alarm door bell circuit using ic um 66 part 1
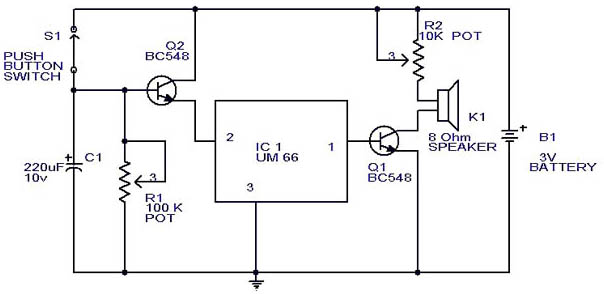
This circuit is a slight modification of a previous design. In the earlier version, the switch needed to be held down for the entire duration of the music playback. In this updated circuit, pressing the push button once charges capacitor C1, allowing transistor Q2 to keep the integrated circuit (IC) playing the music until it finishes. The playback duration is determined by the discharge time of C1, which can be adjusted using resistor R1. By setting R1, the user can select the desired playback time, whether for the full tone or a shorter segment with a single press. Transistor Q2 is responsible for driving the speaker.
This circuit utilizes a push-button switch to initiate playback of an audio signal generated by an integrated circuit (IC). The functionality hinges on the interaction between the capacitor C1, resistor R1, and transistor Q2. Upon pressing the push-button switch, C1 begins to charge, creating a voltage that turns on transistor Q2. This transistor acts as a switch, allowing current to flow from the power source to the speaker, thus enabling sound output.
The discharge time of capacitor C1, which directly influences the duration of the audio playback, is controlled by the resistor R1. By varying the resistance value of R1, the time constant of the RC (resistor-capacitor) circuit can be adjusted. A larger resistance value will result in a longer discharge time, allowing the IC to play for an extended period, while a smaller resistance will shorten the playback duration. This feature provides flexibility in the circuit's operation, accommodating different user preferences for audio playback length.
Transistor Q2 is selected based on its ability to handle the current required by the speaker. It should have sufficient gain and current rating to ensure reliable operation without distortion of the audio signal. The circuit may also include additional components such as diodes for protection against back EMF generated by the speaker, ensuring the longevity of the transistor and IC.
Overall, this design offers an efficient and user-friendly approach to audio playback, making it suitable for various applications where controlled sound output is needed.This is a slight modification of that circuit. In the previous circuit you have to keep the switch pressed for making the IC play the full music. Here if once the push button is pressed C1 is charged and the transistor Q2 will keep the IC playing the music till it ends. The time for the IC to play depends on discharging time of C1 which can be se t by R1. Set R1 to select your time, whether full tone or a part in one press. Transistor Q2 drives the speaker. 🔗 External reference
This circuit utilizes a push-button switch to initiate playback of an audio signal generated by an integrated circuit (IC). The functionality hinges on the interaction between the capacitor C1, resistor R1, and transistor Q2. Upon pressing the push-button switch, C1 begins to charge, creating a voltage that turns on transistor Q2. This transistor acts as a switch, allowing current to flow from the power source to the speaker, thus enabling sound output.
The discharge time of capacitor C1, which directly influences the duration of the audio playback, is controlled by the resistor R1. By varying the resistance value of R1, the time constant of the RC (resistor-capacitor) circuit can be adjusted. A larger resistance value will result in a longer discharge time, allowing the IC to play for an extended period, while a smaller resistance will shorten the playback duration. This feature provides flexibility in the circuit's operation, accommodating different user preferences for audio playback length.
Transistor Q2 is selected based on its ability to handle the current required by the speaker. It should have sufficient gain and current rating to ensure reliable operation without distortion of the audio signal. The circuit may also include additional components such as diodes for protection against back EMF generated by the speaker, ensuring the longevity of the transistor and IC.
Overall, this design offers an efficient and user-friendly approach to audio playback, making it suitable for various applications where controlled sound output is needed.This is a slight modification of that circuit. In the previous circuit you have to keep the switch pressed for making the IC play the full music. Here if once the push button is pressed C1 is charged and the transistor Q2 will keep the IC playing the music till it ends. The time for the IC to play depends on discharging time of C1 which can be se t by R1. Set R1 to select your time, whether full tone or a part in one press. Transistor Q2 drives the speaker. 🔗 External reference