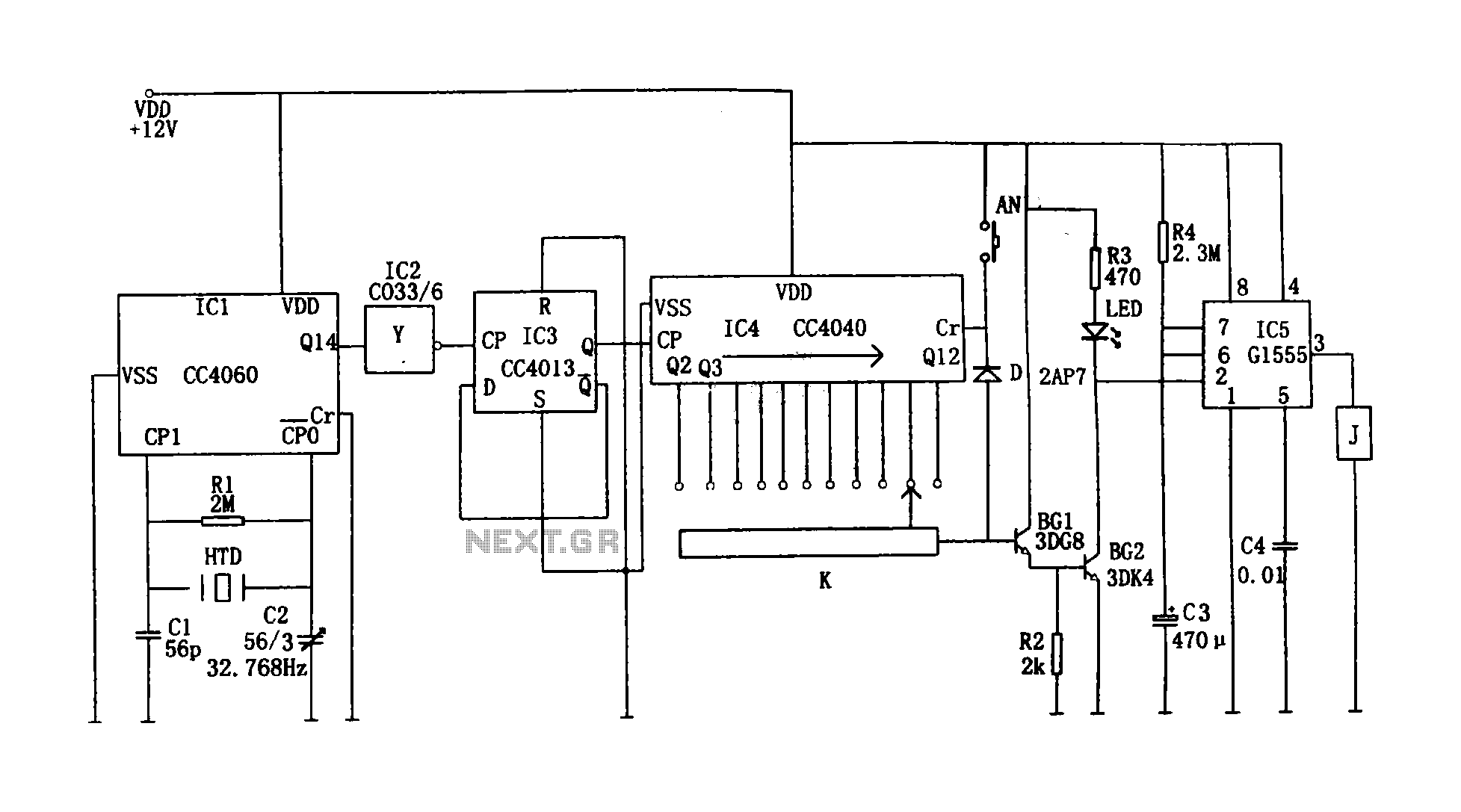
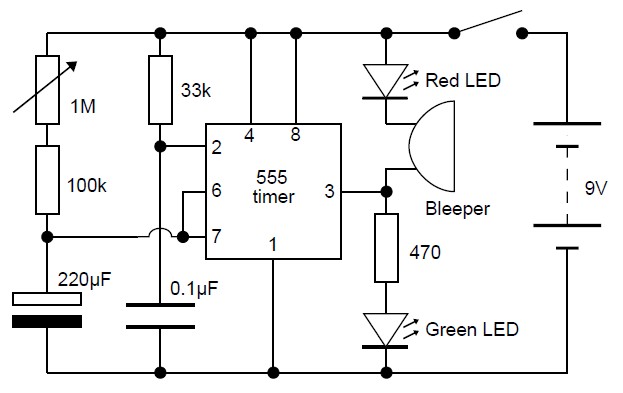
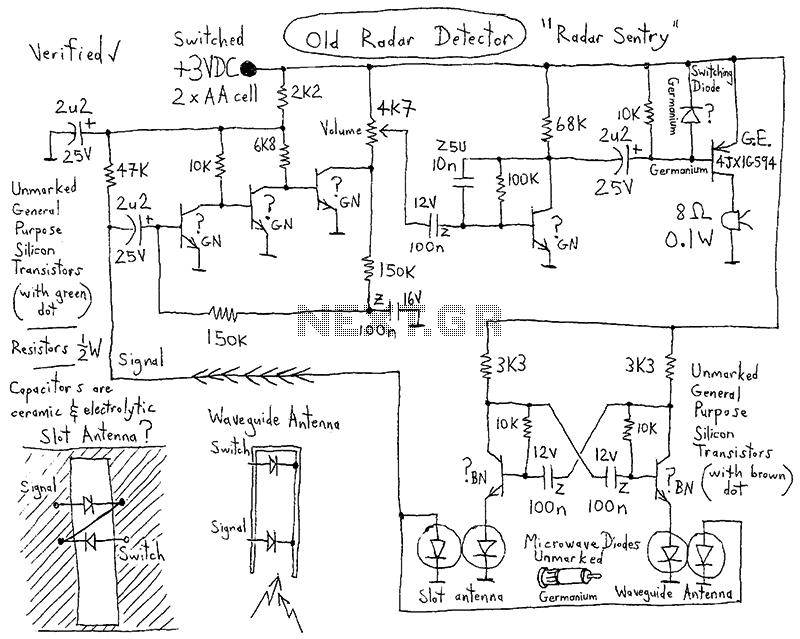
When using the lamp base circuit delay circuit 2
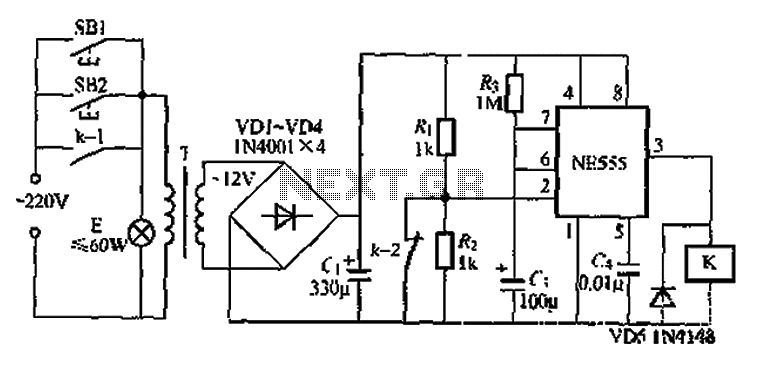
Another application involves the use of a NE555 delay lamp circuit, where components SB1 and SH2 act as J-light buttons that can be installed in two different locations. The lamp can be activated by pressing either SB1 or SB2, which energizes the E lamp to emit light. The circuit utilizes a VDL VD4 bridge rectifier to provide approximately 12V DC output. At this point, the NE555 timebase circuit's pin 2 is activated, causing the output to switch high. This action energizes relay K, closing contact K1 and locking the gate circuit; contact K2 trips due to resistors R, which stabilize the voltage to approximately 2/3V, ensuring the E lamp remains illuminated. When the voltage drops, the capacitor C discharges quickly through pin 3 of the NE555, preparing for the next activation of the delay lamp. Meanwhile, relay K releases, opening contact K1, and the E lamp turns off. The circuit is designed to consume minimal power after the light is turned off, utilizing a small electromagnetic relay, such as the JRX-13F, rated for DC 12V.
