Analog Timing Light Project
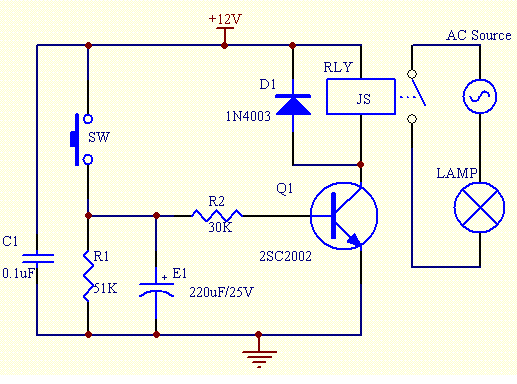
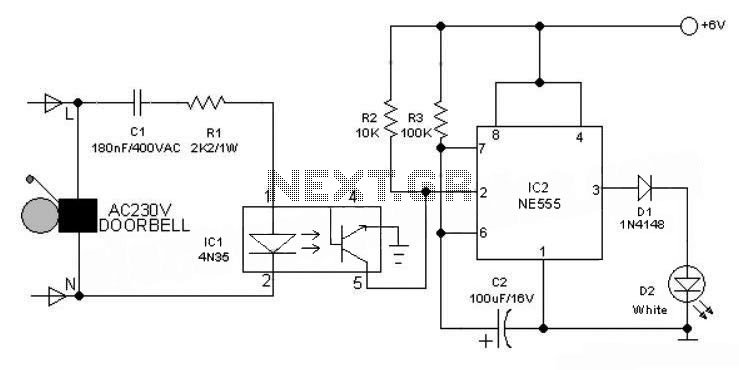
This simple electronics timing light uses an RC circuit as a delay-off timer to control an incandescent lamp via a relay.
The described timing light circuit employs a resistor-capacitor (RC) network to create a time delay that governs the operation of an incandescent lamp. The fundamental operation relies on charging and discharging the capacitor through the resistor, which determines the time interval before the relay deactivates the lamp.
In this circuit, the capacitor is charged through the resistor when power is supplied. The time constant, defined as the product of the resistance (R) and capacitance (C) values (τ = R × C), dictates how long the capacitor takes to charge to a specific voltage level. Once the voltage across the capacitor reaches a predetermined threshold, typically set by the relay's control voltage, the relay is activated, allowing current to flow to the incandescent lamp.
The relay acts as an electronic switch, enabling the control of higher power loads without the need for a direct switch. When the capacitor discharges after reaching the threshold, the relay is deactivated, turning off the lamp. This mechanism ensures that the lamp remains lit for a specified duration after the triggering event, providing functionality for applications such as automotive timing lights or decorative lighting systems.
Additional components may include a diode across the relay coil to prevent back EMF from damaging other circuit elements, as well as a potentiometer to allow for adjustable timing settings. Proper selection of the resistor and capacitor values is essential to achieve the desired delay time, making this circuit versatile for various timing applications.
Overall, this simple yet effective timing light circuit demonstrates the practical use of RC timing principles in controlling incandescent lamps through relay actuation.This simple electronics timing light uses RC circuit as a delay OFF timer to control an incandescent lamp by using a relay 🔗 External reference
The described timing light circuit employs a resistor-capacitor (RC) network to create a time delay that governs the operation of an incandescent lamp. The fundamental operation relies on charging and discharging the capacitor through the resistor, which determines the time interval before the relay deactivates the lamp.
In this circuit, the capacitor is charged through the resistor when power is supplied. The time constant, defined as the product of the resistance (R) and capacitance (C) values (τ = R × C), dictates how long the capacitor takes to charge to a specific voltage level. Once the voltage across the capacitor reaches a predetermined threshold, typically set by the relay's control voltage, the relay is activated, allowing current to flow to the incandescent lamp.
The relay acts as an electronic switch, enabling the control of higher power loads without the need for a direct switch. When the capacitor discharges after reaching the threshold, the relay is deactivated, turning off the lamp. This mechanism ensures that the lamp remains lit for a specified duration after the triggering event, providing functionality for applications such as automotive timing lights or decorative lighting systems.
Additional components may include a diode across the relay coil to prevent back EMF from damaging other circuit elements, as well as a potentiometer to allow for adjustable timing settings. Proper selection of the resistor and capacitor values is essential to achieve the desired delay time, making this circuit versatile for various timing applications.
Overall, this simple yet effective timing light circuit demonstrates the practical use of RC timing principles in controlling incandescent lamps through relay actuation.This simple electronics timing light uses RC circuit as a delay OFF timer to control an incandescent lamp by using a relay 🔗 External reference