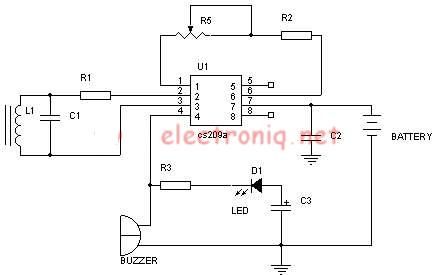
Thermocouple thermometer circuit
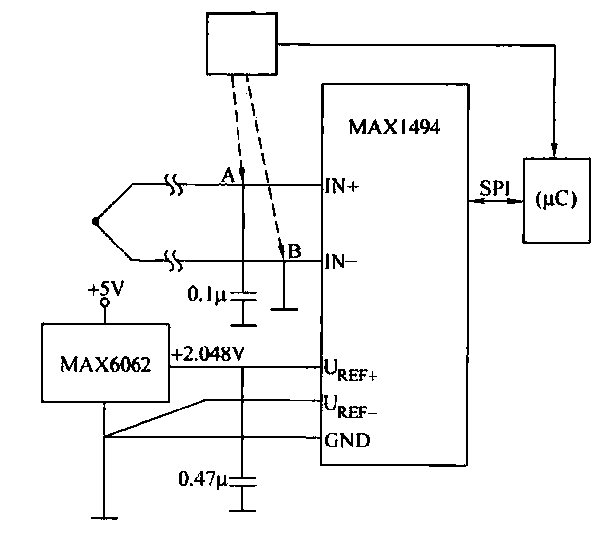
The circuit consists of the MAX1494 and a thermocouple temperature measurement system. The MAX1494 is terminated at 1N GND 5-32. An external temperature sensor, such as the DS75, can be utilized for junction temperature compensation. The MAX1494 employs an external reference voltage provided by the MAX6062, which outputs +2.048V.
The circuit design integrates the MAX1494, a precision analog front-end device, specifically tailored for thermocouple applications. It is responsible for converting the small voltage generated by the thermocouple into a digital signal that can be processed by a microcontroller or other digital systems. The termination at 1N GND 5-32 indicates the grounding scheme utilized, which is crucial for maintaining signal integrity and minimizing noise in the system.
In this setup, the DS75 external temperature sensor plays a vital role in providing accurate temperature readings. It can be interfaced with the MAX1494 to perform junction temperature compensation, ensuring that the temperature measurements reflect the actual conditions of the thermocouple junction. This compensation is essential for applications requiring high accuracy, as it accounts for any temperature differences that may affect the measurement accuracy.
The MAX6062 voltage reference is used to provide a stable reference voltage of +2.048V to the MAX1494. This external reference is critical for the performance of the MAX1494, as it ensures that the analog-to-digital conversion process is consistent and reliable, minimizing drift and enhancing the overall precision of the temperature measurements.
Overall, this combination of components creates a robust and accurate temperature measurement system suitable for various industrial and scientific applications, where precise temperature monitoring is essential.Circuit from the MAX1494 and thermocouple temperature measurement system as shown, MAX1494 termination of 1N GND 5-32. The use of an external temperature sensor (for example, DS75) and SCM can be done carry junction temperature compensation work.
MAX1494 uses an external reference provided by the MAX6062 reference voltage +2. 048V is.
The circuit design integrates the MAX1494, a precision analog front-end device, specifically tailored for thermocouple applications. It is responsible for converting the small voltage generated by the thermocouple into a digital signal that can be processed by a microcontroller or other digital systems. The termination at 1N GND 5-32 indicates the grounding scheme utilized, which is crucial for maintaining signal integrity and minimizing noise in the system.
In this setup, the DS75 external temperature sensor plays a vital role in providing accurate temperature readings. It can be interfaced with the MAX1494 to perform junction temperature compensation, ensuring that the temperature measurements reflect the actual conditions of the thermocouple junction. This compensation is essential for applications requiring high accuracy, as it accounts for any temperature differences that may affect the measurement accuracy.
The MAX6062 voltage reference is used to provide a stable reference voltage of +2.048V to the MAX1494. This external reference is critical for the performance of the MAX1494, as it ensures that the analog-to-digital conversion process is consistent and reliable, minimizing drift and enhancing the overall precision of the temperature measurements.
Overall, this combination of components creates a robust and accurate temperature measurement system suitable for various industrial and scientific applications, where precise temperature monitoring is essential.Circuit from the MAX1494 and thermocouple temperature measurement system as shown, MAX1494 termination of 1N GND 5-32. The use of an external temperature sensor (for example, DS75) and SCM can be done carry junction temperature compensation work.
MAX1494 uses an external reference provided by the MAX6062 reference voltage +2. 048V is.