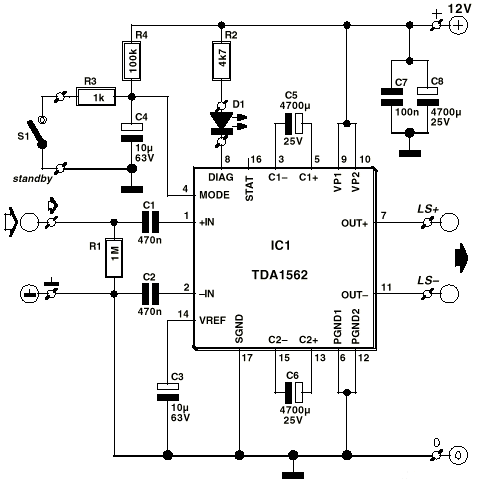
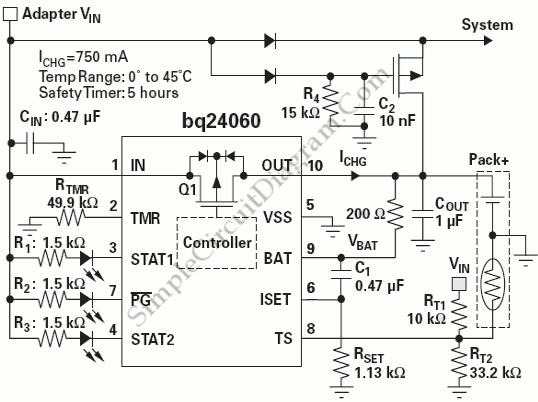
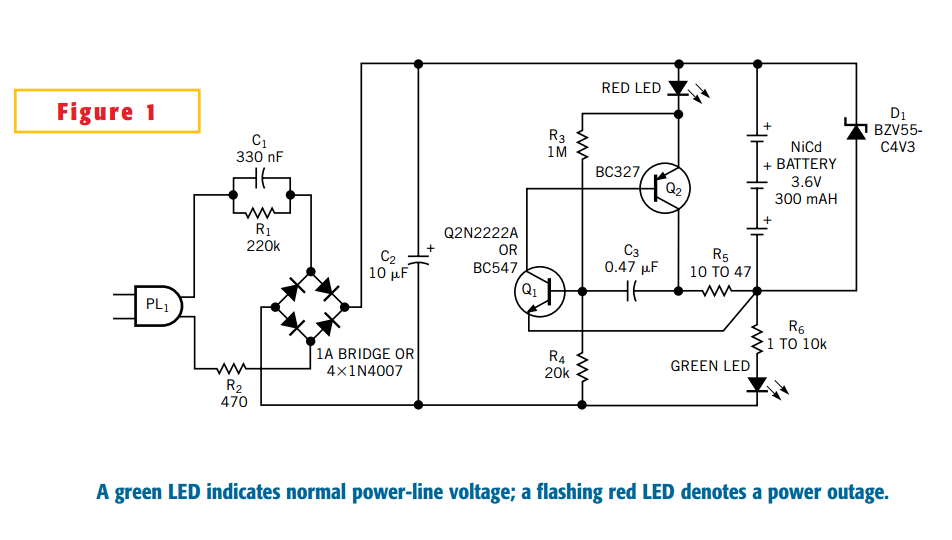
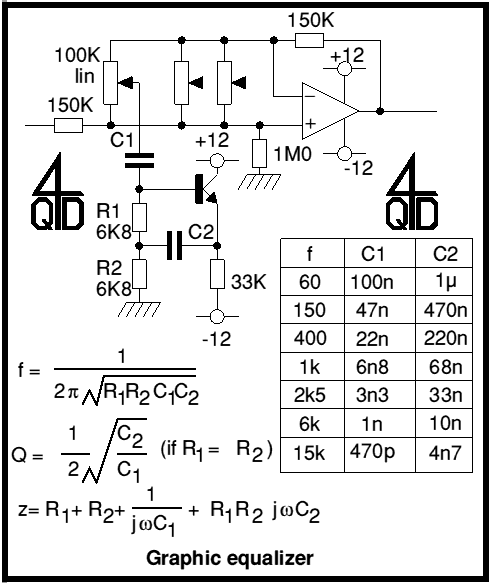
Audio Power Limiter
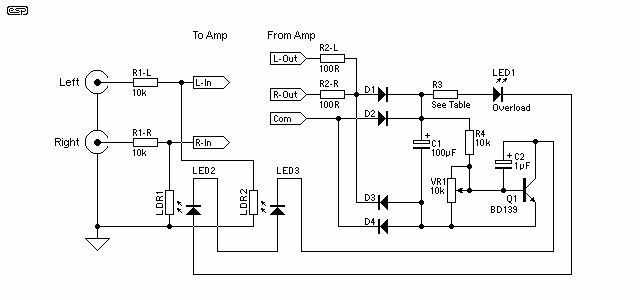
The gain control element is a Light Dependent Resistor (LDR). These are blessed with a few very useful features for our purposes, one of which is low distortion even at quite high signal levels. Being light activated, all we need is a LED to provide illumination when the preset power level is reached. More: Once this point is reached, a very small increase in amplifier output voltage (and power) will cause the LED to provide much more light, reducing the value of the LDR, and thus reducing the input voltage. The effect is to keep the level more or less constant.
