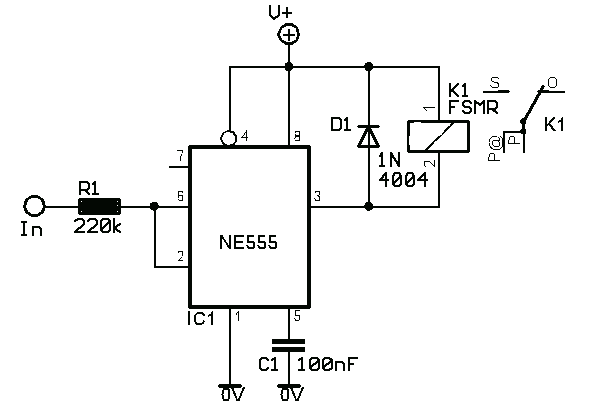
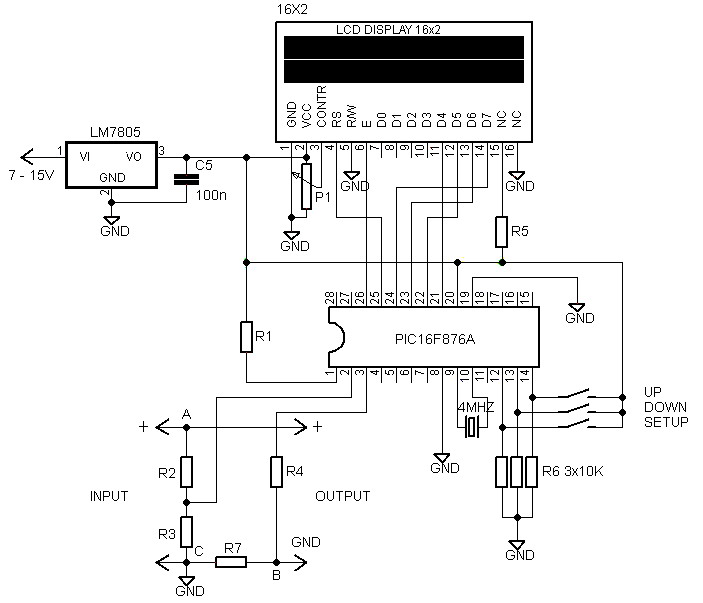
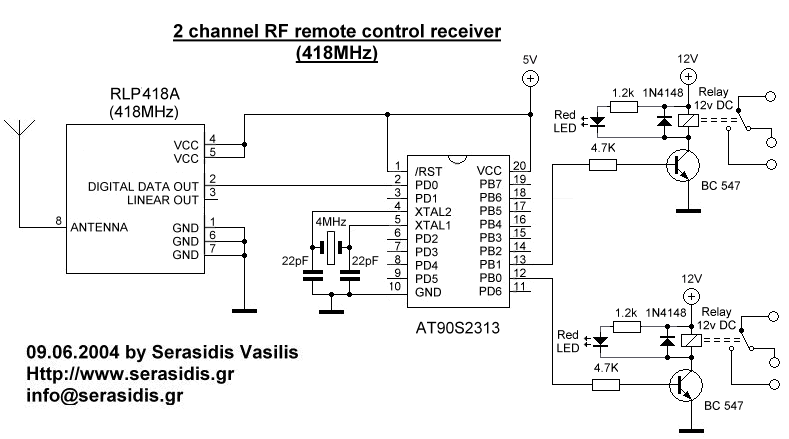
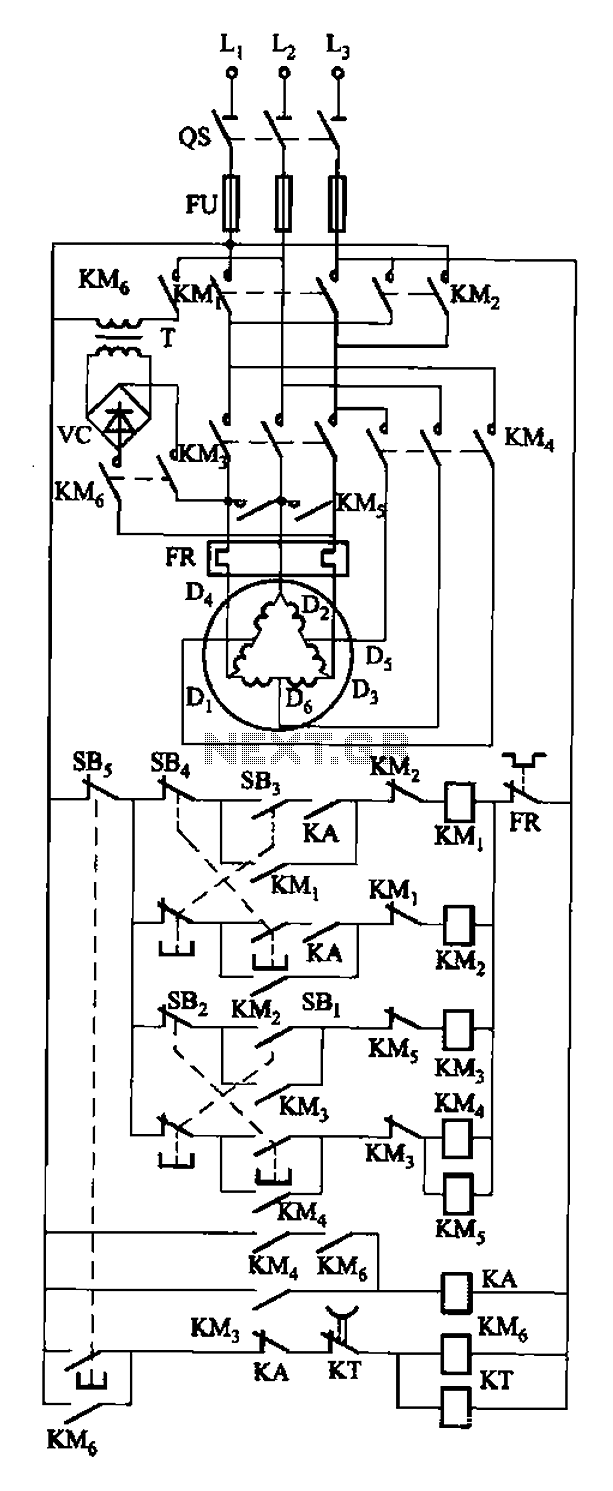
A given frequency control multiple motors operating in parallel circuits
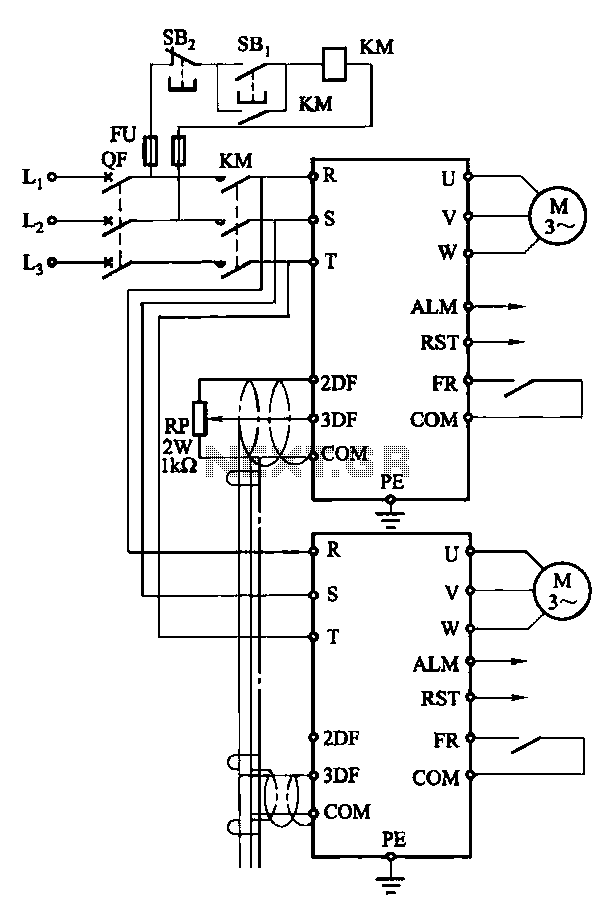
Each motor operates with an independent drive; however, only one frequency is utilized for a specific device. This setup employs a single RP potentiometer to control multiple motors in parallel.
In this configuration, the circuit design allows for multiple motors to be controlled simultaneously while maintaining individual operational characteristics. Each motor drive circuit is designed to be independent, ensuring that variations in load or performance do not adversely affect the operation of other motors in the system. The single frequency signal is generated by a common oscillator circuit, which is then fed into each motor drive circuit.
The RP (rotational position) potentiometer serves as a critical component in this design, allowing for the adjustment of the signal amplitude that is sent to each motor. This enables fine-tuning of motor speed and torque characteristics while ensuring that all motors receive the same frequency signal. The potentiometer can be adjusted to change the resistance in the circuit, thereby altering the voltage supplied to the motors and allowing for synchronized operation.
The schematic for this system would typically include the following components: a power supply to provide the necessary voltage and current to the motors, an oscillator circuit to generate the frequency signal, the RP potentiometer for signal adjustment, and individual drive circuits for each motor, which may include transistors or MOSFETs for switching and amplifying the control signal. Additionally, protection components such as diodes may be included to prevent back EMF from the motors from damaging the circuit.
