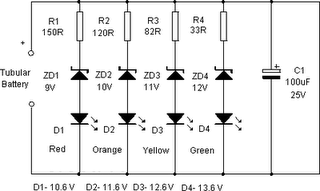
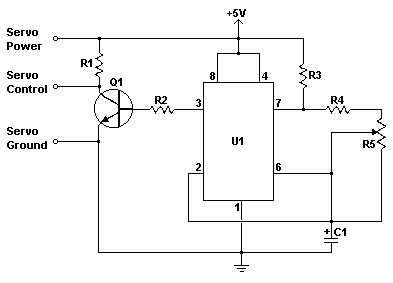
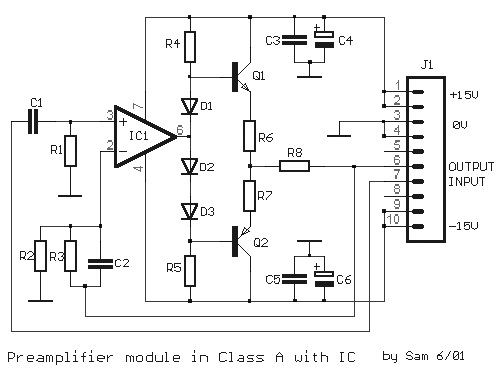
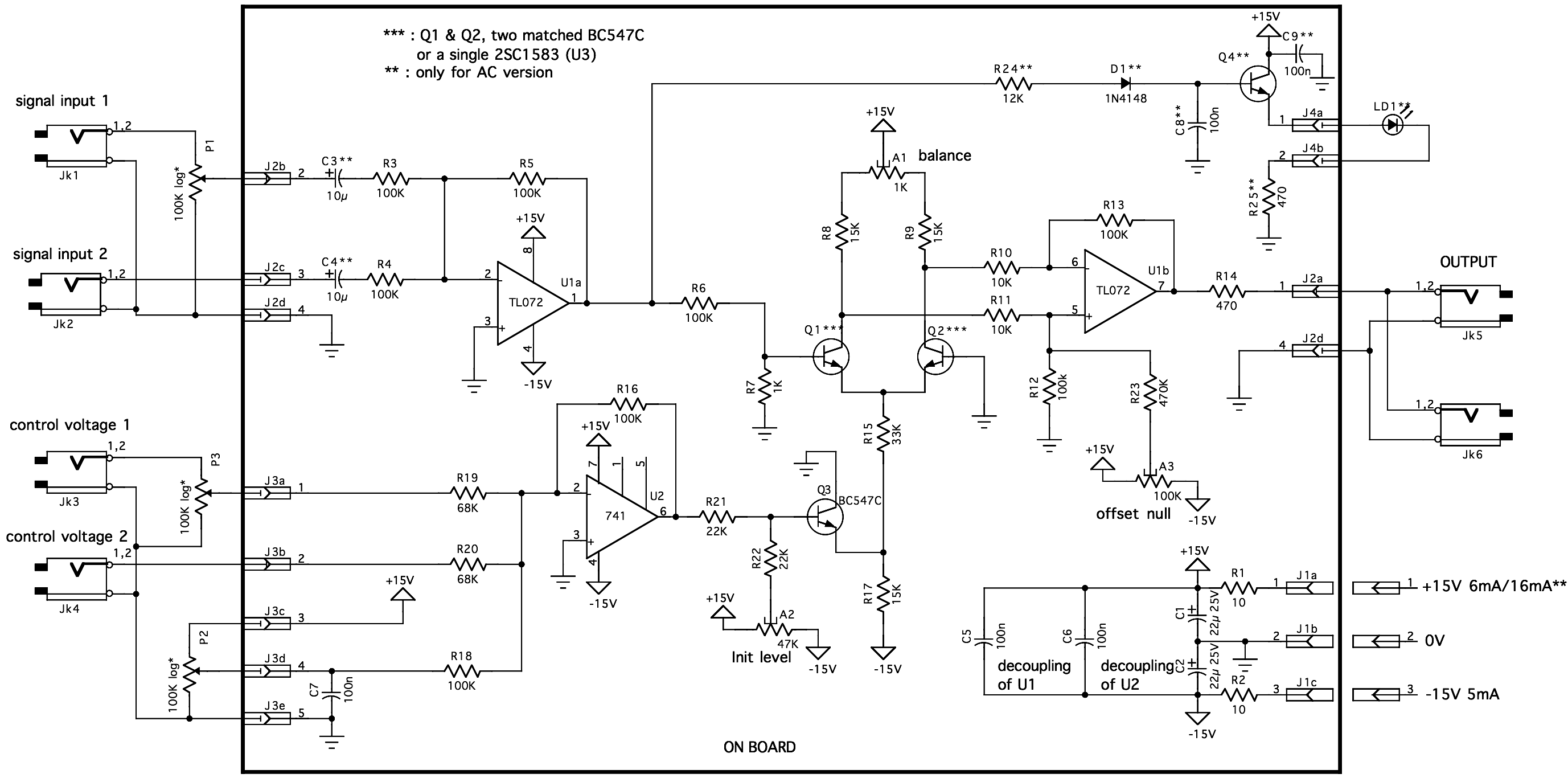
Alc (Automatic Level Control) Circuit
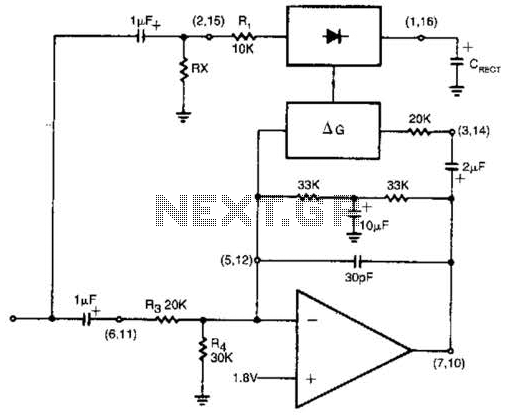
The rectifier input is connected to the input, establishing a relationship where gain is inversely proportional to the input level. Consequently, a 20-dB reduction in input level results in a 20-dB increase in gain. The output is designed to remain at a constant level, maintaining an output of 1 dB for an input range from +14 to -43 dB at a frequency of 1 kHz. Furthermore, additional external components will enable the adjustment of the output level.
The described circuit functions as a specialized rectifier with a feedback mechanism that ensures a consistent output level despite variations in input signal strength. The core principle of this design relies on the inverse relationship between input level and gain. Specifically, when the input signal decreases, the gain compensates by increasing, thereby stabilizing the output.
The rectifier component receives the input signal, which can vary significantly within the specified range. The circuit is engineered to maintain a fixed output of 1 dB, regardless of whether the input signal is at its maximum of +14 dB or its minimum of -43 dB. This feature is particularly beneficial in applications requiring stable output levels, such as audio processing or signal conditioning.
Incorporating additional external components allows for fine-tuning of the output level, providing flexibility in adapting the circuit to different operational needs. These components may include variable resistors, capacitors, or operational amplifiers, which can be configured to modify the gain characteristics or output response of the circuit.