The circuit utilizes a Light Dependent Resistor (LDR) as a key component for gain control in an audio amplifier application. The LDR is characterized by its resistance decreasing with increasing light levels, making it suitable for automatic gain control (AGC) systems. The LDR is connected in a voltage divider configuration, where it pairs with a fixed resistor to form a reference voltage for the amplifier's input stage.
An LED is employed as the illumination source for the LDR. When the amplifier reaches a predetermined output level, the LED is activated, emitting light that strikes the LDR. As the LED brightness increases, the resistance of the LDR decreases significantly, leading to a reduction in the voltage at the amplifier's input. This feedback mechanism effectively stabilizes the output level by preventing the amplifier from exceeding the set threshold.
The circuit can be designed to include additional components such as operational amplifiers or transistors to enhance performance and provide further control over the gain characteristics. The choice of the fixed resistor in the voltage divider will determine the sensitivity of the gain control, allowing for adjustments based on the desired output level and response time.
The overall design ensures that the system maintains low distortion across a range of signal levels, providing a reliable and efficient method for automatic gain control in audio applications. The use of an LDR and LED combination not only simplifies the circuitry but also enhances the adaptability of the amplifier to varying input conditions, making it a robust solution for dynamic audio environments.The gain control element is a Light Dependent Resistor (LDR). These are blessed with a few very useful features for our purposes, one of which is low distortion even at quite high signal levels. Being light activated, all we need is a LED to provide illumination when the preset power level is reached.
Once this point is reached, a very small increase in amplifier output voltage (and power) will cause the LED to provide much more light, reducing the value of the LDR, and thus reducing the input voltage. The effect is to keep the level more or less const 🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes a Light Dependent Resistor (LDR) as a key component for gain control in an audio amplifier application. The LDR is characterized by its resistance decreasing with increasing light levels, making it suitable for automatic gain control (AGC) systems. The LDR is connected in a voltage divider configuration, where it pairs with a fixed resistor to form a reference voltage for the amplifier's input stage.
An LED is employed as the illumination source for the LDR. When the amplifier reaches a predetermined output level, the LED is activated, emitting light that strikes the LDR. As the LED brightness increases, the resistance of the LDR decreases significantly, leading to a reduction in the voltage at the amplifier's input. This feedback mechanism effectively stabilizes the output level by preventing the amplifier from exceeding the set threshold.
The circuit can be designed to include additional components such as operational amplifiers or transistors to enhance performance and provide further control over the gain characteristics. The choice of the fixed resistor in the voltage divider will determine the sensitivity of the gain control, allowing for adjustments based on the desired output level and response time.
The overall design ensures that the system maintains low distortion across a range of signal levels, providing a reliable and efficient method for automatic gain control in audio applications. The use of an LDR and LED combination not only simplifies the circuitry but also enhances the adaptability of the amplifier to varying input conditions, making it a robust solution for dynamic audio environments.The gain control element is a Light Dependent Resistor (LDR). These are blessed with a few very useful features for our purposes, one of which is low distortion even at quite high signal levels. Being light activated, all we need is a LED to provide illumination when the preset power level is reached.
Once this point is reached, a very small increase in amplifier output voltage (and power) will cause the LED to provide much more light, reducing the value of the LDR, and thus reducing the input voltage. The effect is to keep the level more or less const 🔗 External reference