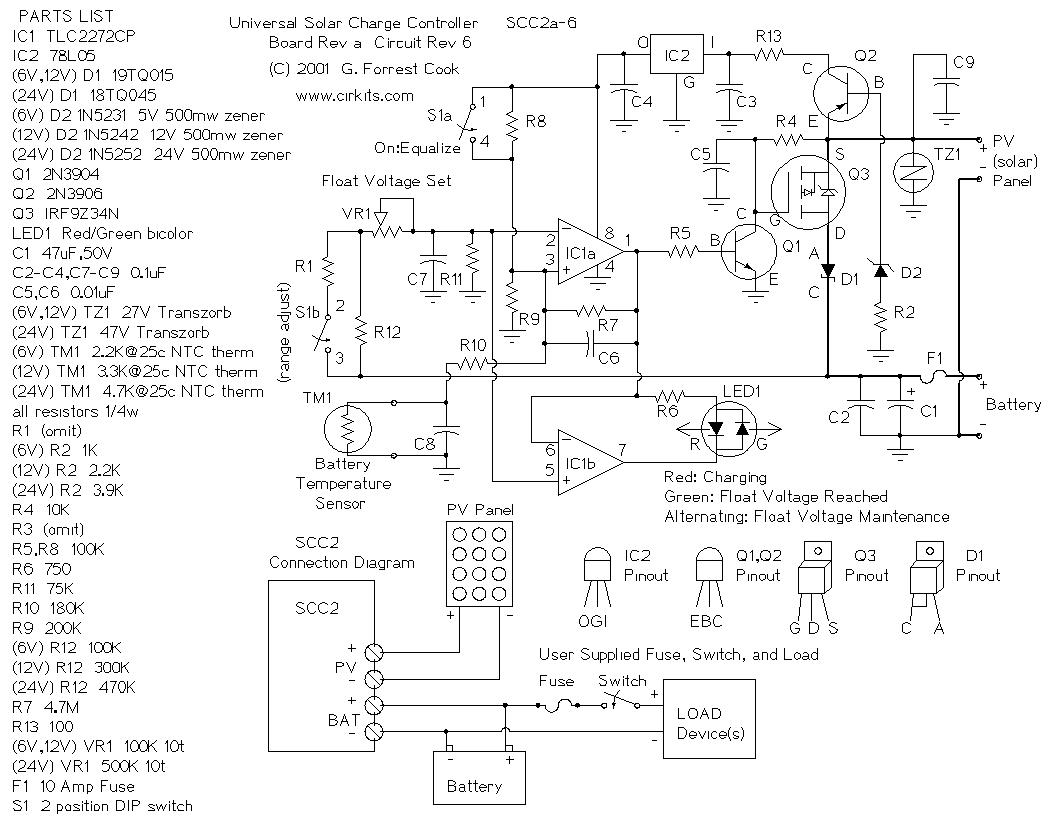
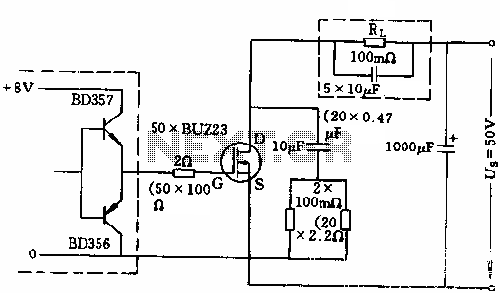
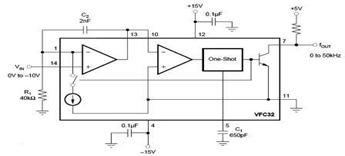
Audio signal control circuit
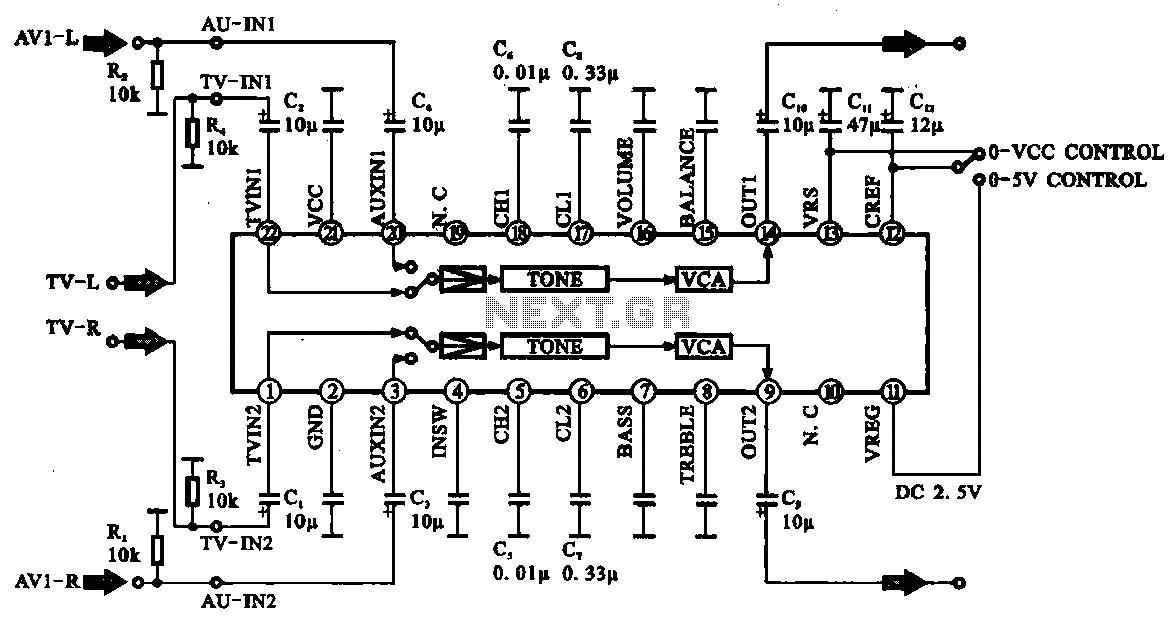
Audio signal control circuit. It illustrates a typical audio signal control circuit where two audio signals enter the integrated circuit through switching and tone controls (treble and bass), subsequently adjusting the output sent to the audio power amplifier.
The audio signal control circuit serves as a crucial component in audio processing systems, allowing for the manipulation of sound signals before amplification. This circuit typically consists of an integrated circuit (IC) that incorporates various functionalities, including input switching, tone adjustment, and output control.
In this configuration, two audio signals are fed into the IC, which can be selected based on user preference or system requirements. The switching mechanism is often implemented using analog switches or digital multiplexers, enabling seamless transitions between the audio sources without introducing noise or distortion.
Once the desired audio source is selected, the signal passes through tone control stages where treble and bass adjustments are made. These adjustments are typically achieved using passive components such as capacitors and resistors, or through active components like operational amplifiers configured in tone control circuits. The treble control adjusts the higher frequency response, enhancing or attenuating specific ranges, while the bass control modifies lower frequencies, allowing users to tailor the audio output to their liking.
After the tone adjustments are completed, the processed audio signal is then sent to an audio power amplifier. The amplifier's role is to increase the signal's power level to drive speakers or other output devices effectively. The output stage may include additional filtering to ensure that the final audio signal is free from unwanted noise and distortion, providing a clean and high-quality sound experience.
