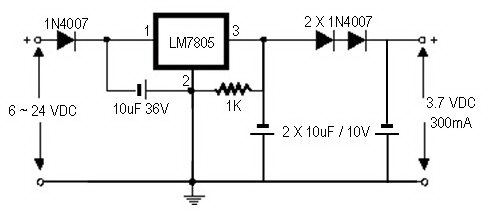
autoconnect disconnect battery charger
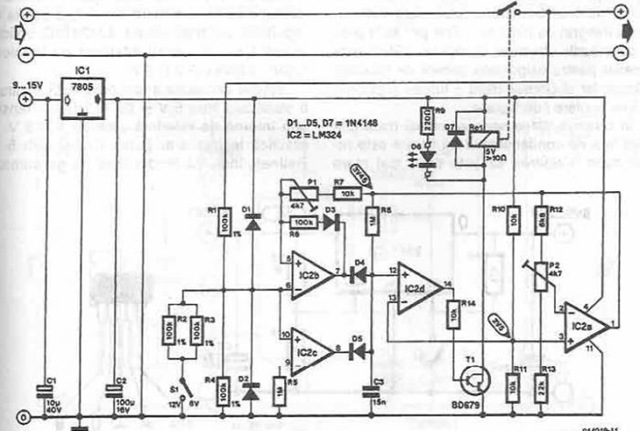
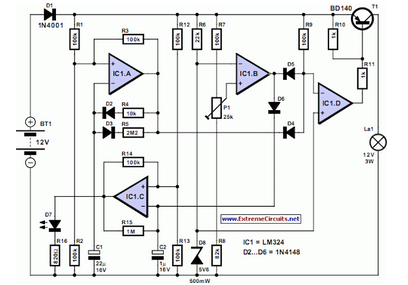
A simple battery charger is designed to disconnect the battery when the charge voltage reaches its nominal level and reconnect when the battery voltage drops below a predefined threshold. This is achieved using a circuit diagram that incorporates a voltage divider consisting of resistors R1, R2, R3, and R4 to sample a fraction of the battery voltage for comparison with a reference voltage using an operational amplifier (AO). Initially, when the battery voltage is 0 V, the input current of AO generates a small voltage drop across resistor R5, resulting in output 0 from IC2c, keeping the relay disengaged. Upon connecting the battery, a low residual voltage triggers IC2c, reverse biasing diodes D4 and D5, and a reference voltage is applied to the non-inverting input of IC2d, activating the relay. During this state, the battery charges until its voltage reaches the nominal level. Calibration is performed using a voltmeter connected to the output of IC2a, adjusting potentiometer P2 to indicate 3.45 V. Subsequently, P1 is adjusted to maximize resistance. To set the output voltage for charging, the battery is replaced with a stabilized power supply and set to either 6V (switch S1 in the 6V position) or 12V (switch S1 in the 12V position), which corresponds to the voltage at which charging is interrupted, and P1 is adjusted until the relay engages.
The described battery charger circuit operates on the principle of voltage monitoring and relay control. The voltage divider formed by resistors R1, R2, R3, and R4 allows for a scaled-down representation of the battery voltage, which is critical for ensuring accurate charging control. The operational amplifier (AO) serves as a comparator, assessing the voltage derived from the divider against a reference voltage. The output from the AO determines the state of the relay, which functions as the switching mechanism to connect or disconnect the battery from the charging circuit.
In the charging phase, when the battery is connected, the low voltage across the battery allows for the activation of the relay through the control circuit involving IC2c and associated diodes. The reverse biasing of diodes D4 and D5 prevents current from flowing in the wrong direction, ensuring that the charging path is correctly established. As the battery charges, the voltage rises, and once it reaches the predefined nominal voltage, the operational amplifier output switches, deactivating the relay and cutting off the charging current to prevent overcharging.
Calibration is a crucial aspect of this circuit, allowing the user to set the correct voltage levels for operation. The use of a voltmeter to measure the output of IC2a ensures that the system can be accurately adjusted to the desired voltage levels. The adjustments via potentiometers P1 and P2 allow for fine-tuning, ensuring that the charging process is both efficient and safe.
