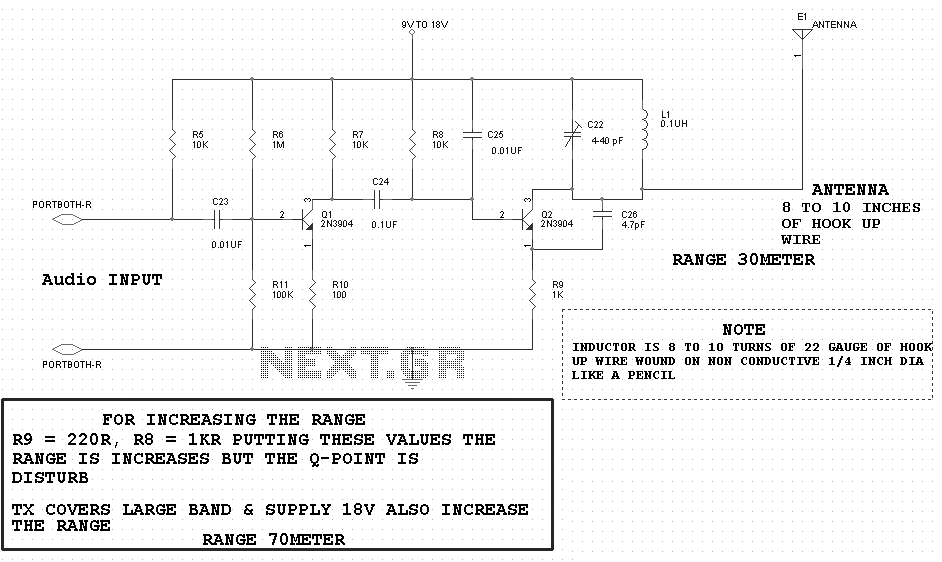
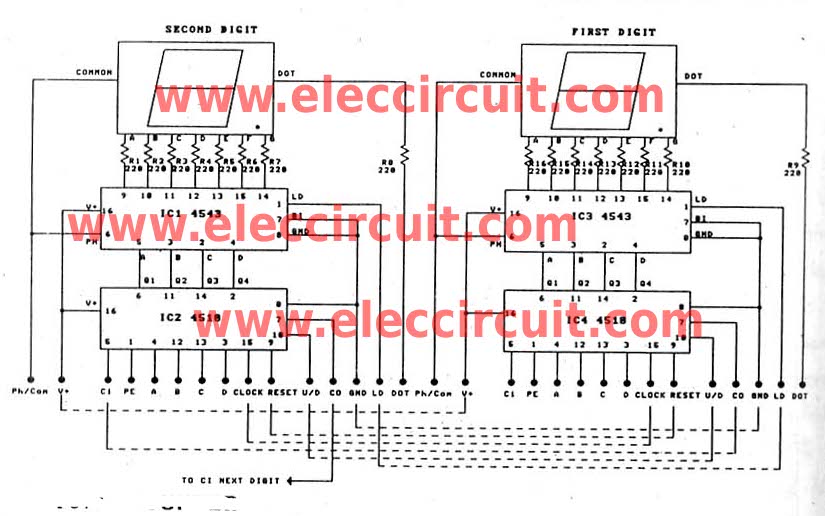
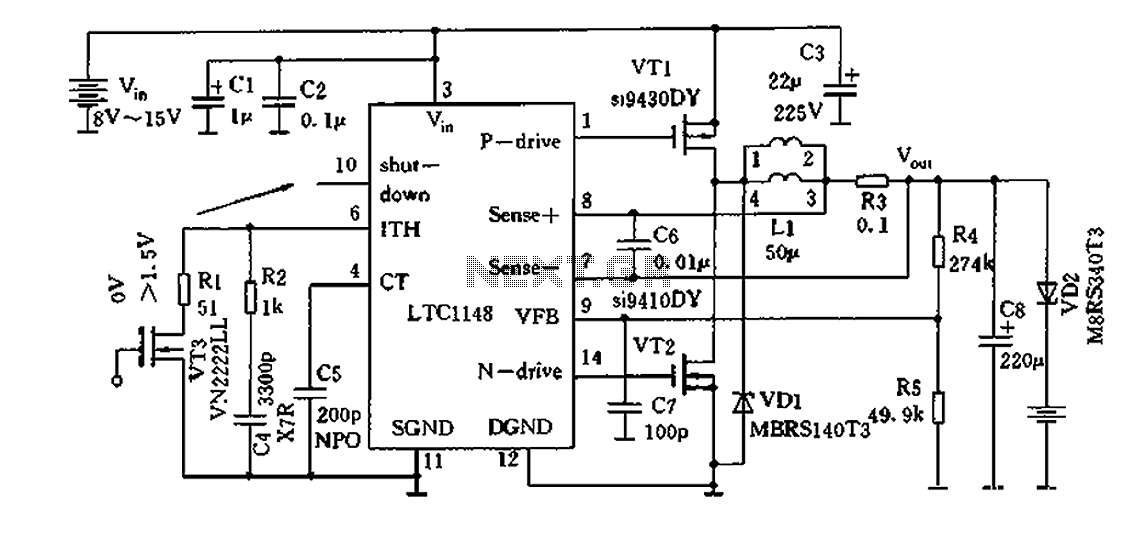
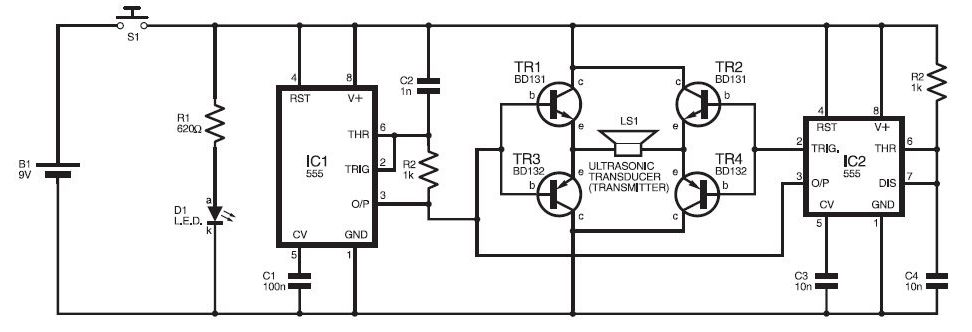
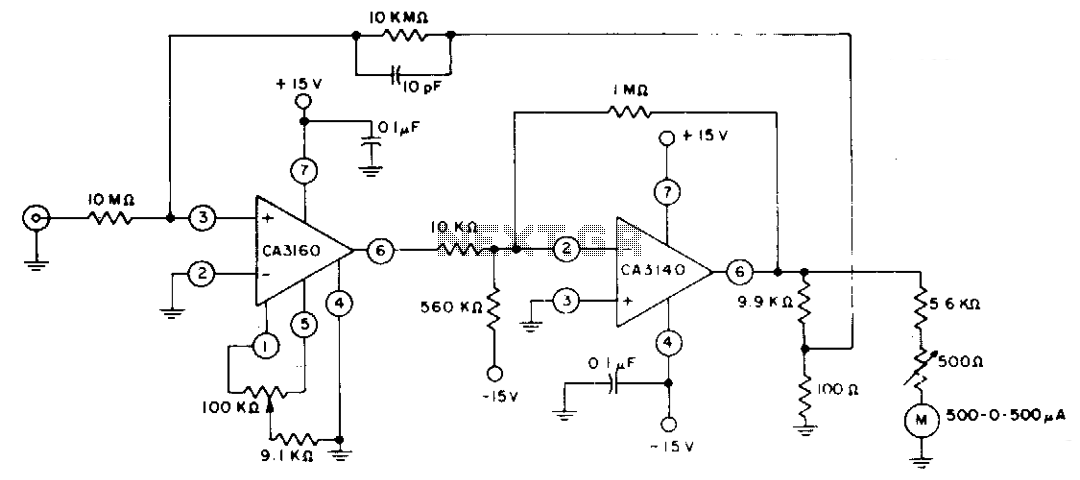
A typical laptop power adapter circuit
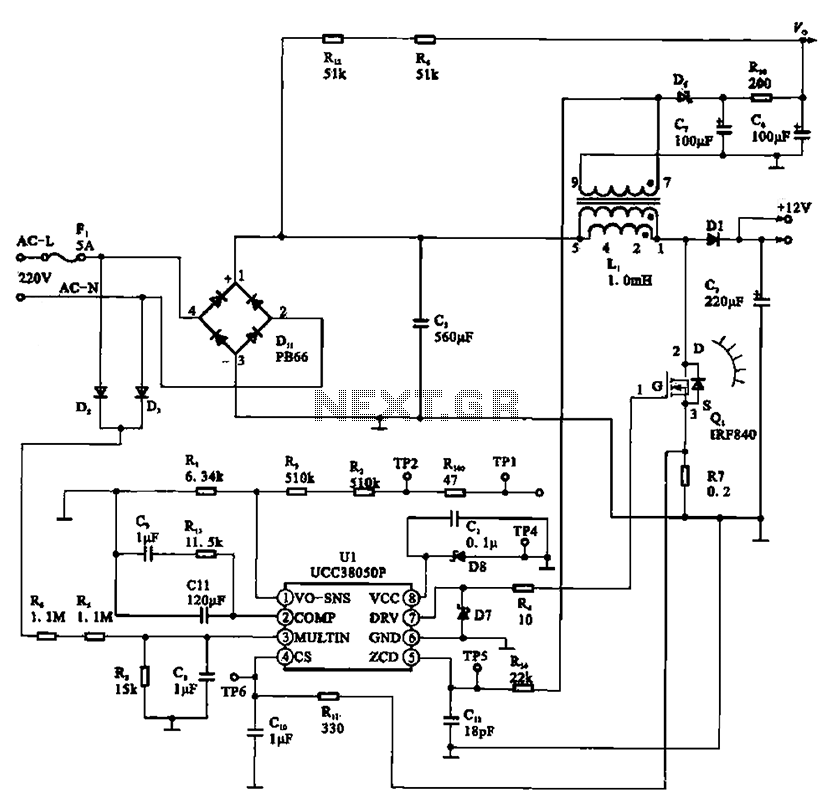
A typical laptop power adapter circuit converts an AC input of 22V through a rectifier and filter circuit to produce an output of +30V DC. This voltage is then processed by a switch oscillation circuit (U1, UCC38050P), which controls the switch and drives a transformer (L1). The secondary output of the transformer is rectified to provide +12V DC voltage.
The laptop power adapter circuit operates by first taking the incoming 22V AC voltage and converting it to a higher DC voltage of +30V using a rectifier bridge followed by a smoothing capacitor. The rectifier circuit typically consists of four diodes arranged in a bridge configuration, allowing for full-wave rectification. The smoothing capacitor filters out the ripples in the rectified voltage to ensure a steady DC output.
The UCC38050P integrated circuit serves as a pulse-width modulation (PWM) controller, providing efficient control of the switching element, usually a MOSFET. This PWM controller regulates the output voltage by adjusting the duty cycle of the switching signal, ensuring stable operation under varying load conditions.
