Amplifier Circuit Output Relay Delay Audio
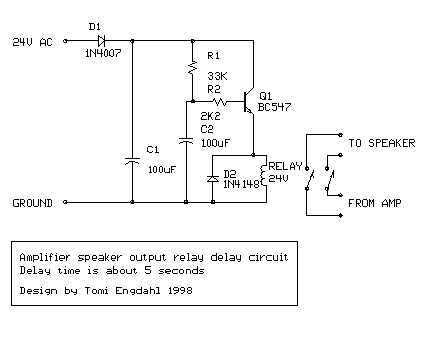
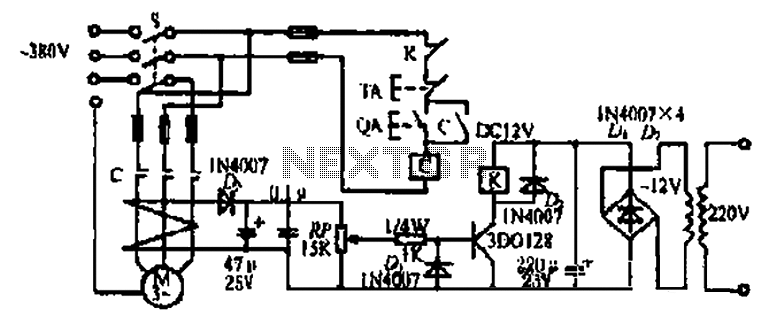
This is a simple circuit designed for an audio amplifier project to control the speaker output relay. The purpose of this circuit is to manage the relay that activates the speaker output in the audio amplifier. The circuit is designed to wait approximately five seconds after power-up before connecting the speakers to the amplifier output, thereby avoiding an annoying thump sound from the speakers. Additionally, this circuit disconnects the speakers immediately when power to the amplifier is turned off, preventing unpleasant sounds during equipment shutdown. When power is applied to the circuit's input, the positive phase of the AC voltage charges capacitor C1. Capacitor C2 begins to charge slowly through resistor R1. As the voltage across C2 rises, the emitter output voltage of transistor Q1 also increases in tandem with the voltage on C2. When the output voltage of transistor Q2 reaches a sufficient level (typically around 16 to 20V), the relay is activated, connecting the speakers to the amplifier output. The relay typically engages around five seconds after power-up, though the exact timing depends on the capacitance of C2, the relay voltage, and the circuit input voltage. When the power is turned off, C1 discharges quickly, and C2 also discharges rapidly through resistor R2. In less than 0.5 seconds, the speakers are disconnected from the amplifier output. While this circuit may not be the most precise or elegant design, it has proven effective in a small home-built PA amplifier. This circuit can also be utilized in various other applications requiring a turn-on delay of a few seconds. The delay time can be adjusted by changing the size of C2; increasing its capacitance will lengthen the delay, while decreasing it will shorten the delay. However, it is important to note that the delay is not very precise due to the simplicity of the circuit and the wide tolerance range of typical electrolytic capacitors, which can vary from -20% to +50%.
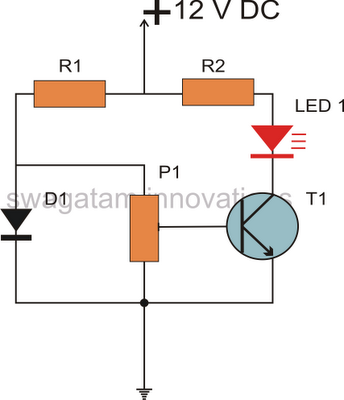
The circuit operates by utilizing a relay to manage the connection of speakers to an audio amplifier, providing both a delay in activation and immediate disconnection upon power loss. The key components include two capacitors (C1 and C2), two resistors (R1 and R2), and two transistors (Q1 and Q2). The charging and discharging characteristics of C2, in conjunction with the resistors, create the desired delay in speaker activation. The relay serves as a switch that connects or disconnects the speakers based on the control signals from the transistors.
The circuit's design can be optimized for various applications by selecting appropriate values for the capacitors and resistors. For instance, using a larger capacitor for C2 will increase the delay before the speakers are activated, which may be beneficial in applications where a longer delay is necessary to prevent thumping sounds. Conversely, a smaller capacitor will result in a quicker activation, suitable for different scenarios.
In terms of practical implementation, consideration should be given to the specifications of the relay used, ensuring it can handle the load of the speakers without failure. Additionally, the transistors must be chosen based on their voltage and current ratings to ensure reliable operation. Proper thermal management may also be necessary, depending on the power levels involved.
