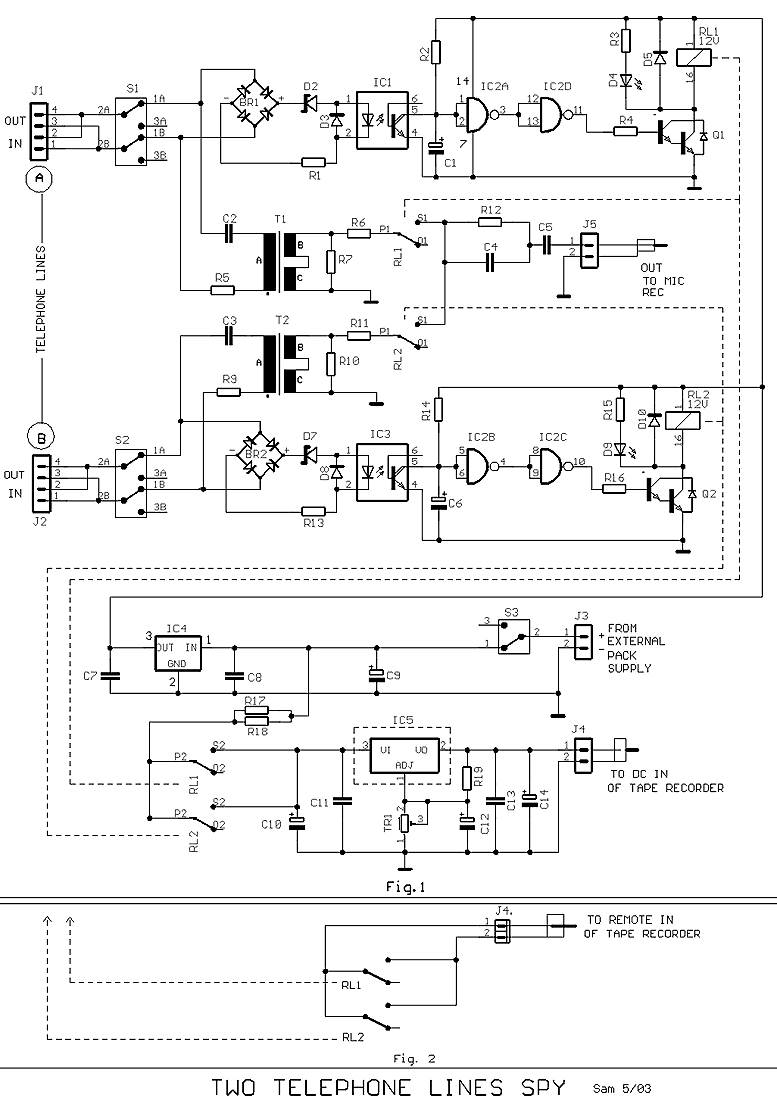
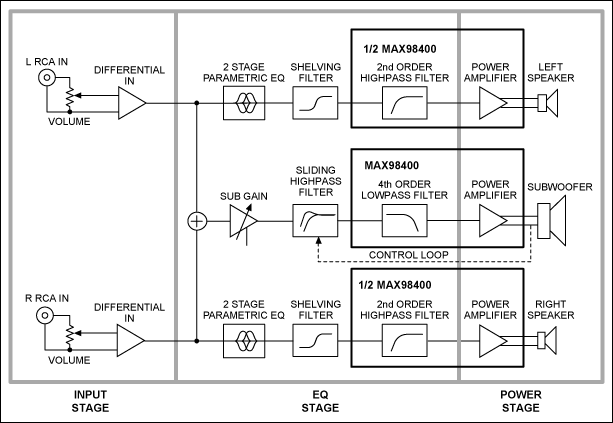
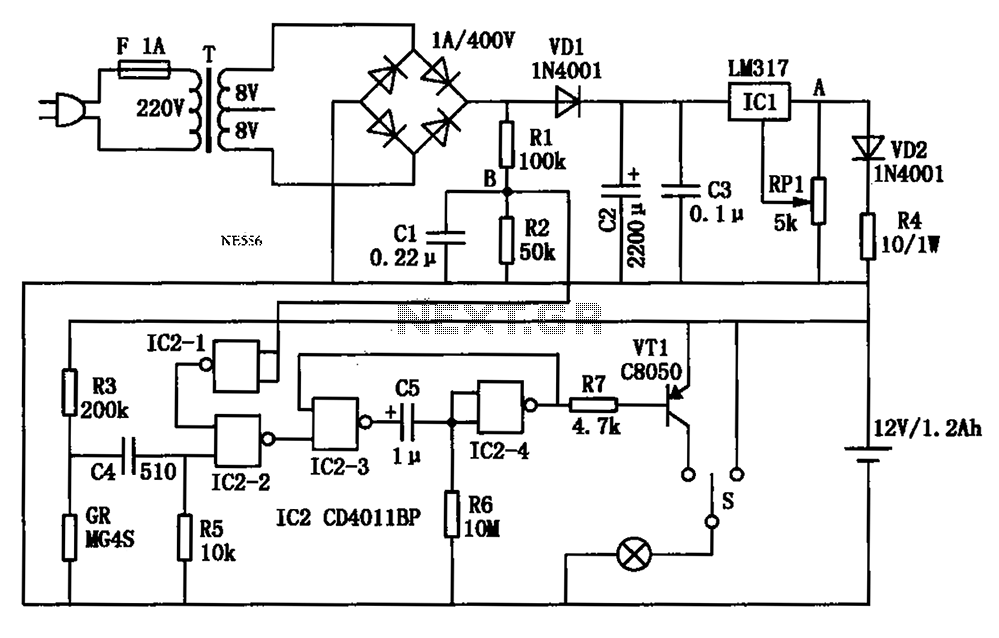
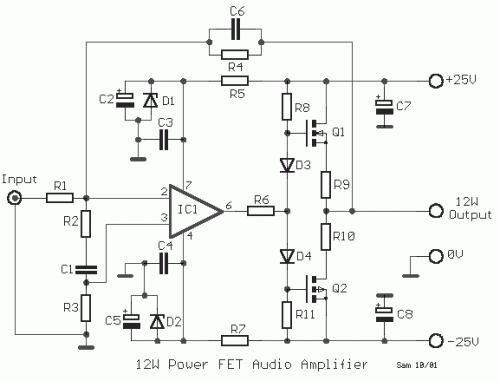
auto off for audio gear

The circuit features a sensitive LM358-based comparator, IC1A, which keeps the monostable IC2A (a 4538) activated as long as an audio signal is detected at the input. The input signal is taken from the hot side of the loudspeaker or headphones in the audio equipment through coupling capacitor C1. The monostable will time out 2 seconds after being triggered, with the delay determined by resistors R6 and capacitor C3.
The circuit utilizes the LM358 operational amplifier in a comparator configuration. The output of the comparator, IC1A, is connected to the trigger input of the 4538 monostable multivibrator, IC2A. When an audio signal is present, the voltage level at the non-inverting input of the LM358 rises above the reference voltage set at the inverting input, causing the output to switch high. This high output activates the 4538 monostable, which is designed to generate a single pulse of a specific duration—in this case, 2 seconds.
The timing characteristics of the 4538 are determined by the external resistor R6 and capacitor C3. The time period (T) for which the monostable remains in the high state can be calculated using the formula T = 0.7 * R6 * C3. In this configuration, R6 and C3 should be selected to provide the desired timing interval of 2 seconds.
The coupling capacitor C1 serves to block any DC component from the audio signal while allowing the AC audio signal to pass through. This ensures that only the variations in the audio signal are detected by the comparator, preventing false triggering from any DC offset that may be present in the audio source.
Overall, this circuit can be effectively used in applications where it is necessary to detect audio signals and generate a timed output, such as in audio signal processing, sound-activated devices, or other related electronic systems. Proper selection of components and careful layout design will ensure reliable operation and performance in the intended application.The circuit consists of a sensitive LM358 based comparator, IC1A, which keeps monostable IC2A (a 4538) triggered as long as an audio signal is detected at the input. Via coupling capacitor C1 the circuit takes its input signal from the hot` side of the loudspeaker or headphones in your audio gear.
