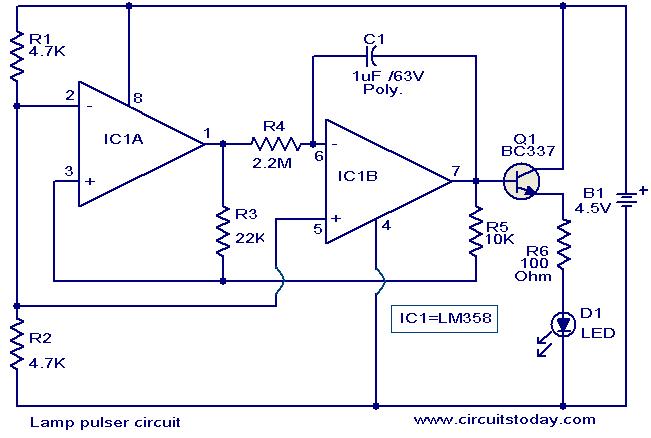
A pulse booster circuit
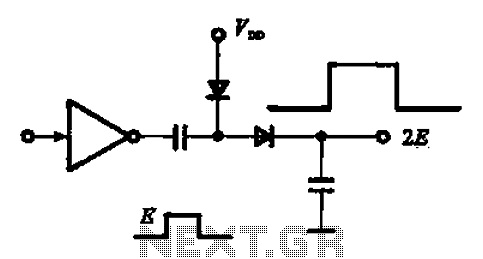
A pulse booster circuit is utilized to increase the pulse amplitude. The structure illustrated in figure (a) of the circuit can output a pulse amplitude that is twice that of the input. Figure (b) of the circuit can achieve twice the amplitude of the negative pulse.
The pulse booster circuit is designed to enhance the amplitude of input pulses, making it suitable for applications where signal strength is critical. The circuit typically employs a combination of transistors, capacitors, and resistors to achieve the desired amplification. In figure (a), the circuit configuration is likely to include a transistor configured as a common emitter amplifier, where the input pulse is fed into the base terminal. The collector terminal outputs a pulse that is amplified, resulting in an output that is double the amplitude of the input pulse.
In figure (b), the circuit is configured to amplify negative pulses. This may involve using a complementary push-pull arrangement of transistors to ensure that both positive and negative portions of the input waveform are effectively amplified. The design may also include feedback mechanisms to stabilize the output and prevent distortion, ensuring that the pulse shape is maintained while increasing amplitude.
The choice of components such as the type of transistors (e.g., NPN or PNP), the values of resistors and capacitors, and the power supply voltage will significantly influence the performance of the pulse booster circuit. Proper selection and configuration of these components are essential for achieving the desired amplification while maintaining signal integrity. Additionally, considerations regarding bandwidth, rise and fall times, and thermal management should be taken into account when designing and implementing a pulse booster circuit for specific applications.A pulse booster circuit When you need to increase the pulse amplitude, pulse boost circuit can be used, its structure, the figure (a) of the circuit can output pulse amplitude is twice the amplitude of the input, figure (b) of the circuit can be obtain twice the amplitude of the negative pulse.
The pulse booster circuit is designed to enhance the amplitude of input pulses, making it suitable for applications where signal strength is critical. The circuit typically employs a combination of transistors, capacitors, and resistors to achieve the desired amplification. In figure (a), the circuit configuration is likely to include a transistor configured as a common emitter amplifier, where the input pulse is fed into the base terminal. The collector terminal outputs a pulse that is amplified, resulting in an output that is double the amplitude of the input pulse.
In figure (b), the circuit is configured to amplify negative pulses. This may involve using a complementary push-pull arrangement of transistors to ensure that both positive and negative portions of the input waveform are effectively amplified. The design may also include feedback mechanisms to stabilize the output and prevent distortion, ensuring that the pulse shape is maintained while increasing amplitude.
The choice of components such as the type of transistors (e.g., NPN or PNP), the values of resistors and capacitors, and the power supply voltage will significantly influence the performance of the pulse booster circuit. Proper selection and configuration of these components are essential for achieving the desired amplification while maintaining signal integrity. Additionally, considerations regarding bandwidth, rise and fall times, and thermal management should be taken into account when designing and implementing a pulse booster circuit for specific applications.A pulse booster circuit When you need to increase the pulse amplitude, pulse boost circuit can be used, its structure, the figure (a) of the circuit can output pulse amplitude is twice the amplitude of the input, figure (b) of the circuit can be obtain twice the amplitude of the negative pulse.