This circuit is versatile and can be adapted for use in various audio applications, including home audio systems, public address systems, and other electronic projects requiring controlled speaker output.This is a simple circuit which I built to one of my audio amplifier projects to control the speaker output relay. The purpose of this circuit is to control the relay which turns on the speaker output relay in the audio amplifier.
The idea of the circuit is wait around 5 seconds ofter the power up until the spakers are switched to the amplfier outp ut to avoid annoying thump sound from the speakers. Another feeature of this circuit is that is disconnects the speaker immdiatly when the power in the amplifier is cut off, so avoinding sometimes nasty sounds when you turn the equipments off. Then power is applied to the power input of the circuit, the positive phase of AC voltage charges C1.
Then C2 starts to charge slowly through R1. When the voltage in C2 rises, the emitter output voltage of Q1 rises tigether with voltage on C2. When the output voltage of Q2 is high enough (typically around 16. 20V) the relay goes to on state and the relay witches connect the speakers to the amplifier output. It takes typically around 5 seconds after power up until the relay starts to condict (at absolute time depends on the size of C2, relay voltage and circuit input voltage). When the power is switched off, C1 will loose it`s energu quite quicly. Also C2 will be charged quite quicly through R2. In less than 0. 5 seconds the speakers are disconnected from the amplifier output. This circuit is not the most accurate and elegant design, but it has worked nicely in my small homebuilt PA amplifier.
This circuit can be also used in many other applications where a turn on delay of few seconds is needed. The delay time can be increased by using bigger C2 and decreased by using a smaller C2 value. Note that the delay is not very accurate because of simplicity of this circuit and large tolerance of typical electrolytic capacitors (can be -20%.
+50% in some capcitors). 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by utilizing a relay to manage the connection of speakers to an audio amplifier, providing both a delay in activation and immediate disconnection upon power loss. The key components include two capacitors (C1 and C2), two resistors (R1 and R2), and two transistors (Q1 and Q2). The charging and discharging characteristics of C2, in conjunction with the resistors, create the desired delay in speaker activation. The relay serves as a switch that connects or disconnects the speakers based on the control signals from the transistors.
The circuit's design can be optimized for various applications by selecting appropriate values for the capacitors and resistors. For instance, using a larger capacitor for C2 will increase the delay before the speakers are activated, which may be beneficial in applications where a longer delay is necessary to prevent thumping sounds. Conversely, a smaller capacitor will result in a quicker activation, suitable for different scenarios.
In terms of practical implementation, consideration should be given to the specifications of the relay used, ensuring it can handle the load of the speakers without failure. Additionally, the transistors must be chosen based on their voltage and current ratings to ensure reliable operation. Proper thermal management may also be necessary, depending on the power levels involved.
This circuit is versatile and can be adapted for use in various audio applications, including home audio systems, public address systems, and other electronic projects requiring controlled speaker output.This is a simple circuit which I built to one of my audio amplifier projects to control the speaker output relay. The purpose of this circuit is to control the relay which turns on the speaker output relay in the audio amplifier.
The idea of the circuit is wait around 5 seconds ofter the power up until the spakers are switched to the amplfier outp ut to avoid annoying thump sound from the speakers. Another feeature of this circuit is that is disconnects the speaker immdiatly when the power in the amplifier is cut off, so avoinding sometimes nasty sounds when you turn the equipments off. Then power is applied to the power input of the circuit, the positive phase of AC voltage charges C1.
Then C2 starts to charge slowly through R1. When the voltage in C2 rises, the emitter output voltage of Q1 rises tigether with voltage on C2. When the output voltage of Q2 is high enough (typically around 16. 20V) the relay goes to on state and the relay witches connect the speakers to the amplifier output. It takes typically around 5 seconds after power up until the relay starts to condict (at absolute time depends on the size of C2, relay voltage and circuit input voltage). When the power is switched off, C1 will loose it`s energu quite quicly. Also C2 will be charged quite quicly through R2. In less than 0. 5 seconds the speakers are disconnected from the amplifier output. This circuit is not the most accurate and elegant design, but it has worked nicely in my small homebuilt PA amplifier.
This circuit can be also used in many other applications where a turn on delay of few seconds is needed. The delay time can be increased by using bigger C2 and decreased by using a smaller C2 value. Note that the delay is not very accurate because of simplicity of this circuit and large tolerance of typical electrolytic capacitors (can be -20%.
+50% in some capcitors). 🔗 External reference