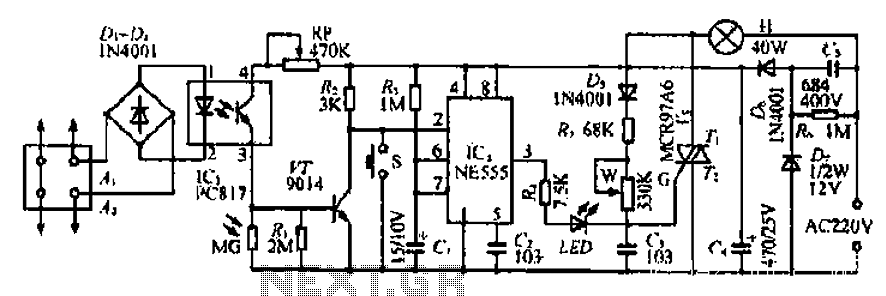
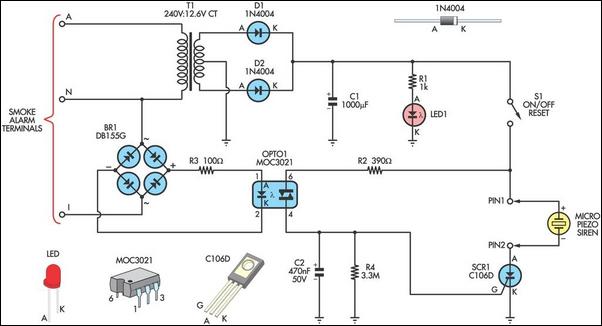
AC-SSR application circuit
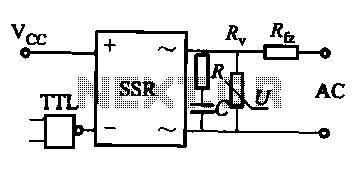
This document discusses the AC solid-state relay (AC-SSR) and presents its basic application circuit as illustrated in Figure (a). Additionally, it includes a TTL drive SSR circuit depicted in Figure (b), a CMOS driver circuit for the SSR shown in Figure (c), and a thyristor drive circuit for the SSR presented in Figure (d).
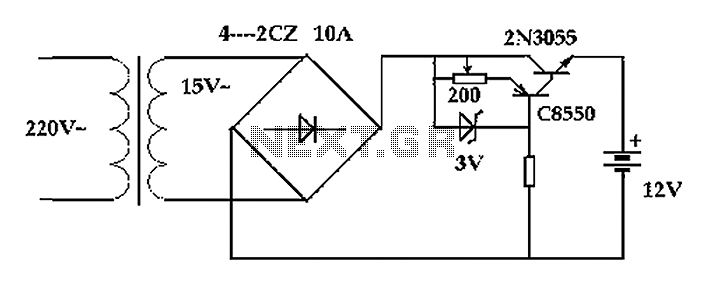
The AC solid-state relay (AC-SSR) is an electronic switching device that utilizes semiconductor components to perform the switching operation, eliminating the mechanical parts found in traditional electromechanical relays. This results in improved reliability, faster switching times, and a longer operational lifespan. The basic application circuit for the AC-SSR typically involves a control input that activates the relay, allowing it to conduct AC power to the load.
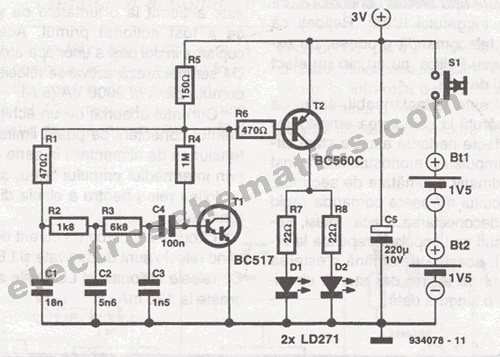
The TTL drive SSR circuit (Figure b) employs a Transistor-Transistor Logic (TTL) signal to control the relay. TTL circuits are known for their high-speed operation and low power consumption, making them suitable for interfacing with microcontrollers and digital systems. This configuration typically includes a series resistor to limit the current into the input of the SSR, ensuring that the control signal is within acceptable levels for reliable operation.
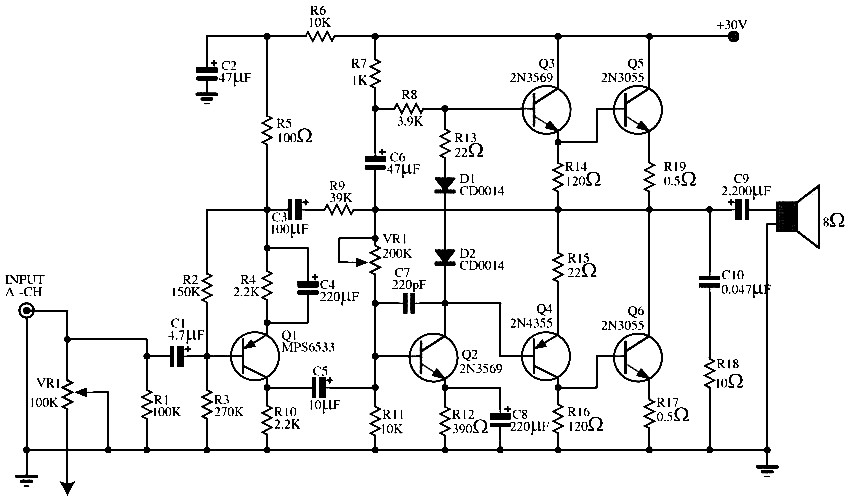
In the CMOS driver circuit (Figure c), Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (CMOS) technology is utilized to provide a high input impedance and low power consumption. This type of driver is particularly advantageous in battery-powered applications where energy efficiency is critical. The circuit may include pull-up or pull-down resistors to stabilize the input signal and prevent floating states.