The NE555 timer, configured in a monostable mode, serves as the core of the delay lamp circuit. When either button SB1 or SB2 is pressed, the circuit triggers a pulse that causes the NE555 to output a high signal. This high signal is responsible for energizing the relay K, which in turn closes contact K1 to maintain the circuit's operation and keep the E lamp illuminated. The use of a bridge rectifier (VDL VD4) ensures that the circuit receives a stable DC voltage from an AC source, which is crucial for the reliable operation of the NE555 timer.
The stability of the lamp's illumination is maintained by the voltage divider formed by resistors R, which ensures that the voltage at pin 2 of the NE555 remains above the threshold level required for the timer to continue its output. When the capacitor C charges to approximately 2/3 of the supply voltage, the NE555 transitions back to its low state, deactivating relay K and consequently turning off the E lamp.
This design effectively manages power consumption by utilizing an electromagnetic relay that minimizes energy usage when the lamp is off. The choice of a compact relay, such as the JRX-13F, allows for a space-efficient design while ensuring reliable performance in switching applications. Overall, this NE555 delay lamp circuit is a practical solution for applications requiring delayed lighting with minimal power consumption.Another is the use of money when NE55S delay lamp circuit group circuit, SB1, SH2 are J-light button, can be installed in two different places, the lamp can be operated E. Pres s F SB1 or SB2, the E lamp that is energized to emit light. While alternating purple T Buck, VDL VD4 bridge rectifier in j two ends about 12 DC output voltage. At this point NE55j timebase circuit feet because contacts k 2 closed together is low, the time base circuit is set feet high output, relay K station, which station contact k 1 closed, the gate circuit lock; break contact k-2 tripped due to R, R. Partial pressure foot level stabilization in]/2v m, circuit status will not change, so the E lamp remains lit.
Then power through resistor R. Ask ( electricity crisis, when charged to the supply voltage of 2/3, just reset circuit group, C, store charge quickly through feet to NE555 internal vent tube put q three - cho ready for the next turn on the lights ashamed delay, Meanwhile lemma relay K release, contact k1, k-2 complex position, lamp E goes out. book circuit characteristics after the lights, and then a small circuit consume any power relay K Gallery has adopted two silk small electric shock to convert electromagnetic relays, such as JRX-13F, DC12V type.
The NE555 timer, configured in a monostable mode, serves as the core of the delay lamp circuit. When either button SB1 or SB2 is pressed, the circuit triggers a pulse that causes the NE555 to output a high signal. This high signal is responsible for energizing the relay K, which in turn closes contact K1 to maintain the circuit's operation and keep the E lamp illuminated. The use of a bridge rectifier (VDL VD4) ensures that the circuit receives a stable DC voltage from an AC source, which is crucial for the reliable operation of the NE555 timer.
The stability of the lamp's illumination is maintained by the voltage divider formed by resistors R, which ensures that the voltage at pin 2 of the NE555 remains above the threshold level required for the timer to continue its output. When the capacitor C charges to approximately 2/3 of the supply voltage, the NE555 transitions back to its low state, deactivating relay K and consequently turning off the E lamp.
This design effectively manages power consumption by utilizing an electromagnetic relay that minimizes energy usage when the lamp is off. The choice of a compact relay, such as the JRX-13F, allows for a space-efficient design while ensuring reliable performance in switching applications. Overall, this NE555 delay lamp circuit is a practical solution for applications requiring delayed lighting with minimal power consumption.Another is the use of money when NE55S delay lamp circuit group circuit, SB1, SH2 are J-light button, can be installed in two different places, the lamp can be operated E. Pres s F SB1 or SB2, the E lamp that is energized to emit light. While alternating purple T Buck, VDL VD4 bridge rectifier in j two ends about 12 DC output voltage. At this point NE55j timebase circuit feet because contacts k 2 closed together is low, the time base circuit is set feet high output, relay K station, which station contact k 1 closed, the gate circuit lock; break contact k-2 tripped due to R, R. Partial pressure foot level stabilization in]/2v m, circuit status will not change, so the E lamp remains lit.
Then power through resistor R. Ask ( electricity crisis, when charged to the supply voltage of 2/3, just reset circuit group, C, store charge quickly through feet to NE555 internal vent tube put q three - cho ready for the next turn on the lights ashamed delay, Meanwhile lemma relay K release, contact k1, k-2 complex position, lamp E goes out. book circuit characteristics after the lights, and then a small circuit consume any power relay K Gallery has adopted two silk small electric shock to convert electromagnetic relays, such as JRX-13F, DC12V type.