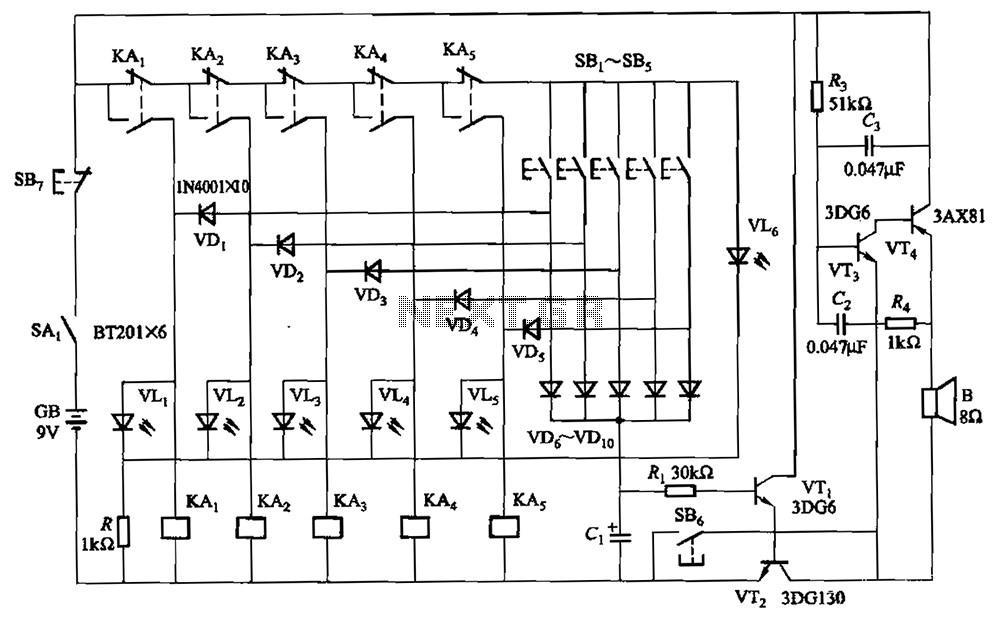
Audio Sound Effects Circuit
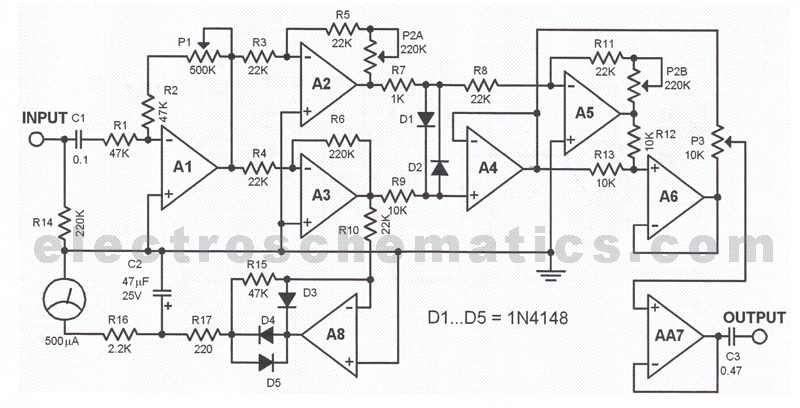
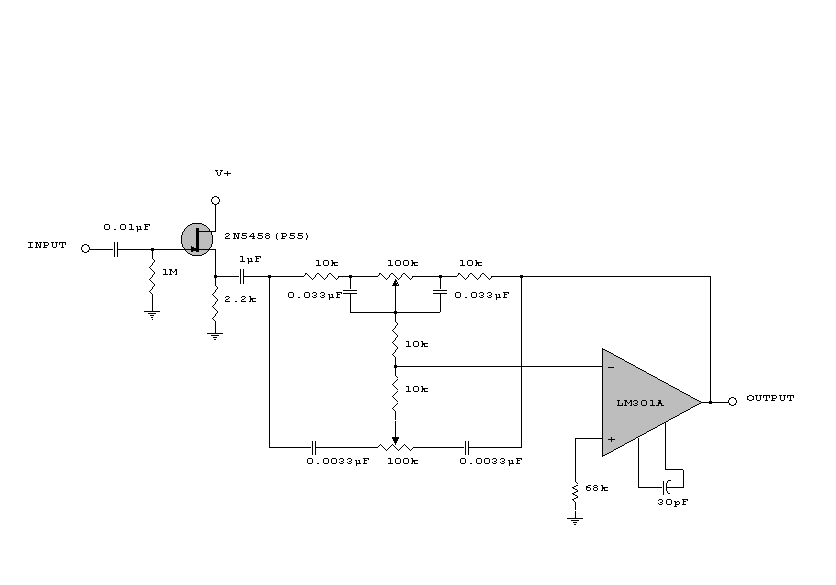
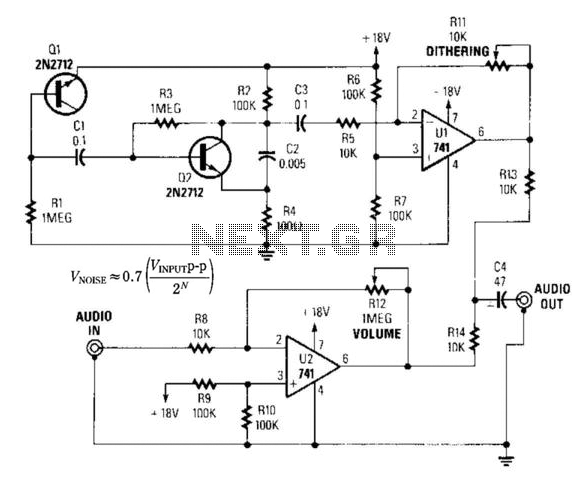
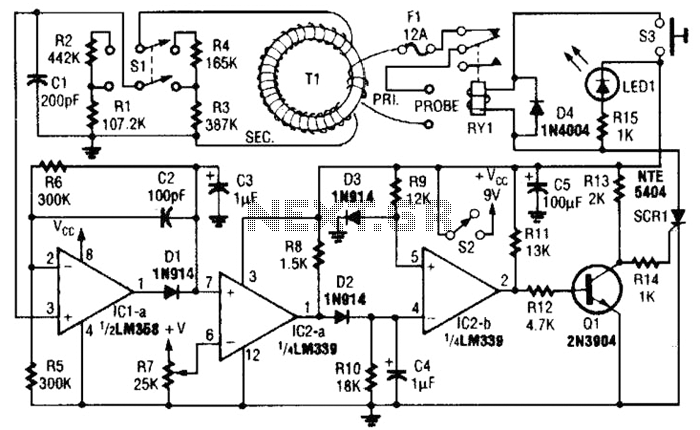
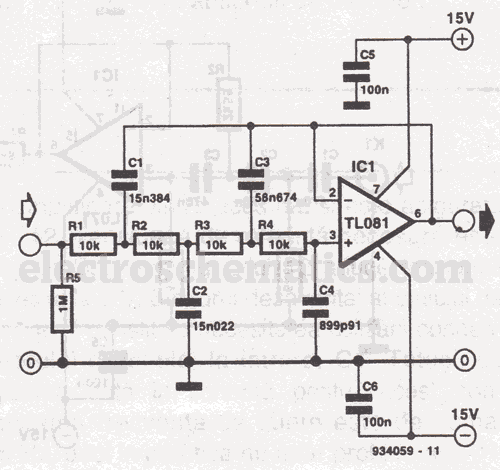
This sound effects circuit is designed to function as a signal distorter. When utilized with an electric guitar, it enables the creation of unique sound effects.
The sound effects circuit operates by manipulating the input audio signal from the electric guitar, introducing non-linearities that result in distortion. The primary components of this circuit typically include operational amplifiers (op-amps), diodes, resistors, and capacitors.
The circuit begins with the input stage, where the guitar signal is fed into a buffer amplifier. This buffer prevents loading effects that could alter the sound characteristics. Following this, the signal is directed to a distortion stage, which often employs an op-amp configured in a non-inverting mode. The gain of this stage can be adjusted using a variable resistor, allowing users to control the level of distortion.
Diodes are commonly used in the feedback loop of the op-amp to clip the signal peaks, creating the desired distortion effect. The choice of diodes can significantly affect the tonal characteristics, with silicon diodes producing a sharper clipping compared to germanium diodes, which yield a warmer sound.
After the distortion stage, the signal may pass through a tone control circuit consisting of capacitors and resistors that shape the frequency response, allowing users to enhance or attenuate specific frequencies. Finally, the output stage may include another buffer to drive the output signal to an amplifier or effects chain without degradation.
This circuit can be housed in a compact enclosure with input and output jacks, a power supply connector, and control knobs for gain and tone adjustments, providing musicians with a versatile tool for enhancing their sound. The design can be adapted with additional features such as a bypass switch, LED indicators, or even a built-in reverb effect, making it a valuable addition to any guitarist's setup.This sound effects circuit is designed to work as a signal distorter. If used with an electric guitar, it allows the production of special sound effects. T.. 🔗 External reference
