Add 12V Output To 5V Buck Regulator Circuit
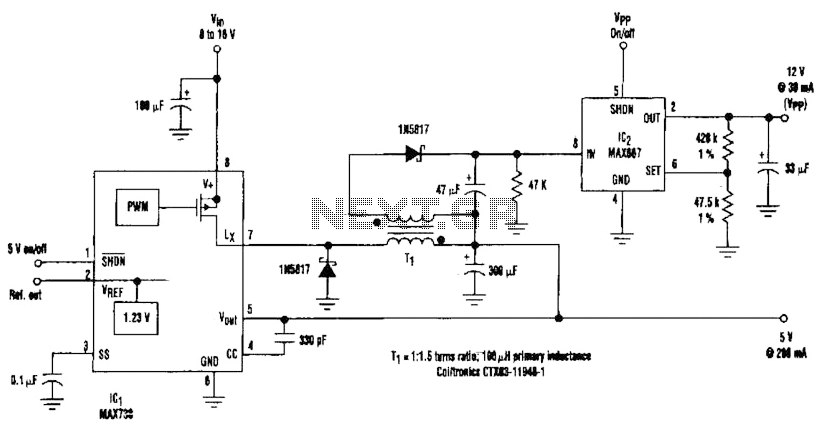
By adding a flyback winding to a buck-regulator switching converter, which functions as a 5-V supply with a 200-mA output capability, a 12-V output can be generated. The flyback winding on the main inductor, forming transformer T1, allows for an additional low-dropout linear regulator (IC2) to produce the necessary 12-V output voltage for programming EEPROMs. The required input voltage ranges from 8 to 16 V.
The circuit described integrates a buck-regulator switching converter configured to provide a stable 5-V output with a current capacity of 200 mA. The addition of a flyback winding on the inductor (designated as T1) transforms the basic buck converter into a more versatile power supply capable of generating a higher voltage output of 12 V. This is achieved by utilizing the energy stored in the inductor during the buck conversion process, which is then transferred via the flyback winding.
The flyback winding operates by inducing a voltage when the magnetic field collapses, effectively allowing the converter to step up the voltage. This induced voltage is subsequently regulated down to the required 12 V using a low-dropout linear regulator (IC2). This type of regulator is particularly advantageous in applications where the input voltage is only slightly higher than the desired output voltage, as it minimizes power loss and heat generation.
The input voltage for this circuit is specified to be within the range of 8 to 16 V, ensuring that the buck converter operates efficiently while providing adequate headroom for the linear regulator. This design is particularly suitable for applications requiring precise voltage levels, such as programming EEPROMs, where stable and reliable power supply is critical. The combination of the buck converter and flyback winding allows for a compact and efficient solution to meet the voltage requirements of modern electronic components. By adding a flyback winding to a buck-regulator switching converter (see the figure), wliich is essentially a 5-V supply with a 200-mA output capability, a 12-V output ) can be produced. The flyback winding on the main inductor (forming transformer Tl) enables an additional low- dropout linear regulator (IC2) to create the 12-V output voltage that`s needed to program EEPROMs.
The required input voltage is 8 to 16 V.
The circuit described integrates a buck-regulator switching converter configured to provide a stable 5-V output with a current capacity of 200 mA. The addition of a flyback winding on the inductor (designated as T1) transforms the basic buck converter into a more versatile power supply capable of generating a higher voltage output of 12 V. This is achieved by utilizing the energy stored in the inductor during the buck conversion process, which is then transferred via the flyback winding.
The flyback winding operates by inducing a voltage when the magnetic field collapses, effectively allowing the converter to step up the voltage. This induced voltage is subsequently regulated down to the required 12 V using a low-dropout linear regulator (IC2). This type of regulator is particularly advantageous in applications where the input voltage is only slightly higher than the desired output voltage, as it minimizes power loss and heat generation.
The input voltage for this circuit is specified to be within the range of 8 to 16 V, ensuring that the buck converter operates efficiently while providing adequate headroom for the linear regulator. This design is particularly suitable for applications requiring precise voltage levels, such as programming EEPROMs, where stable and reliable power supply is critical. The combination of the buck converter and flyback winding allows for a compact and efficient solution to meet the voltage requirements of modern electronic components. By adding a flyback winding to a buck-regulator switching converter (see the figure), wliich is essentially a 5-V supply with a 200-mA output capability, a 12-V output ) can be produced. The flyback winding on the main inductor (forming transformer Tl) enables an additional low- dropout linear regulator (IC2) to create the 12-V output voltage that`s needed to program EEPROMs.
The required input voltage is 8 to 16 V.