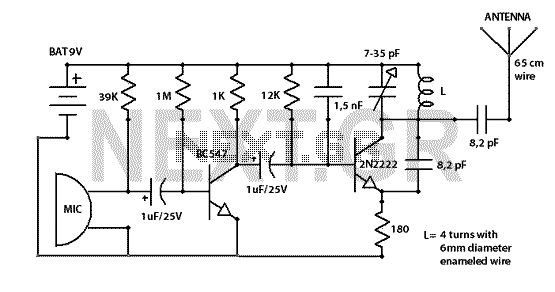
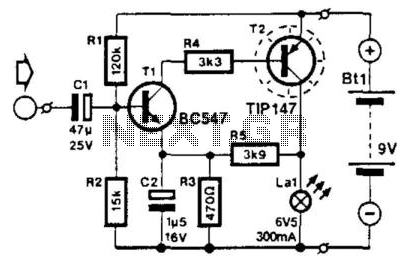
AM Transmitter
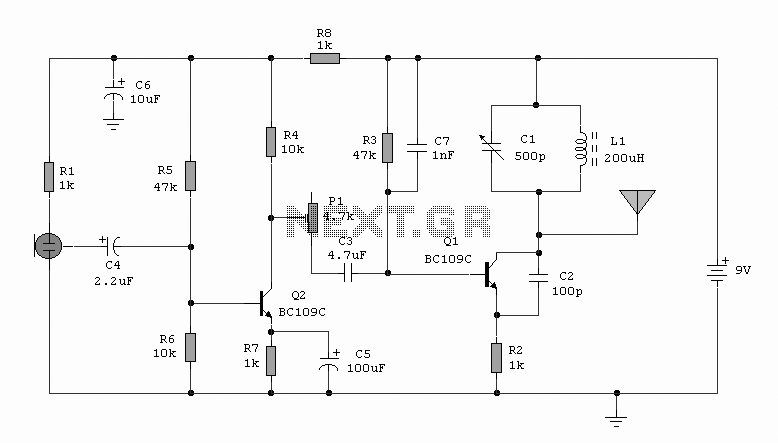
This is an AM transmitter schematic diagram. The circuit is divided into two halves: an audio amplifier and an RF oscillator. The oscillator is constructed around Q1 and its associated components. The tank circuit, consisting of L1 and VC1, is tunable from approximately 500 kHz to 1600 kHz.
The AM transmitter circuit is designed to modulate audio signals onto a carrier wave for transmission. The audio amplifier section processes the input audio signal, enhancing its amplitude to a level suitable for modulation. Typically, this section may include operational amplifiers or transistor-based amplifiers to achieve the desired gain.
The RF oscillator generates the carrier frequency, which is crucial for AM transmission. It operates using Q1, which is likely a transistor or a field-effect transistor (FET), along with passive components such as resistors and capacitors. The oscillator's frequency is determined by the tank circuit formed by inductor L1 and variable capacitor VC1. The tunable nature of VC1 allows the user to adjust the frequency, enabling operation across a range from 500 kHz to 1600 kHz, which is suitable for AM broadcasting.
In this schematic, the output of the RF oscillator can be connected to an antenna for transmission. The design must consider impedance matching to ensure efficient power transfer to the antenna. Additionally, filtering components may be included to suppress harmonics and ensure that the transmitted signal meets regulatory standards for spectral purity.
Overall, this AM transmitter schematic diagram illustrates a fundamental approach to building a basic AM transmitter, suitable for educational purposes or hobbyist projects. Proper attention to component selection, layout, and tuning will enhance the performance and reliability of the transmitter.This is AM transmitter schematic diagram. The circuit is in two halfs, an audio amplifier and an RF oscillator. The oscillator is built around Q1 and associated components. The tank circuit L1 and VC1 is tunable from about 500kHz to 1600KHz.. 🔗 External reference
The AM transmitter circuit is designed to modulate audio signals onto a carrier wave for transmission. The audio amplifier section processes the input audio signal, enhancing its amplitude to a level suitable for modulation. Typically, this section may include operational amplifiers or transistor-based amplifiers to achieve the desired gain.
The RF oscillator generates the carrier frequency, which is crucial for AM transmission. It operates using Q1, which is likely a transistor or a field-effect transistor (FET), along with passive components such as resistors and capacitors. The oscillator's frequency is determined by the tank circuit formed by inductor L1 and variable capacitor VC1. The tunable nature of VC1 allows the user to adjust the frequency, enabling operation across a range from 500 kHz to 1600 kHz, which is suitable for AM broadcasting.
In this schematic, the output of the RF oscillator can be connected to an antenna for transmission. The design must consider impedance matching to ensure efficient power transfer to the antenna. Additionally, filtering components may be included to suppress harmonics and ensure that the transmitted signal meets regulatory standards for spectral purity.
Overall, this AM transmitter schematic diagram illustrates a fundamental approach to building a basic AM transmitter, suitable for educational purposes or hobbyist projects. Proper attention to component selection, layout, and tuning will enhance the performance and reliability of the transmitter.This is AM transmitter schematic diagram. The circuit is in two halfs, an audio amplifier and an RF oscillator. The oscillator is built around Q1 and associated components. The tank circuit L1 and VC1 is tunable from about 500kHz to 1600KHz.. 🔗 External reference