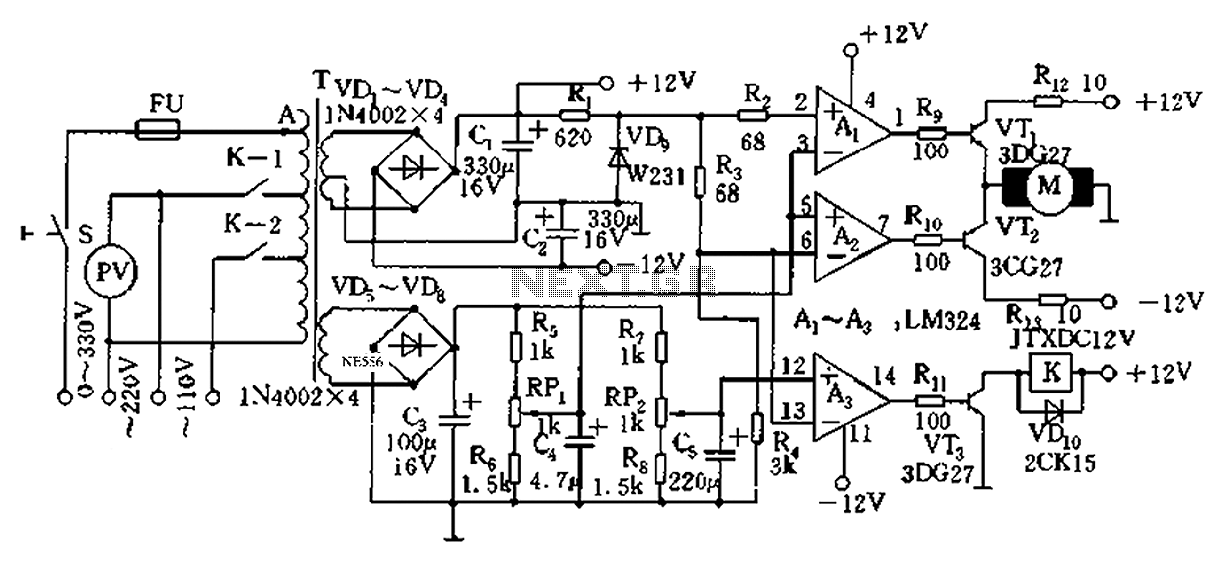
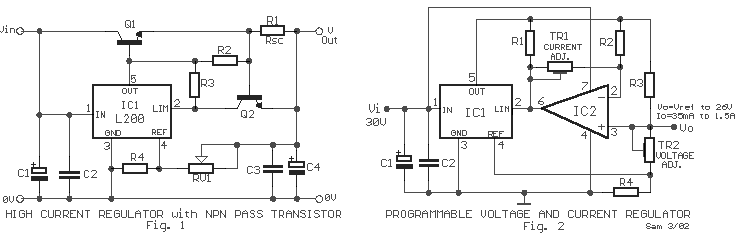
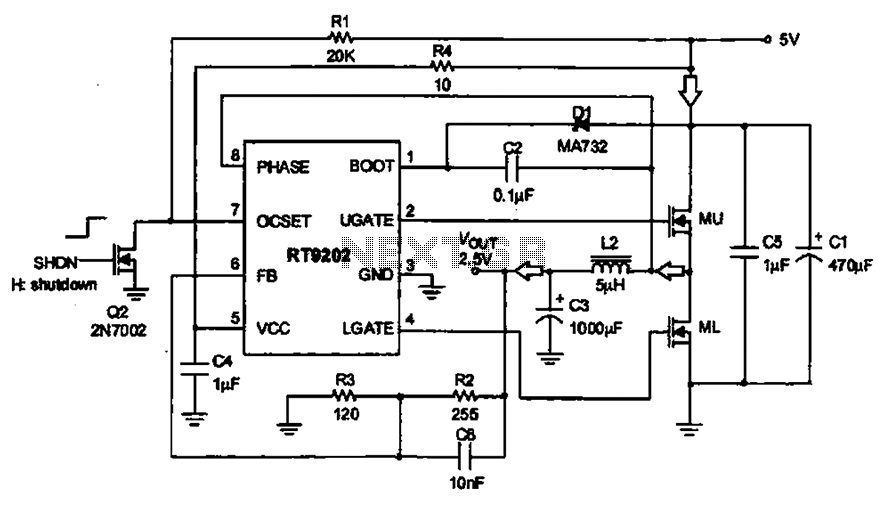
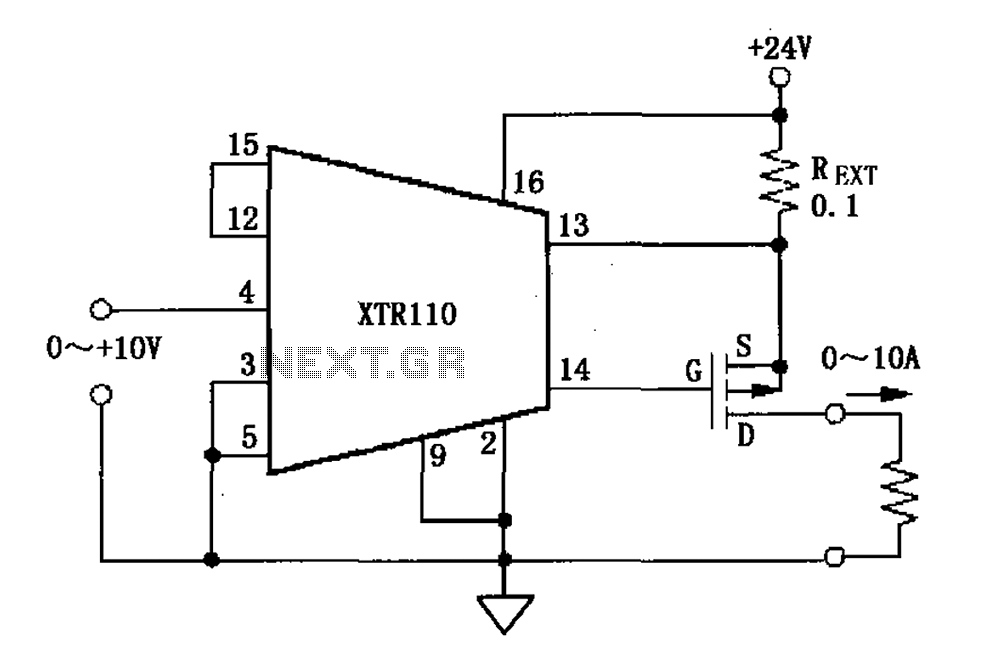
Pulse Width to Analog Voltage Demodulator
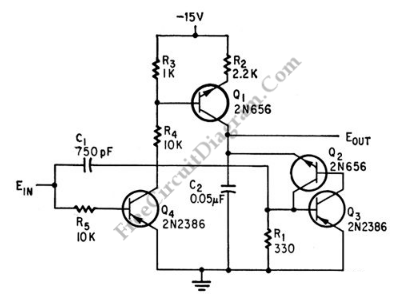
This is a schematic diagram of a pulse width to analog demodulator circuit. This circuit is used to demodulate the pulse width to an analog voltage level.
The pulse width to analog demodulator circuit is designed to convert pulse-width modulated (PWM) signals into corresponding analog voltage levels. This conversion is essential in various applications, such as motor control, audio signal processing, and sensor interfacing, where a PWM signal needs to be translated into a usable analog format.
The core components of the circuit typically include an operational amplifier (op-amp), resistors, and capacitors. The PWM input signal is fed into the circuit, where the op-amp is configured to integrate the pulse widths over a specified time period. This integration process effectively averages the PWM signal, resulting in a smooth analog output voltage that corresponds to the duty cycle of the input pulses.
The resistors in the circuit can be used to set the gain of the op-amp, allowing for adjustments in the output voltage range. Capacitors are employed to filter high-frequency noise and stabilize the output, ensuring that the analog signal is clean and representative of the PWM input.
