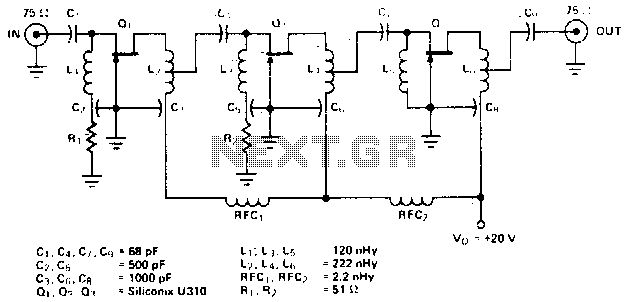
100W Guitar Amplifier 2
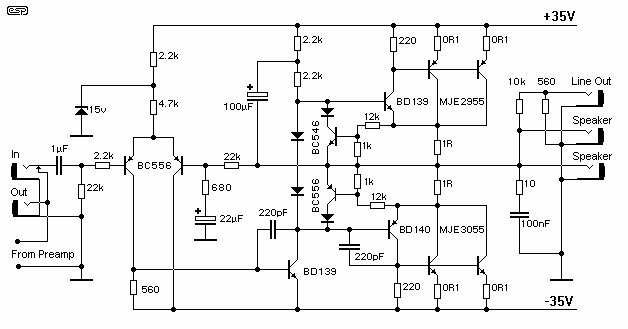
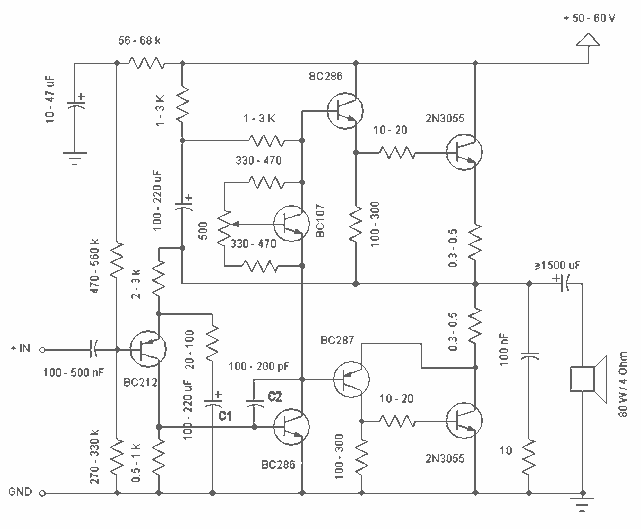
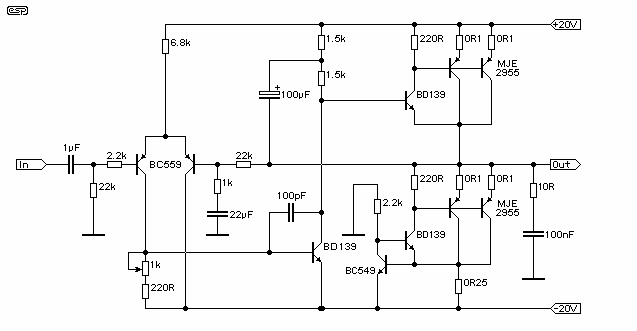
The schematic has been modified slightly to improve the tone control performance (04 Jan 2002). A new schematic is now on line - the differences are relatively minor, but make the component values for the tone controls a bit cheaper (smaller value caps, and higher value pots). The power amp has been heavily revised, and the new version is also available. More: If a really quiet amp is desired, you should substitute a 5532 dual opamp. These are more expensive (and harder to get), but will offer a substantial noise reduction. If you don`t need all the gain that is available, simply increase the value of the
The modified schematic presents a refined approach to tone control, enhancing performance through strategic component value adjustments. The tone control circuit now utilizes smaller capacitance values in conjunction with higher resistance potentiometers, which not only reduces costs but also optimizes the circuit's response to audio signals. This configuration is particularly beneficial for achieving a smoother tonal balance without compromising sound quality.
The power amplifier section has undergone significant revisions, likely addressing previous limitations in output fidelity and efficiency. The new design may incorporate improved transistor configurations and feedback mechanisms, contributing to a more robust amplification process. Specific changes in component ratings and types could lead to enhanced thermal performance and lower distortion levels, making the amplifier more suitable for high-fidelity audio applications.
For users seeking a quieter operation, the recommendation to replace the standard op-amp with a 5532 dual op-amp is noteworthy. This component is recognized for its low noise characteristics, which can dramatically reduce background hiss and improve the overall signal-to-noise ratio. While the 5532 may present challenges in terms of availability and cost, its implementation is justified for applications where audio clarity is paramount. Furthermore, adjusting the gain settings by increasing the feedback resistor values can tailor the amplifier's output to meet specific requirements without introducing excess noise, ensuring that the circuit remains versatile for various audio setups.The schematic has been modified slightly to improve the tone control performance (04 Jan 2002). A new schematic is now on line - the differences are relatively minor, but make the component values for the tone controls a bit cheaper (smaller value caps, and higher value pots). The power amp has been heavily revised, and the new version is also available. If a really quiet amp is desired, you should substitute a 5532 dual opamp. These are more expensive (and harder to get), but will offer a substantial noise reduction. If you don`t need all the gain that is available, simply increase the value of the 🔗 External reference
The modified schematic presents a refined approach to tone control, enhancing performance through strategic component value adjustments. The tone control circuit now utilizes smaller capacitance values in conjunction with higher resistance potentiometers, which not only reduces costs but also optimizes the circuit's response to audio signals. This configuration is particularly beneficial for achieving a smoother tonal balance without compromising sound quality.
The power amplifier section has undergone significant revisions, likely addressing previous limitations in output fidelity and efficiency. The new design may incorporate improved transistor configurations and feedback mechanisms, contributing to a more robust amplification process. Specific changes in component ratings and types could lead to enhanced thermal performance and lower distortion levels, making the amplifier more suitable for high-fidelity audio applications.
For users seeking a quieter operation, the recommendation to replace the standard op-amp with a 5532 dual op-amp is noteworthy. This component is recognized for its low noise characteristics, which can dramatically reduce background hiss and improve the overall signal-to-noise ratio. While the 5532 may present challenges in terms of availability and cost, its implementation is justified for applications where audio clarity is paramount. Furthermore, adjusting the gain settings by increasing the feedback resistor values can tailor the amplifier's output to meet specific requirements without introducing excess noise, ensuring that the circuit remains versatile for various audio setups.The schematic has been modified slightly to improve the tone control performance (04 Jan 2002). A new schematic is now on line - the differences are relatively minor, but make the component values for the tone controls a bit cheaper (smaller value caps, and higher value pots). The power amp has been heavily revised, and the new version is also available. If a really quiet amp is desired, you should substitute a 5532 dual opamp. These are more expensive (and harder to get), but will offer a substantial noise reduction. If you don`t need all the gain that is available, simply increase the value of the 🔗 External reference