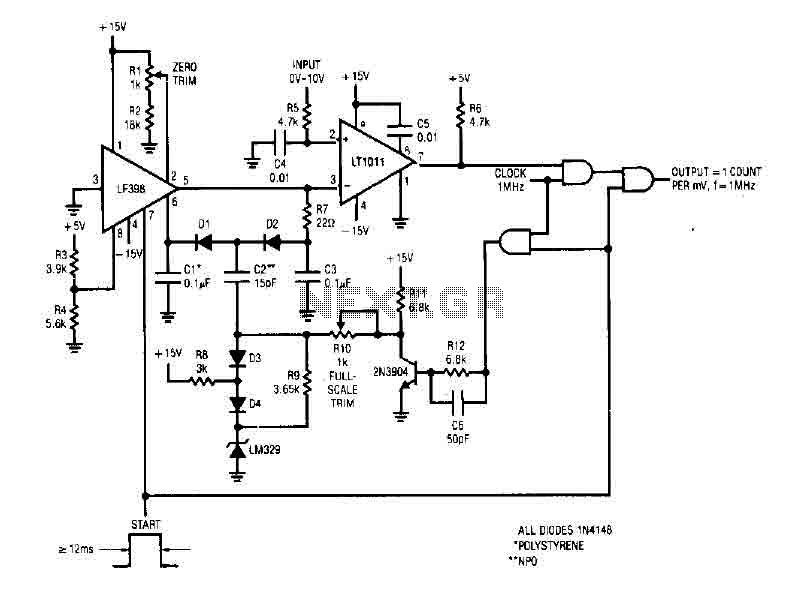
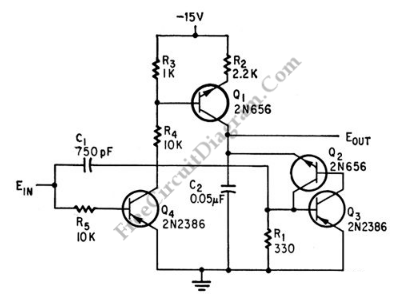
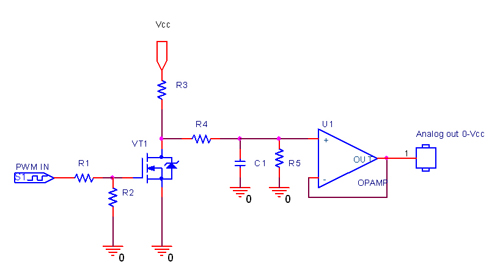
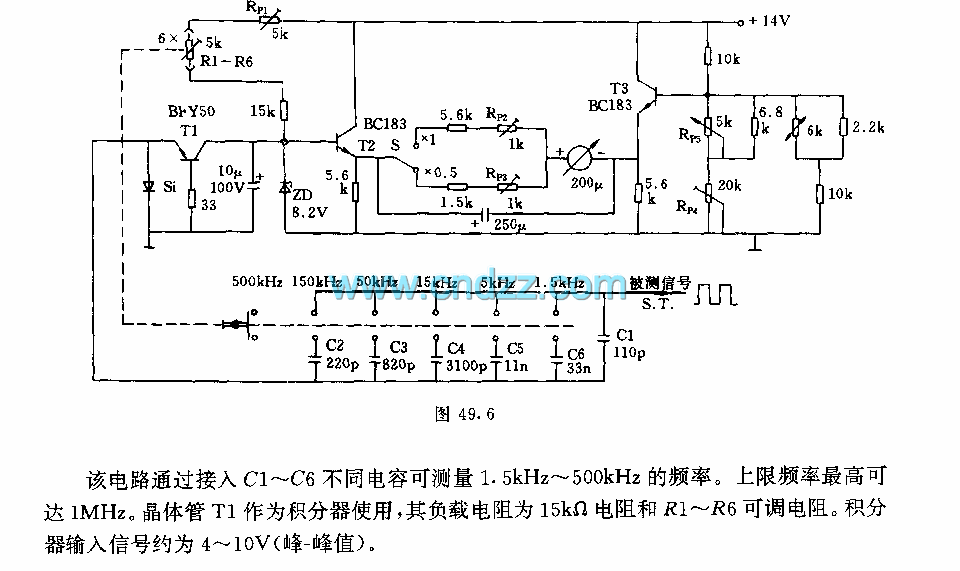
Analog Input Tutorial
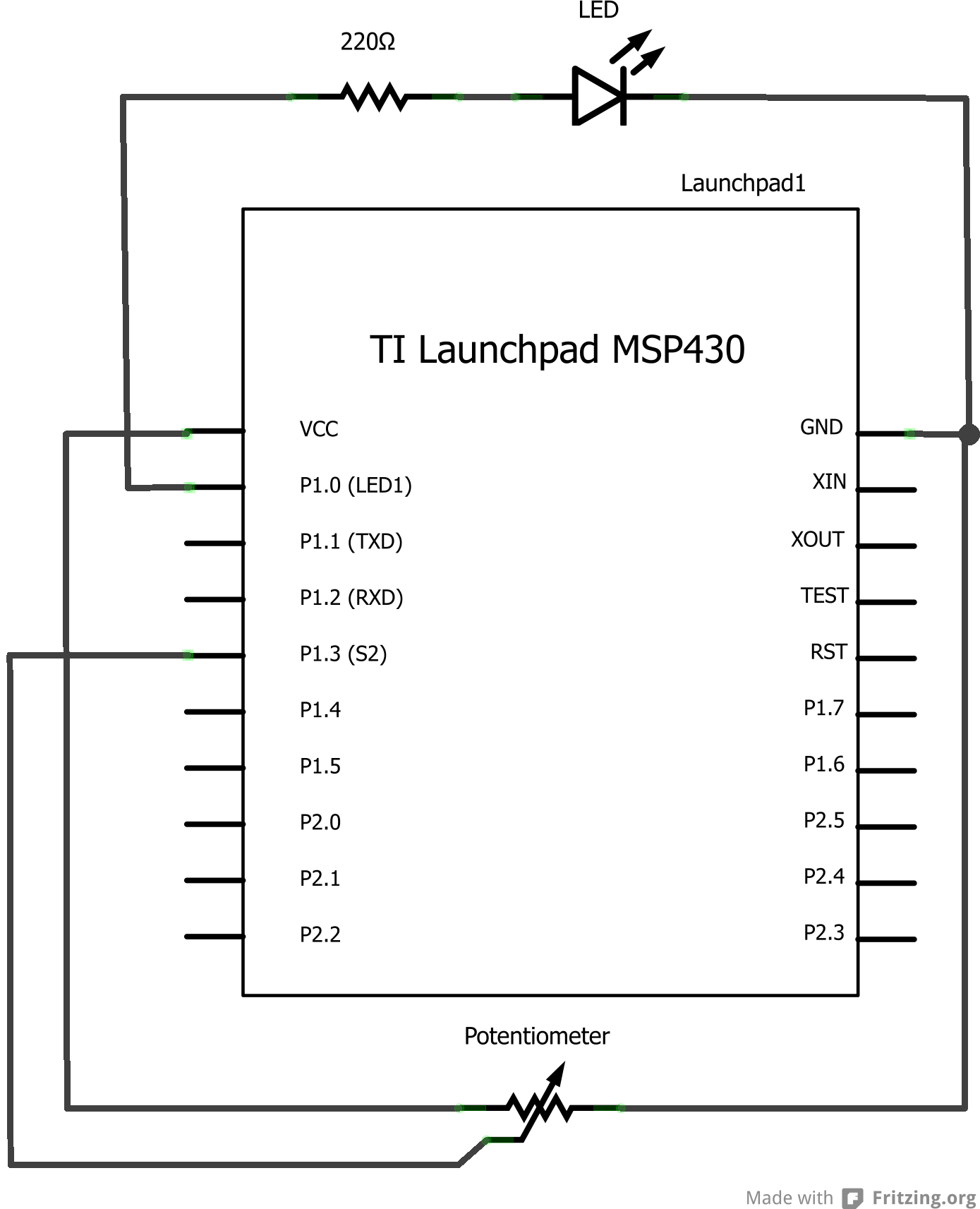
Energia is a rapid prototyping platform for the Texas Instruments MCU Launchpad. It is based on Wiring and Arduino and utilizes the Processing IDE.
Energia serves as an accessible development environment designed specifically for Texas Instruments' microcontroller (MCU) Launchpad series. The platform leverages the simplicity of the Wiring framework and the familiarity of the Arduino programming language, making it easier for developers to create and test applications efficiently. The Processing Integrated Development Environment (IDE) enhances user experience by providing a straightforward interface for writing, debugging, and uploading code to the MCU.
The Energia platform supports a wide range of Texas Instruments MCUs, allowing for versatile application development across various projects. It includes a library of pre-built functions and examples, enabling users to quickly implement features such as digital I/O, analog input, and communication protocols (I2C, SPI, UART). This extensive library simplifies the process of interfacing with sensors, actuators, and other peripherals.
Energia also promotes rapid iteration and prototyping through its ability to compile and upload code seamlessly. Developers can modify their code and immediately test changes on the hardware, facilitating a more dynamic development cycle. The platform's compatibility with various hardware configurations and its community-driven support further enhance its utility for both novice and experienced engineers.
In summary, Energia is a robust and user-friendly platform that streamlines the development process for projects utilizing Texas Instruments MCU Launchpads, fostering innovation and creativity in embedded systems design.Energia is a rapid prototyping platform for the Texas Instruments MCU Launchpad. Energia is based on Wiring and Arduino and uses the Processing IDE.. 🔗 External reference
