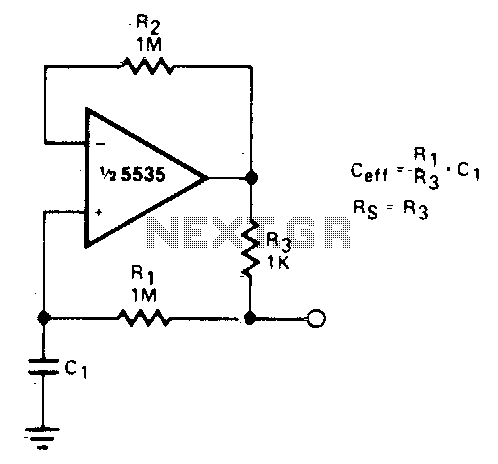
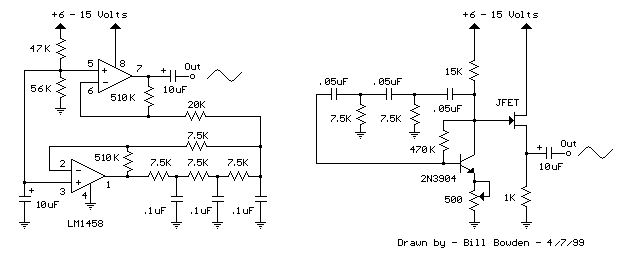
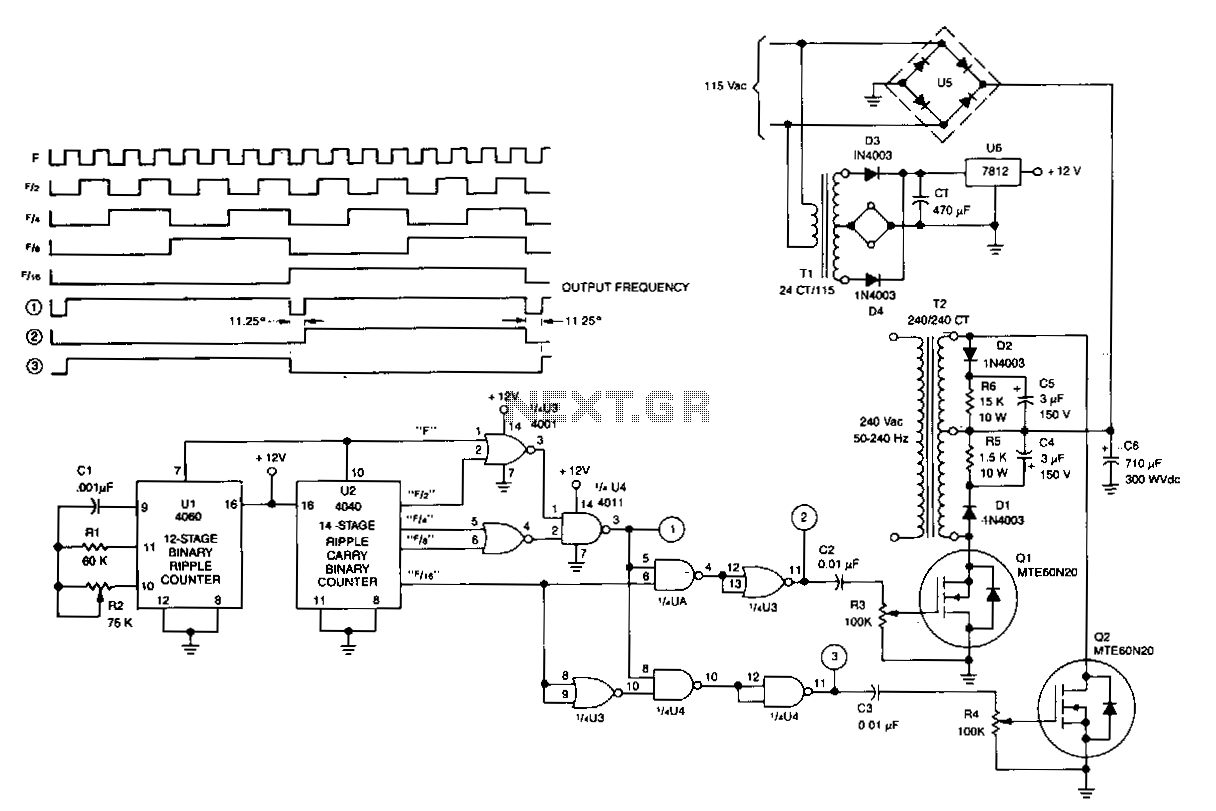
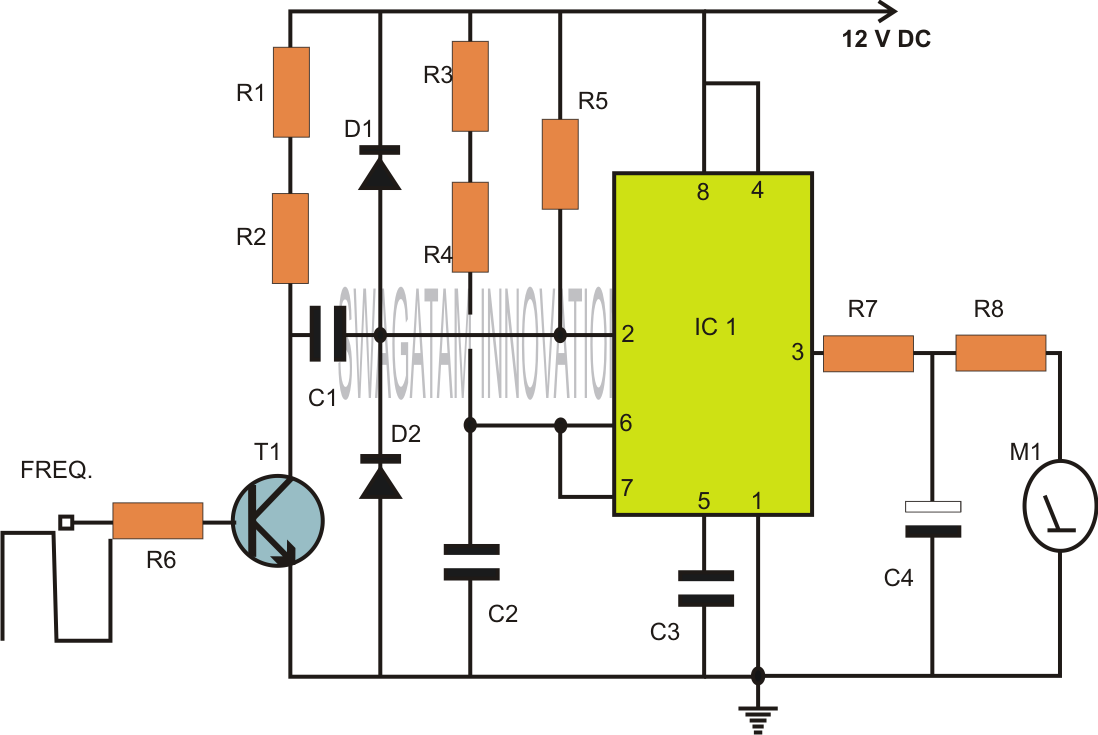
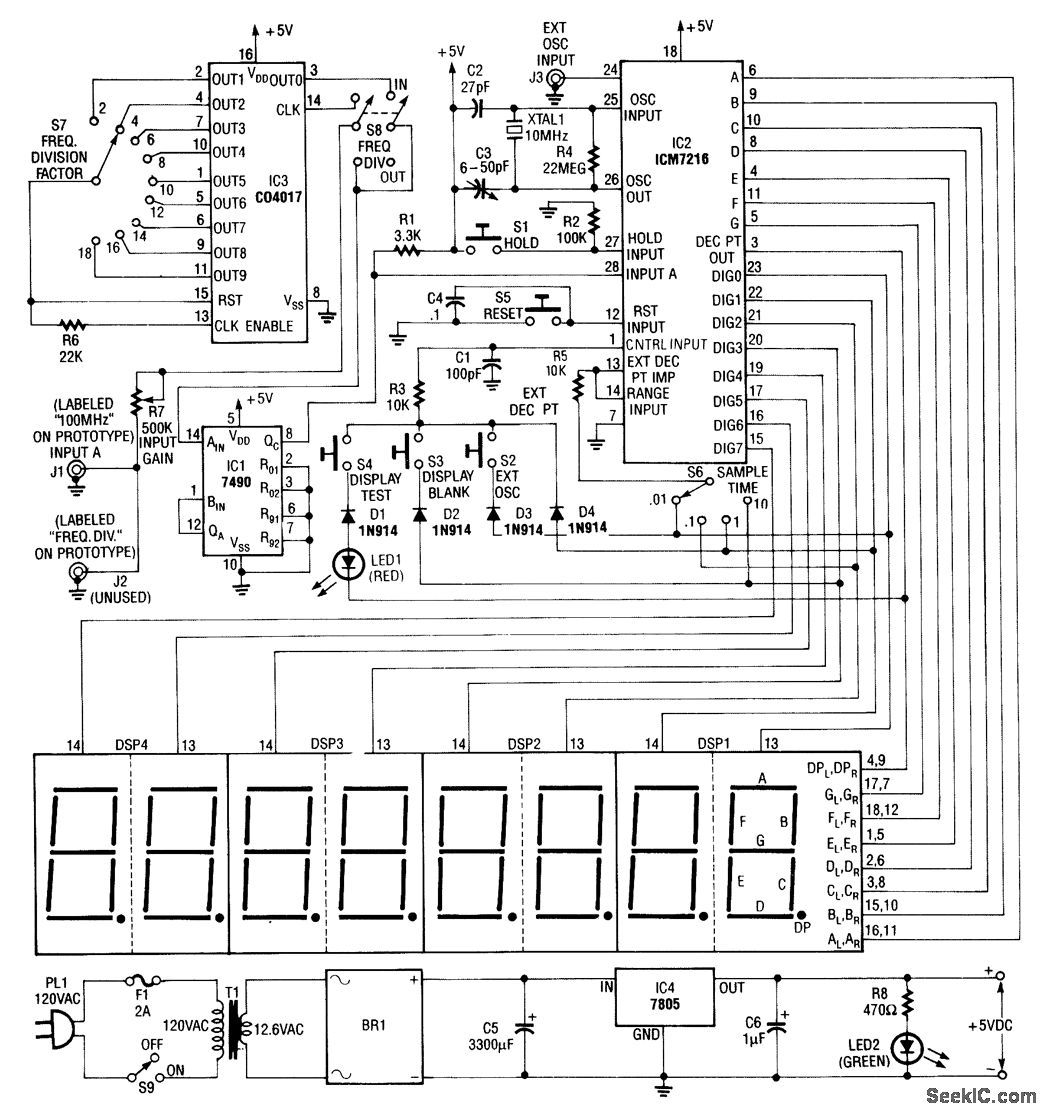
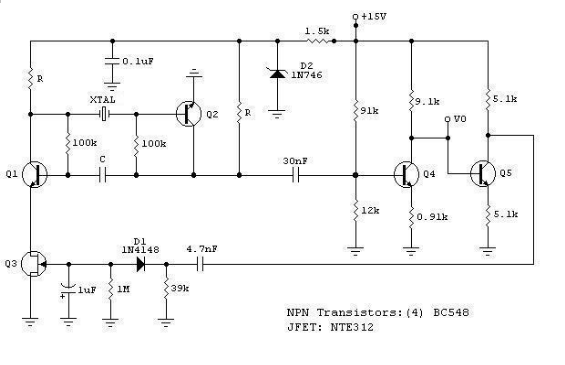
A frequency multiplier in depth
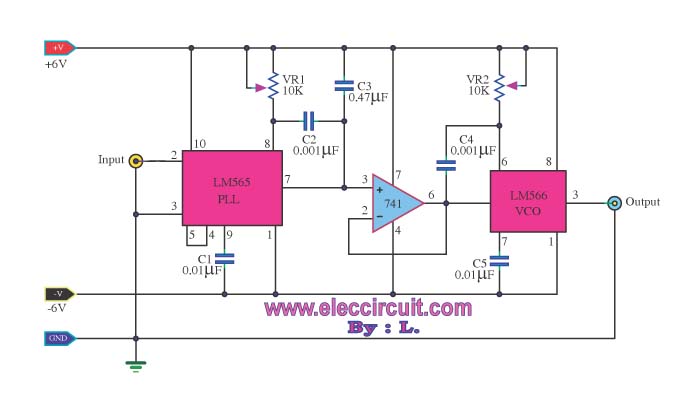
Most frequency multiplier circuits utilize an integrated circuit (IC) phase-locked loop (PLL). These circuits typically increase the frequency by an integer factor only. However, this particular circuit is capable of doubling the frequency.
Frequency multiplier circuits are essential in various applications where signal frequency needs to be increased for better performance or functionality. The phase-locked loop (PLL) is a fundamental component in these circuits, as it synchronizes the output frequency to a reference frequency input.