The monostable will time out 2 s after being triggered, the delay being deter-mined by R6 and C3. 🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes the LM358 operational amplifier in a comparator configuration. The output of the comparator, IC1A, is connected to the trigger input of the 4538 monostable multivibrator, IC2A. When an audio signal is present, the voltage level at the non-inverting input of the LM358 rises above the reference voltage set at the inverting input, causing the output to switch high. This high output activates the 4538 monostable, which is designed to generate a single pulse of a specific duration—in this case, 2 seconds.
The timing characteristics of the 4538 are determined by the external resistor R6 and capacitor C3. The time period (T) for which the monostable remains in the high state can be calculated using the formula T = 0.7 * R6 * C3. In this configuration, R6 and C3 should be selected to provide the desired timing interval of 2 seconds.
The coupling capacitor C1 serves to block any DC component from the audio signal while allowing the AC audio signal to pass through. This ensures that only the variations in the audio signal are detected by the comparator, preventing false triggering from any DC offset that may be present in the audio source.
Overall, this circuit can be effectively used in applications where it is necessary to detect audio signals and generate a timed output, such as in audio signal processing, sound-activated devices, or other related electronic systems. Proper selection of components and careful layout design will ensure reliable operation and performance in the intended application.The circuit consists of a sensitive LM358 based comparator, IC1A, which keeps monostable IC2A (a 4538) triggered as long as an audio signal is detected at the input. Via coupling capacitor C1 the circuit takes its input signal from the hot` side of the loudspeaker or headphones in your audio gear.
The monostable will time out 2 s after being triggered, the delay being deter-mined by R6 and C3. 🔗 External reference