This design is particularly useful in applications where multiple motors need to operate in unison, such as in robotics, conveyor systems, or automated machinery, allowing for efficient and coordinated movement.Each motor with independent drive, but only one frequency for a given device, which uses the same RP potentiometer to achieve a multiple motors in parallel.
In this configuration, the circuit design allows for multiple motors to be controlled simultaneously while maintaining individual operational characteristics. Each motor drive circuit is designed to be independent, ensuring that variations in load or performance do not adversely affect the operation of other motors in the system. The single frequency signal is generated by a common oscillator circuit, which is then fed into each motor drive circuit.
The RP (rotational position) potentiometer serves as a critical component in this design, allowing for the adjustment of the signal amplitude that is sent to each motor. This enables fine-tuning of motor speed and torque characteristics while ensuring that all motors receive the same frequency signal. The potentiometer can be adjusted to change the resistance in the circuit, thereby altering the voltage supplied to the motors and allowing for synchronized operation.
The schematic for this system would typically include the following components: a power supply to provide the necessary voltage and current to the motors, an oscillator circuit to generate the frequency signal, the RP potentiometer for signal adjustment, and individual drive circuits for each motor, which may include transistors or MOSFETs for switching and amplifying the control signal. Additionally, protection components such as diodes may be included to prevent back EMF from the motors from damaging the circuit.
This design is particularly useful in applications where multiple motors need to operate in unison, such as in robotics, conveyor systems, or automated machinery, allowing for efficient and coordinated movement.Each motor with independent drive, but only one frequency for a given device, which uses the same RP potentiometer to achieve a multiple motors in parallel.