Overall, this design exemplifies a robust solution for applications where consistent output is crucial, and the ability to adjust output levels adds versatility to the circuit's functionality. The rectifier input is tied to the input. This makes gain inversely proportional to input level so that a 20-dB drop in input level will produce a 20-dB increase in gain. The output will remain fixed at a constant level. The circuit will maintain an output level of 1 dB for an input range of +14 to -43 dB at 1 kHz. Additional external components will allow the output-level to be adjusted.
The described circuit functions as a specialized rectifier with a feedback mechanism that ensures a consistent output level despite variations in input signal strength. The core principle of this design relies on the inverse relationship between input level and gain. Specifically, when the input signal decreases, the gain compensates by increasing, thereby stabilizing the output.
The rectifier component receives the input signal, which can vary significantly within the specified range. The circuit is engineered to maintain a fixed output of 1 dB, regardless of whether the input signal is at its maximum of +14 dB or its minimum of -43 dB. This feature is particularly beneficial in applications requiring stable output levels, such as audio processing or signal conditioning.
Incorporating additional external components allows for fine-tuning of the output level, providing flexibility in adapting the circuit to different operational needs. These components may include variable resistors, capacitors, or operational amplifiers, which can be configured to modify the gain characteristics or output response of the circuit.
Overall, this design exemplifies a robust solution for applications where consistent output is crucial, and the ability to adjust output levels adds versatility to the circuit's functionality. The rectifier input is tied to the input. This makes gain inversely proportional to input level so that a 20-dB drop in input level will produce a 20-dB increase in gain. The output will remain fixed at a constant level. The circuit will maintain an output level of 1 dB for an input range of +14 to -43 dB at 1 kHz. Additional external components will allow the output-level to be adjusted.