In this specific frequency doubling circuit, the PLL is configured to achieve a multiplication factor of two. The core components include a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO), a phase comparator, and a loop filter. The VCO generates a frequency that is controlled by the input signal. The phase comparator compares the phase of the input signal with the VCO output and generates an error signal that drives the loop filter. The loop filter smooths this error signal to provide a stable control voltage to the VCO, ensuring that the output frequency is precisely double that of the input frequency.
The circuit design may also incorporate additional features such as frequency stability enhancements, noise reduction techniques, and output buffering to ensure the doubled frequency signal maintains integrity across various loads and conditions. Proper layout considerations, including minimizing parasitic capacitance and inductance, are crucial in achieving optimal performance in high-frequency applications.
This frequency doubling circuit using a PLL is widely applicable in communication systems, RF transmission, and signal processing where precise frequency control is paramount.Most of the frequency multiplier circuit using IC phase locked loop (PLL).It will increase the frequency to an integer only. But this circuit can double the.. 🔗 External reference
Frequency multiplier circuits are essential in various applications where signal frequency needs to be increased for better performance or functionality. The phase-locked loop (PLL) is a fundamental component in these circuits, as it synchronizes the output frequency to a reference frequency input.
In this specific frequency doubling circuit, the PLL is configured to achieve a multiplication factor of two. The core components include a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO), a phase comparator, and a loop filter. The VCO generates a frequency that is controlled by the input signal. The phase comparator compares the phase of the input signal with the VCO output and generates an error signal that drives the loop filter. The loop filter smooths this error signal to provide a stable control voltage to the VCO, ensuring that the output frequency is precisely double that of the input frequency.
The circuit design may also incorporate additional features such as frequency stability enhancements, noise reduction techniques, and output buffering to ensure the doubled frequency signal maintains integrity across various loads and conditions. Proper layout considerations, including minimizing parasitic capacitance and inductance, are crucial in achieving optimal performance in high-frequency applications.
This frequency doubling circuit using a PLL is widely applicable in communication systems, RF transmission, and signal processing where precise frequency control is paramount.Most of the frequency multiplier circuit using IC phase locked loop (PLL).It will increase the frequency to an integer only. But this circuit can double the.. 🔗 External reference