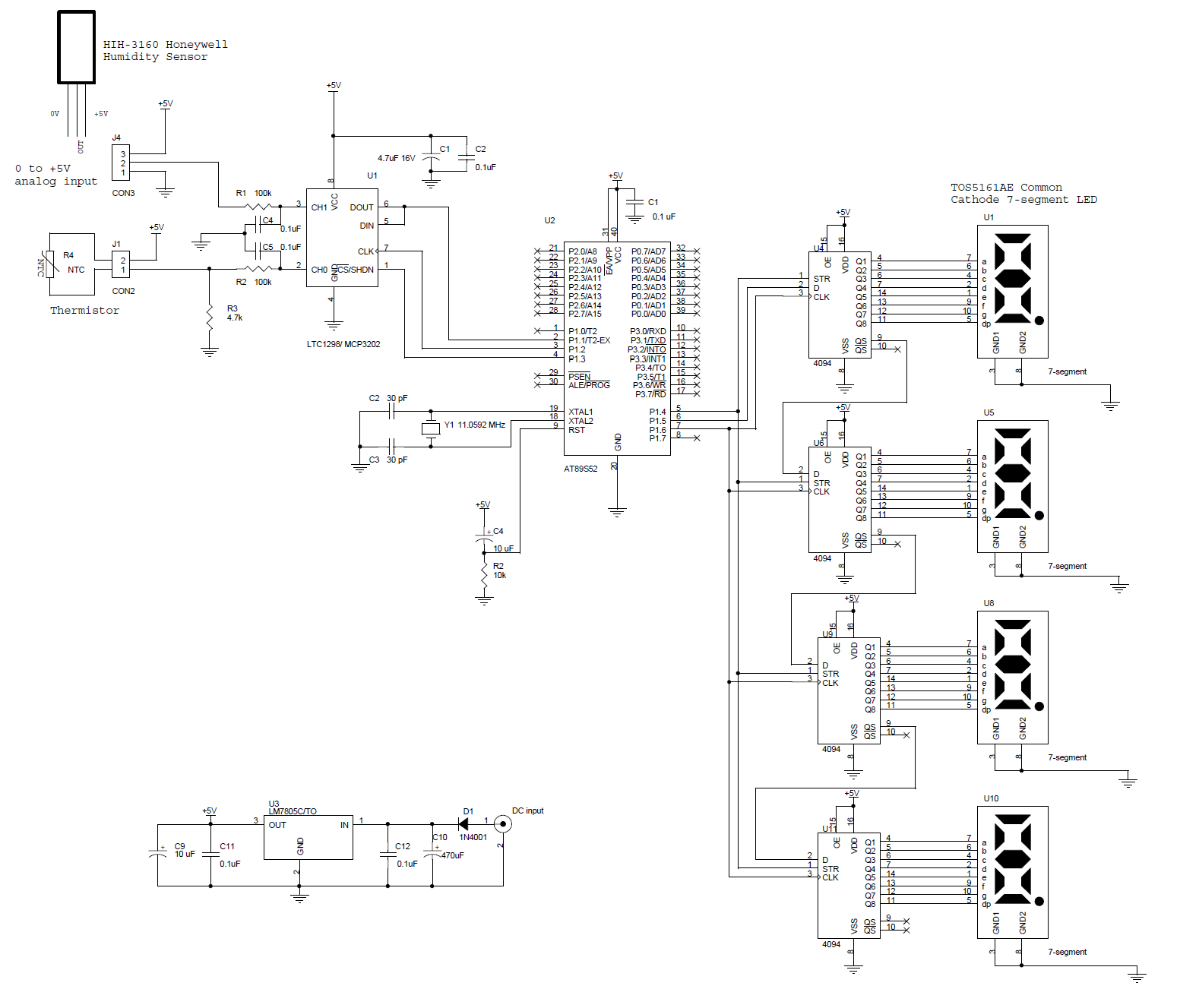
arduino serial thermometer
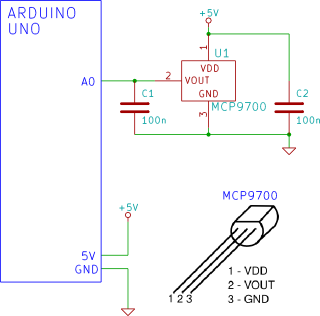
The Arduino reads temperature from an MCP9700 temperature sensor IC and displays the temperature in the Arduino IDE serial monitor window.
The circuit utilizes an Arduino microcontroller along with an MCP9700 temperature sensor integrated circuit (IC) to measure ambient temperature. The MCP9700 operates within a voltage range of 2.7V to 5.5V and outputs an analog voltage that is linearly proportional to the temperature, with a scale factor of 19.5 mV/°C.
In this configuration, the MCP9700 is connected to one of the analog input pins of the Arduino. The output pin of the MCP9700 is connected to an analog input pin, typically labeled A0 on the Arduino board. A power supply connection is established by connecting the VDD pin of the MCP9700 to the Arduino's 5V output and the GND pin to the common ground.
The Arduino is programmed to read the analog voltage output from the MCP9700. This voltage is converted into a temperature reading using the formula:
Temperature (°C) = (Analog Read Value * 5V / 1024 - 0.5) / 0.0195
The calculated temperature is then displayed in the Arduino IDE's serial monitor, providing real-time temperature readings. The code structure includes initializing the serial communication in the setup function and continuously reading the analog input in the loop function, followed by the conversion of the analog value to temperature and outputting the result to the serial monitor.
This setup is suitable for various applications, including environmental monitoring, weather stations, and educational projects to demonstrate temperature sensing and data acquisition using microcontrollers.The Arduino reads temperature from a MCP9700 temperature sensor IC and displays the temperature in the Arduino IDE serial monitor window.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes an Arduino microcontroller along with an MCP9700 temperature sensor integrated circuit (IC) to measure ambient temperature. The MCP9700 operates within a voltage range of 2.7V to 5.5V and outputs an analog voltage that is linearly proportional to the temperature, with a scale factor of 19.5 mV/°C.
In this configuration, the MCP9700 is connected to one of the analog input pins of the Arduino. The output pin of the MCP9700 is connected to an analog input pin, typically labeled A0 on the Arduino board. A power supply connection is established by connecting the VDD pin of the MCP9700 to the Arduino's 5V output and the GND pin to the common ground.
The Arduino is programmed to read the analog voltage output from the MCP9700. This voltage is converted into a temperature reading using the formula:
Temperature (°C) = (Analog Read Value * 5V / 1024 - 0.5) / 0.0195
The calculated temperature is then displayed in the Arduino IDE's serial monitor, providing real-time temperature readings. The code structure includes initializing the serial communication in the setup function and continuously reading the analog input in the loop function, followed by the conversion of the analog value to temperature and outputting the result to the serial monitor.
This setup is suitable for various applications, including environmental monitoring, weather stations, and educational projects to demonstrate temperature sensing and data acquisition using microcontrollers.The Arduino reads temperature from a MCP9700 temperature sensor IC and displays the temperature in the Arduino IDE serial monitor window.. 🔗 External reference