The transformer (L1) is designed to step down the voltage from the primary side to the secondary side. The turns ratio of the transformer is critical, as it determines the output voltage level. The secondary winding of the transformer outputs a lower AC voltage, which is then rectified by another set of diodes to produce the final +12V DC output.
The entire circuit is typically equipped with additional components such as inductors and capacitors for filtering and stability purposes, ensuring that the output voltage is smooth and free from noise. Protection features may also be included, such as over-voltage and over-current protection, to safeguard both the adapter and the connected device. The design of the laptop power adapter circuit is crucial for providing reliable power to laptops while maintaining efficiency and safety standards.A typical laptop power adapter circuit A typical laptop power adapter circuit, the AC 22V voltage through the rectifier filter circuit output after +30V DC voltage, and then th e switch oscillation circuit Ul (UCC38050P), switch control, the transformer Li transformer secondary output rectifier + 12V DC voltage.
The laptop power adapter circuit operates by first taking the incoming 22V AC voltage and converting it to a higher DC voltage of +30V using a rectifier bridge followed by a smoothing capacitor. The rectifier circuit typically consists of four diodes arranged in a bridge configuration, allowing for full-wave rectification. The smoothing capacitor filters out the ripples in the rectified voltage to ensure a steady DC output.
The UCC38050P integrated circuit serves as a pulse-width modulation (PWM) controller, providing efficient control of the switching element, usually a MOSFET. This PWM controller regulates the output voltage by adjusting the duty cycle of the switching signal, ensuring stable operation under varying load conditions.
The transformer (L1) is designed to step down the voltage from the primary side to the secondary side. The turns ratio of the transformer is critical, as it determines the output voltage level. The secondary winding of the transformer outputs a lower AC voltage, which is then rectified by another set of diodes to produce the final +12V DC output.
The entire circuit is typically equipped with additional components such as inductors and capacitors for filtering and stability purposes, ensuring that the output voltage is smooth and free from noise. Protection features may also be included, such as over-voltage and over-current protection, to safeguard both the adapter and the connected device. The design of the laptop power adapter circuit is crucial for providing reliable power to laptops while maintaining efficiency and safety standards.A typical laptop power adapter circuit A typical laptop power adapter circuit, the AC 22V voltage through the rectifier filter circuit output after +30V DC voltage, and then th e switch oscillation circuit Ul (UCC38050P), switch control, the transformer Li transformer secondary output rectifier + 12V DC voltage.