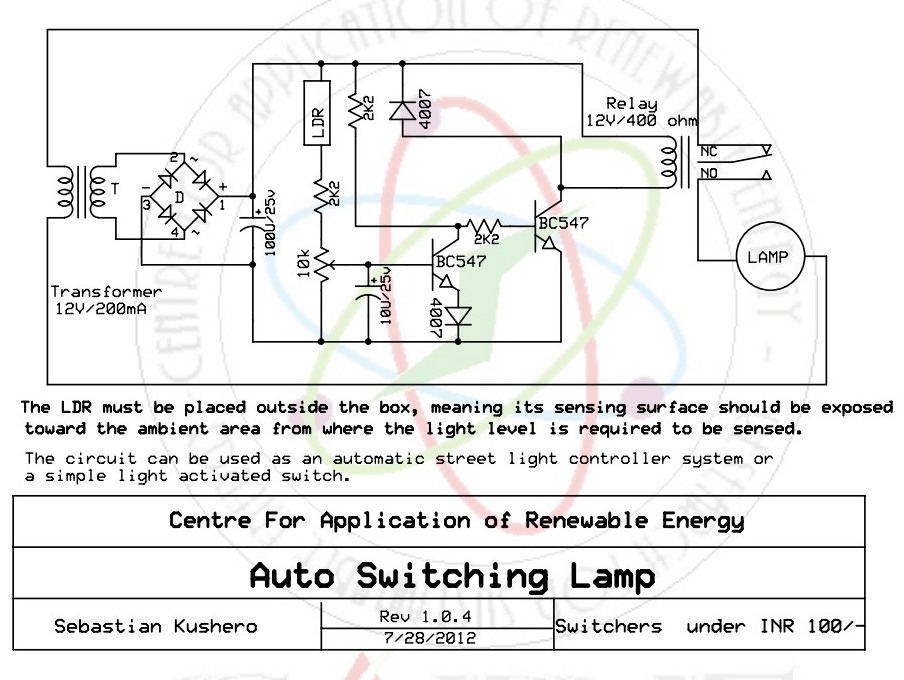
The thyristor drive circuit (Figure d) uses thyristors to control the AC load. Thyristors are semiconductor devices that can handle high voltages and currents, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. The circuit typically includes a gate control mechanism to trigger the thyristor, allowing it to switch on and off in response to the control signal. This type of drive is often employed in applications requiring precise control of AC power, such as motor control and lighting systems.
Overall, the various drive circuits for the AC solid-state relay provide flexibility in design and application, catering to different operational requirements and system architectures.About solid (body) relay AC solid state relay (AC-SSR) of the basic application circuit shown in Figure (a) below; With TTL drive SSR circuit is shown in (b) below; SSR with CMOS driver circuit is shown in (c) below; SSR thyristor drive circuit shown in (d) below.
The AC solid-state relay (AC-SSR) is an electronic switching device that utilizes semiconductor components to perform the switching operation, eliminating the mechanical parts found in traditional electromechanical relays. This results in improved reliability, faster switching times, and a longer operational lifespan. The basic application circuit for the AC-SSR typically involves a control input that activates the relay, allowing it to conduct AC power to the load.
The TTL drive SSR circuit (Figure b) employs a Transistor-Transistor Logic (TTL) signal to control the relay. TTL circuits are known for their high-speed operation and low power consumption, making them suitable for interfacing with microcontrollers and digital systems. This configuration typically includes a series resistor to limit the current into the input of the SSR, ensuring that the control signal is within acceptable levels for reliable operation.
In the CMOS driver circuit (Figure c), Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (CMOS) technology is utilized to provide a high input impedance and low power consumption. This type of driver is particularly advantageous in battery-powered applications where energy efficiency is critical. The circuit may include pull-up or pull-down resistors to stabilize the input signal and prevent floating states.
The thyristor drive circuit (Figure d) uses thyristors to control the AC load. Thyristors are semiconductor devices that can handle high voltages and currents, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. The circuit typically includes a gate control mechanism to trigger the thyristor, allowing it to switch on and off in response to the control signal. This type of drive is often employed in applications requiring precise control of AC power, such as motor control and lighting systems.
Overall, the various drive circuits for the AC solid-state relay provide flexibility in design and application, catering to different operational requirements and system architectures.About solid (body) relay AC solid state relay (AC-SSR) of the basic application circuit shown in Figure (a) below; With TTL drive SSR circuit is shown in (b) below; SSR with CMOS driver circuit is shown in (c) below; SSR thyristor drive circuit shown in (d) below.