The sound effects circuit operates by manipulating the input audio signal from the electric guitar, introducing non-linearities that result in distortion. The primary components of this circuit typically include operational amplifiers (op-amps), diodes, resistors, and capacitors.
The circuit begins with the input stage, where the guitar signal is fed into a buffer amplifier. This buffer prevents loading effects that could alter the sound characteristics. Following this, the signal is directed to a distortion stage, which often employs an op-amp configured in a non-inverting mode. The gain of this stage can be adjusted using a variable resistor, allowing users to control the level of distortion.
Diodes are commonly used in the feedback loop of the op-amp to clip the signal peaks, creating the desired distortion effect. The choice of diodes can significantly affect the tonal characteristics, with silicon diodes producing a sharper clipping compared to germanium diodes, which yield a warmer sound.
After the distortion stage, the signal may pass through a tone control circuit consisting of capacitors and resistors that shape the frequency response, allowing users to enhance or attenuate specific frequencies. Finally, the output stage may include another buffer to drive the output signal to an amplifier or effects chain without degradation.
This circuit can be housed in a compact enclosure with input and output jacks, a power supply connector, and control knobs for gain and tone adjustments, providing musicians with a versatile tool for enhancing their sound. The design can be adapted with additional features such as a bypass switch, LED indicators, or even a built-in reverb effect, making it a valuable addition to any guitarist's setup.This sound effects circuit is designed to work as a signal distorter. If used with an electric guitar, it allows the production of special sound effects. T.. 🔗 External reference