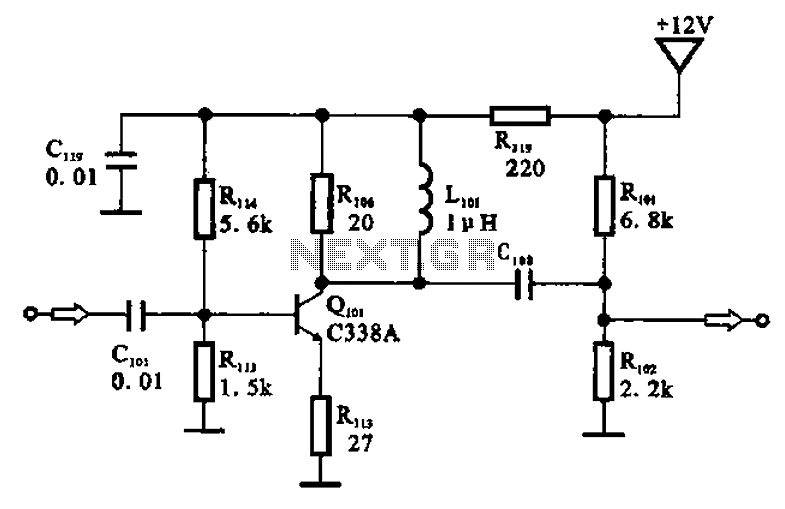
DC Protection Time Delay for Loudspeaker circuit
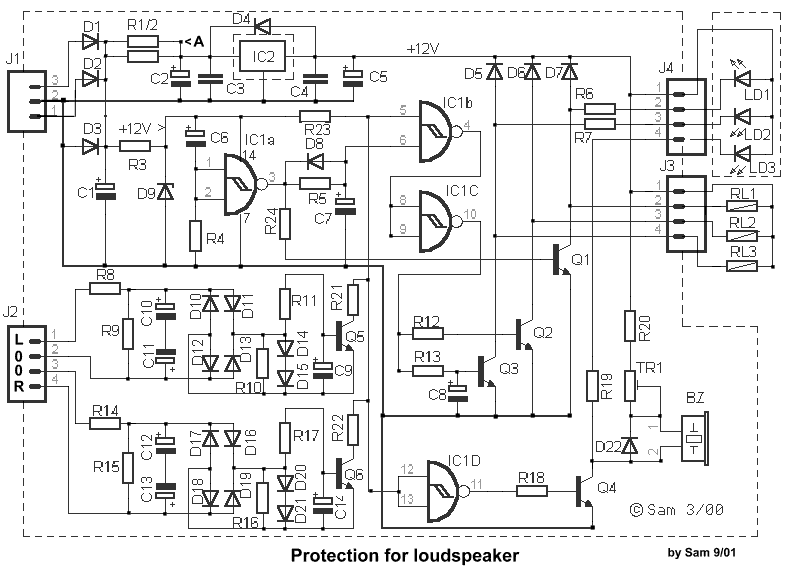
The circuit integrates several functions, including a smooth startup for the AC power line, with a one-second delay before connecting to the power supply transformers of the amplifier through relay RL1 and resistor Rx. This delay is designed to prevent noise from the charging and discharging of power supply capacitors from reaching the headphones. Additionally, the circuit monitors the output of the amplifiers for the presence of direct current (DC). If the conditions are met, the amplifiers are then connected to the loudspeakers.
The circuit design incorporates a relay (RL1) that serves as a switch for controlling the power supply to the amplifier. When the circuit is powered on, a timing mechanism initiates a one-second delay before RL1 closes, allowing the power supply capacitors to charge without introducing audible noise to the headphone output. This delay is critical in ensuring that transient noises do not interfere with the listening experience.
The resistor Rx is strategically placed to help manage the timing characteristics of the relay, ensuring that the delay is consistent and reliable. The choice of resistor value can be adjusted based on the specific requirements of the circuit, such as the charging time of the capacitors and the desired delay duration.
Simultaneously, the circuit includes a monitoring system that checks for the presence of DC voltage at the output of the amplifiers. This feature is essential for protecting the headphones and loudspeakers from potential damage caused by DC signals. If the monitoring system detects that the output is free of DC voltage, the relay activates, allowing the amplifiers to connect to the loudspeakers.
Overall, this circuit design effectively combines delay management and output monitoring to enhance the performance and reliability of audio amplification systems. The careful integration of components ensures that users experience a high-quality audio output without unwanted noise or distortion during startup.The particular circuit combines enough operations, as Smooth departure of benefit of AC line of network, with delay 1sec, to the transformers of power supply of amplifier, via the RL1 and the resistance Rx. (see block diagram). [ 2 ] Delay of connection of expenses of final amplifiers, in headphone, in order that noises emanating from the charge - uncharged of capacitors of power supply, they do not pass in them.
Simultaneously becomes control of exit of amplifiers for existence of continuous voltage [DC]. If all go well it connects, the amplifiers in loudspeaker.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit design incorporates a relay (RL1) that serves as a switch for controlling the power supply to the amplifier. When the circuit is powered on, a timing mechanism initiates a one-second delay before RL1 closes, allowing the power supply capacitors to charge without introducing audible noise to the headphone output. This delay is critical in ensuring that transient noises do not interfere with the listening experience.
The resistor Rx is strategically placed to help manage the timing characteristics of the relay, ensuring that the delay is consistent and reliable. The choice of resistor value can be adjusted based on the specific requirements of the circuit, such as the charging time of the capacitors and the desired delay duration.
Simultaneously, the circuit includes a monitoring system that checks for the presence of DC voltage at the output of the amplifiers. This feature is essential for protecting the headphones and loudspeakers from potential damage caused by DC signals. If the monitoring system detects that the output is free of DC voltage, the relay activates, allowing the amplifiers to connect to the loudspeakers.
Overall, this circuit design effectively combines delay management and output monitoring to enhance the performance and reliability of audio amplification systems. The careful integration of components ensures that users experience a high-quality audio output without unwanted noise or distortion during startup.The particular circuit combines enough operations, as Smooth departure of benefit of AC line of network, with delay 1sec, to the transformers of power supply of amplifier, via the RL1 and the resistance Rx. (see block diagram). [ 2 ] Delay of connection of expenses of final amplifiers, in headphone, in order that noises emanating from the charge - uncharged of capacitors of power supply, they do not pass in them.
Simultaneously becomes control of exit of amplifiers for existence of continuous voltage [DC]. If all go well it connects, the amplifiers in loudspeaker.. 🔗 External reference