Energia serves as an accessible development environment designed specifically for Texas Instruments' microcontroller (MCU) Launchpad series. The platform leverages the simplicity of the Wiring framework and the familiarity of the Arduino programming language, making it easier for developers to create and test applications efficiently. The Processing Integrated Development Environment (IDE) enhances user experience by providing a straightforward interface for writing, debugging, and uploading code to the MCU.
The Energia platform supports a wide range of Texas Instruments MCUs, allowing for versatile application development across various projects. It includes a library of pre-built functions and examples, enabling users to quickly implement features such as digital I/O, analog input, and communication protocols (I2C, SPI, UART). This extensive library simplifies the process of interfacing with sensors, actuators, and other peripherals.
Energia also promotes rapid iteration and prototyping through its ability to compile and upload code seamlessly. Developers can modify their code and immediately test changes on the hardware, facilitating a more dynamic development cycle. The platform's compatibility with various hardware configurations and its community-driven support further enhance its utility for both novice and experienced engineers.
In summary, Energia is a robust and user-friendly platform that streamlines the development process for projects utilizing Texas Instruments MCU Launchpads, fostering innovation and creativity in embedded systems design.Energia is a rapid prototyping platform for the Texas Instruments MCU Launchpad. Energia is based on Wiring and Arduino and uses the Processing IDE.. 🔗 External reference