Overall, this circuit provides a reliable and straightforward solution for battery charging, incorporating essential features such as automatic disconnection and reconnection based on battery voltage levels, thereby enhancing battery longevity and performance. The design can be further modified to accommodate different battery types by adjusting the reference voltage and calibration settings accordingly.A simple battery charger that disconnects the battery when charge voltage reaches its nominal voltage and reconnects when battery voltage falls below a predefined level, can be designed using this circuit diagram. A fraction of the battery voltage is taken from the voltage divider R1-R2-R3-R4 and compare with a reference voltage with the help of I
C2b. As long as the battery voltage is 0 V. The input current of AO produces a small voltage drop on R5, so IC2c pass in 0 ³. Therefore, the relay remains disengaged. When connecting a battery, low residual voltage provide switch of IC2c, diodes D4 and D5 are reverse biased, a voltage reference applied to the noninverting input of IC2d and relay is activated. In these conditions, the battery charge until its voltage reaches the nominal level. Calibration is performed with a voltmeter connected to the output of IC2a, then P2 is adjusted, to obtain an indication of 3.
45 V. Further, P1 rotates in the direction of maximum resistance. Replace battery with a stabilized power supply and set output voltage at 6V (6V position S1) or 12V (S1 in position 12 V), which is the voltage when charge is interrupted and adjust P1 until the relay works. 🔗 External reference
The described battery charger circuit operates on the principle of voltage monitoring and relay control. The voltage divider formed by resistors R1, R2, R3, and R4 allows for a scaled-down representation of the battery voltage, which is critical for ensuring accurate charging control. The operational amplifier (AO) serves as a comparator, assessing the voltage derived from the divider against a reference voltage. The output from the AO determines the state of the relay, which functions as the switching mechanism to connect or disconnect the battery from the charging circuit.
In the charging phase, when the battery is connected, the low voltage across the battery allows for the activation of the relay through the control circuit involving IC2c and associated diodes. The reverse biasing of diodes D4 and D5 prevents current from flowing in the wrong direction, ensuring that the charging path is correctly established. As the battery charges, the voltage rises, and once it reaches the predefined nominal voltage, the operational amplifier output switches, deactivating the relay and cutting off the charging current to prevent overcharging.
Calibration is a crucial aspect of this circuit, allowing the user to set the correct voltage levels for operation. The use of a voltmeter to measure the output of IC2a ensures that the system can be accurately adjusted to the desired voltage levels. The adjustments via potentiometers P1 and P2 allow for fine-tuning, ensuring that the charging process is both efficient and safe.
Overall, this circuit provides a reliable and straightforward solution for battery charging, incorporating essential features such as automatic disconnection and reconnection based on battery voltage levels, thereby enhancing battery longevity and performance. The design can be further modified to accommodate different battery types by adjusting the reference voltage and calibration settings accordingly.A simple battery charger that disconnects the battery when charge voltage reaches its nominal voltage and reconnects when battery voltage falls below a predefined level, can be designed using this circuit diagram. A fraction of the battery voltage is taken from the voltage divider R1-R2-R3-R4 and compare with a reference voltage with the help of I
C2b. As long as the battery voltage is 0 V. The input current of AO produces a small voltage drop on R5, so IC2c pass in 0 ³. Therefore, the relay remains disengaged. When connecting a battery, low residual voltage provide switch of IC2c, diodes D4 and D5 are reverse biased, a voltage reference applied to the noninverting input of IC2d and relay is activated. In these conditions, the battery charge until its voltage reaches the nominal level. Calibration is performed with a voltmeter connected to the output of IC2a, then P2 is adjusted, to obtain an indication of 3.
45 V. Further, P1 rotates in the direction of maximum resistance. Replace battery with a stabilized power supply and set output voltage at 6V (6V position S1) or 12V (S1 in position 12 V), which is the voltage when charge is interrupted and adjust P1 until the relay works. 🔗 External reference