In summary, the pulse width to analog demodulator circuit serves as a crucial interface between digital control signals and analog systems, enabling effective signal processing and control in electronic applications.This is a schematic diagram of a pulse width to analog demodulator circuit. This circuit is used to demodulate the pulse width to analog voltage level. With. 🔗 External reference
The pulse width to analog demodulator circuit is designed to convert pulse-width modulated (PWM) signals into corresponding analog voltage levels. This conversion is essential in various applications, such as motor control, audio signal processing, and sensor interfacing, where a PWM signal needs to be translated into a usable analog format.
The core components of the circuit typically include an operational amplifier (op-amp), resistors, and capacitors. The PWM input signal is fed into the circuit, where the op-amp is configured to integrate the pulse widths over a specified time period. This integration process effectively averages the PWM signal, resulting in a smooth analog output voltage that corresponds to the duty cycle of the input pulses.
The resistors in the circuit can be used to set the gain of the op-amp, allowing for adjustments in the output voltage range. Capacitors are employed to filter high-frequency noise and stabilize the output, ensuring that the analog signal is clean and representative of the PWM input.
In summary, the pulse width to analog demodulator circuit serves as a crucial interface between digital control signals and analog systems, enabling effective signal processing and control in electronic applications.This is a schematic diagram of a pulse width to analog demodulator circuit. This circuit is used to demodulate the pulse width to analog voltage level. With. 🔗 External reference