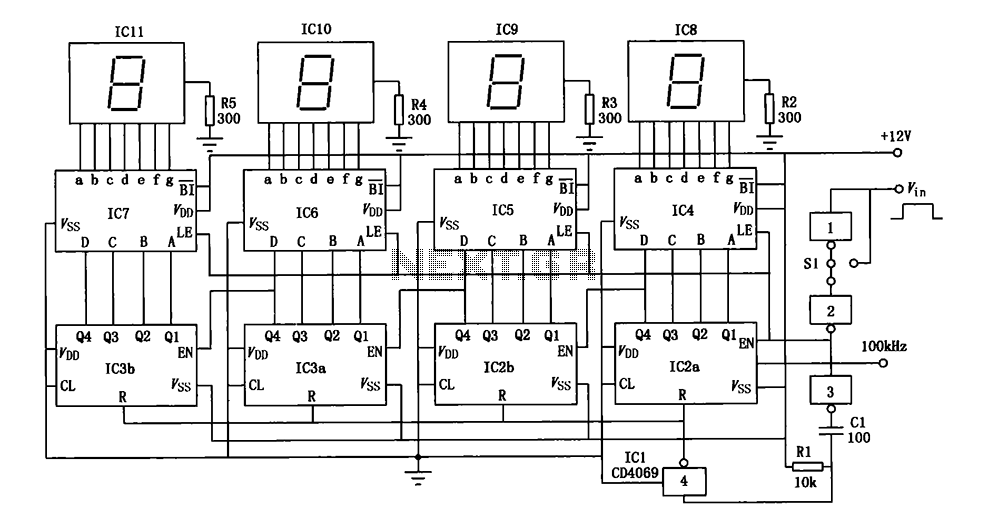
A Dual Temperature Display With Humidity Measurement
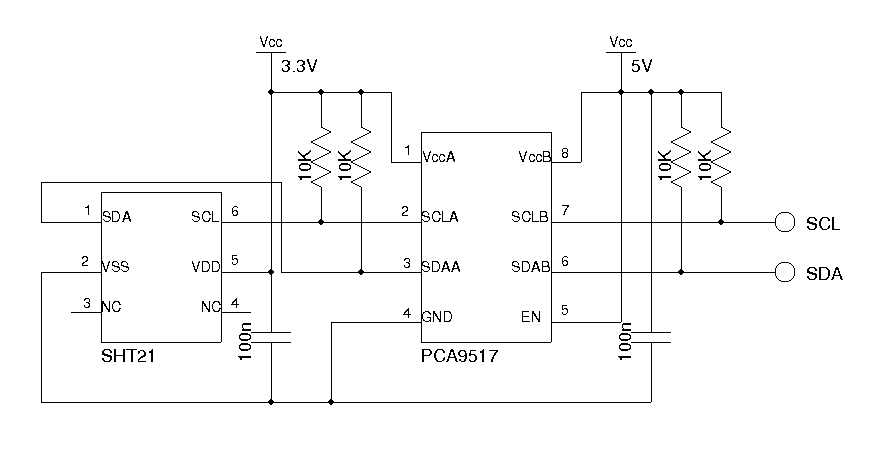
This thermometer employs an LM19 sensor, calibrated to measure a broad temperature range of -55 to 130 degrees Celsius (-67 to 266 degrees Fahrenheit) for outdoor temperature readings. For indoor temperature and humidity measurements, it utilizes an SHT21 digital sensor. An ATmega328 microcontroller is responsible for reading the temperatures from both the analog LM19 sensor, which connects through an analog input pin, and the digital SHT21 sensor via the I2C bus. Since the SHT21 operates at 3V logic while the remainder of the circuit operates at 5V logic, a voltage translation circuit is required to interface the SHT21 with the microcontroller. The Texas Instruments PCA9517 level-translating I2C bus repeater is used as the voltage level shifter. The SHT21 sensor is mounted on a breakout board and linked to the microcontroller board using a short cable. The LM19 sensor is encapsulated in heat-shrinking tubing and connected to the controller via a stereo cable, which can be extended up to 30 feet as long as the load capacitance remains below 300pF.
The thermometer circuit integrates several components to achieve accurate temperature and humidity measurements in both indoor and outdoor environments. The LM19 temperature sensor is a precision analog device that outputs a voltage proportional to the temperature, which is read by the ATmega328 microcontroller through one of its analog input pins. This microcontroller, a member of the popular AVR family, is programmed to process the analog signal and convert it into a digital temperature reading.