Overall, this audio signal control circuit is essential for achieving optimal sound quality and user satisfaction in various audio applications, from home theater systems to professional audio equipment.Audio signal control circuit It shows a typical audio signal control circuit. Two audio signal into the integrated circuit through the switching and tone (treble, then adjust the output sent to the audio power amplifier bass).
The audio signal control circuit serves as a crucial component in audio processing systems, allowing for the manipulation of sound signals before amplification. This circuit typically consists of an integrated circuit (IC) that incorporates various functionalities, including input switching, tone adjustment, and output control.
In this configuration, two audio signals are fed into the IC, which can be selected based on user preference or system requirements. The switching mechanism is often implemented using analog switches or digital multiplexers, enabling seamless transitions between the audio sources without introducing noise or distortion.
Once the desired audio source is selected, the signal passes through tone control stages where treble and bass adjustments are made. These adjustments are typically achieved using passive components such as capacitors and resistors, or through active components like operational amplifiers configured in tone control circuits. The treble control adjusts the higher frequency response, enhancing or attenuating specific ranges, while the bass control modifies lower frequencies, allowing users to tailor the audio output to their liking.
After the tone adjustments are completed, the processed audio signal is then sent to an audio power amplifier. The amplifier's role is to increase the signal's power level to drive speakers or other output devices effectively. The output stage may include additional filtering to ensure that the final audio signal is free from unwanted noise and distortion, providing a clean and high-quality sound experience.
Overall, this audio signal control circuit is essential for achieving optimal sound quality and user satisfaction in various audio applications, from home theater systems to professional audio equipment.Audio signal control circuit It shows a typical audio signal control circuit. Two audio signal into the integrated circuit through the switching and tone (treble, then adjust the output sent to the audio power amplifier bass).