Astable Multivibrator using transistors
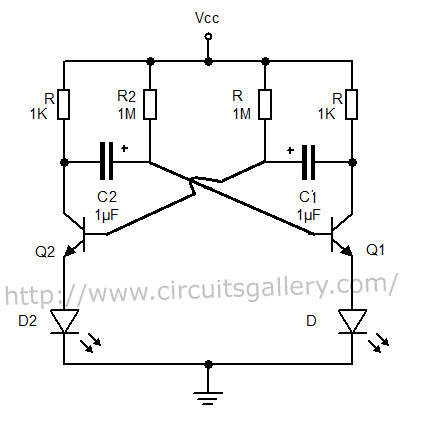
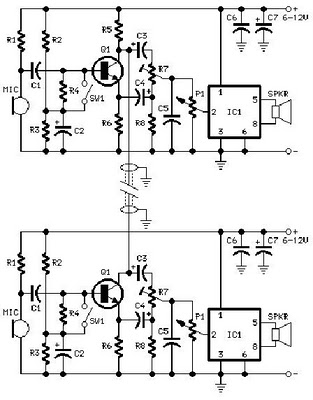
The output can also be taken from the collector terminals of the transistors, as illustrated in the circuit below. To understand the operation of the circuit, it is recommended to read about how a transistor functions as a switch.
In a typical transistor switching circuit, the transistor operates in two states: saturation and cutoff. When the transistor is in saturation, it allows maximum current to flow from the collector to the emitter, effectively acting as a closed switch. Conversely, in the cutoff state, the transistor prevents current flow, acting as an open switch.
The circuit can be configured with various components such as resistors, capacitors, and additional transistors to create more complex switching applications. The base terminal of the transistor is controlled by an input signal, which determines whether the transistor is in the on or off state.
For instance, a resistor may be connected to the base to limit the current flowing into it, ensuring the transistor operates within its safe limits. The collector terminal can be connected to a load, such as an LED or motor, which will be activated when the transistor is in the saturation state.
Understanding the behavior of the transistor in this configuration is essential for designing reliable electronic circuits. Proper biasing and component selection are critical to ensure the transistor switches effectively and does not enter undesirable operating regions. Additionally, the characteristics of the transistor, such as its current gain (beta), must be considered when designing the circuit to achieve the desired output performance.We can also take output from collector terminals of the transistors, such circuit is show below. To know the working of below circuit you must read How transistor acts as a switch 🔗 External reference
In a typical transistor switching circuit, the transistor operates in two states: saturation and cutoff. When the transistor is in saturation, it allows maximum current to flow from the collector to the emitter, effectively acting as a closed switch. Conversely, in the cutoff state, the transistor prevents current flow, acting as an open switch.
The circuit can be configured with various components such as resistors, capacitors, and additional transistors to create more complex switching applications. The base terminal of the transistor is controlled by an input signal, which determines whether the transistor is in the on or off state.
For instance, a resistor may be connected to the base to limit the current flowing into it, ensuring the transistor operates within its safe limits. The collector terminal can be connected to a load, such as an LED or motor, which will be activated when the transistor is in the saturation state.
Understanding the behavior of the transistor in this configuration is essential for designing reliable electronic circuits. Proper biasing and component selection are critical to ensure the transistor switches effectively and does not enter undesirable operating regions. Additionally, the characteristics of the transistor, such as its current gain (beta), must be considered when designing the circuit to achieve the desired output performance.We can also take output from collector terminals of the transistors, such circuit is show below. To know the working of below circuit you must read How transistor acts as a switch 🔗 External reference