For indoor measurements, the SHT21 sensor provides both temperature and humidity data via the I2C communication protocol. The use of the PCA9517 level translator is crucial for ensuring compatibility between the 5V logic of the microcontroller and the 3V logic of the SHT21. This component allows for bidirectional communication on the I2C bus while maintaining signal integrity, thus preventing data loss or corruption.
The physical layout of the circuit is designed for practicality and ease of use. The SHT21 sensor is mounted on a breakout board, which simplifies connections and allows for easy integration with the microcontroller. A short cable connects this breakout board to the main MCU board, ensuring minimal signal loss and interference. The LM19 sensor, protected by heat-shrinking tubing, is connected via a stereo cable, which is advantageous for long-distance applications. The cable can be extended to a maximum length of 30 feet, provided that the total load capacitance does not exceed 300pF, ensuring reliable performance in various environmental conditions.
Overall, this thermometer design effectively combines analog and digital sensing technologies, utilizing a robust microcontroller and appropriate interfacing techniques to deliver accurate and reliable temperature and humidity readings across a wide range of applications.This thermometer uses an LM19 sensor calibrated for measuring a wide temperature range (-55 130 Celsius, -67 266 Fahrenheit) for outdoor temperature measurement and an SHT21 digital thermometer with humidity measurement for indoor use. An ATmega328 microcontroller is used to read the temperatures from both an analog sensor LM19 using an analog input pin and a digital sensor
SHT21 using the I2C bus. Since SHT21 uses 3V logic while the rest of the circuit uses 5V logic, a voltage translation circuit is necessary to interface SHT21 with the MCU. I used Taxes Instruments s PCA9517 level-translating I2C bus repeater as the voltage level shifter. The voltage shifting circuit is shown below: The SHT21 sensor is mounted on a breakout board and connected to the MCU board via a short cable.
The LM19 sensor is encapsulated in a section of heat-shrinking tube and connected to the controller via a stereo cable. The cable length used can easily be extended to as long as 30 feet as long as the load capacitance is less than 300pF.
🔗 External reference
The thermometer circuit integrates several components to achieve accurate temperature and humidity measurements in both indoor and outdoor environments. The LM19 temperature sensor is a precision analog device that outputs a voltage proportional to the temperature, which is read by the ATmega328 microcontroller through one of its analog input pins. This microcontroller, a member of the popular AVR family, is programmed to process the analog signal and convert it into a digital temperature reading.
For indoor measurements, the SHT21 sensor provides both temperature and humidity data via the I2C communication protocol. The use of the PCA9517 level translator is crucial for ensuring compatibility between the 5V logic of the microcontroller and the 3V logic of the SHT21. This component allows for bidirectional communication on the I2C bus while maintaining signal integrity, thus preventing data loss or corruption.
The physical layout of the circuit is designed for practicality and ease of use. The SHT21 sensor is mounted on a breakout board, which simplifies connections and allows for easy integration with the microcontroller. A short cable connects this breakout board to the main MCU board, ensuring minimal signal loss and interference. The LM19 sensor, protected by heat-shrinking tubing, is connected via a stereo cable, which is advantageous for long-distance applications. The cable can be extended to a maximum length of 30 feet, provided that the total load capacitance does not exceed 300pF, ensuring reliable performance in various environmental conditions.
Overall, this thermometer design effectively combines analog and digital sensing technologies, utilizing a robust microcontroller and appropriate interfacing techniques to deliver accurate and reliable temperature and humidity readings across a wide range of applications.This thermometer uses an LM19 sensor calibrated for measuring a wide temperature range (-55 130 Celsius, -67 266 Fahrenheit) for outdoor temperature measurement and an SHT21 digital thermometer with humidity measurement for indoor use. An ATmega328 microcontroller is used to read the temperatures from both an analog sensor LM19 using an analog input pin and a digital sensor
SHT21 using the I2C bus. Since SHT21 uses 3V logic while the rest of the circuit uses 5V logic, a voltage translation circuit is necessary to interface SHT21 with the MCU. I used Taxes Instruments s PCA9517 level-translating I2C bus repeater as the voltage level shifter. The voltage shifting circuit is shown below: The SHT21 sensor is mounted on a breakout board and connected to the MCU board via a short cable.
The LM19 sensor is encapsulated in a section of heat-shrinking tube and connected to the controller via a stereo cable. The cable length used can easily be extended to as long as 30 feet as long as the load capacitance is less than 300pF.
🔗 External reference