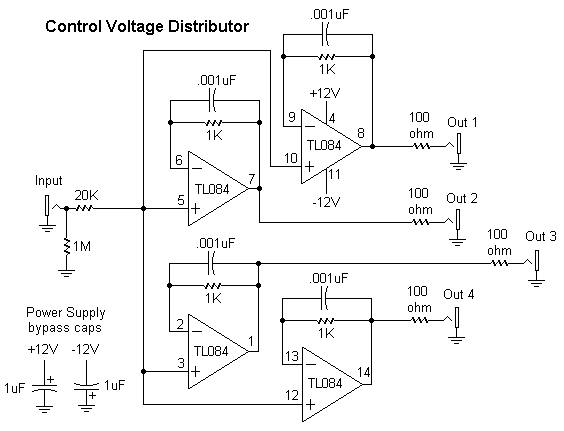
Automatic Gain Control Pre-Amplifier
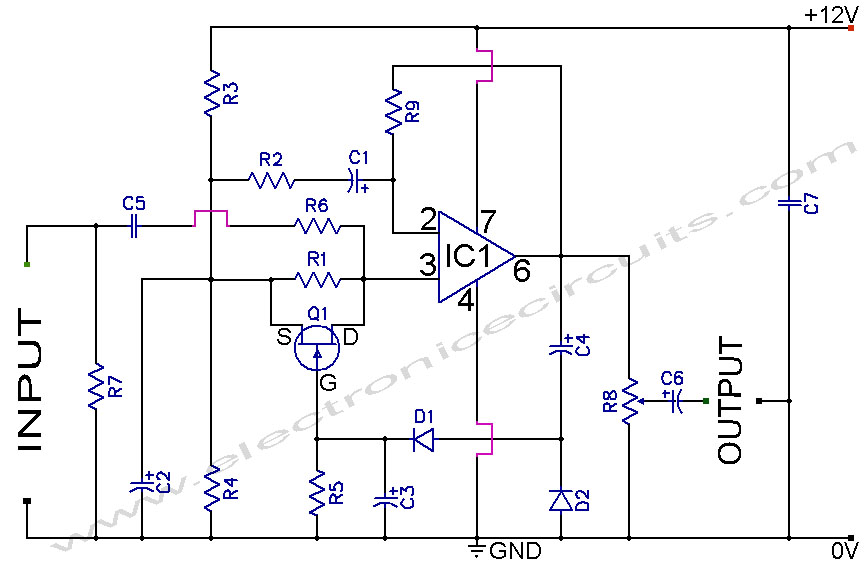
A section of the operational amplifier's output signal is rectified using 1N4148 diodes, followed by filtering, and is then directed to the gate of the FET input shunting circuit. As the output voltage increases, additional input shunting occurs, which means a greater portion of the input signal is bypassed, thereby maintaining a constant output level. The output level can be adjusted from less than unity to nearly the gain of the amplifier, making the circuit suitable for various applications.
The described circuit utilizes operational amplifiers (op-amps) in conjunction with 1N4148 diodes to create a feedback mechanism that stabilizes the output voltage. The rectification process performed by the diodes converts the AC component of the op-amp's output into a DC signal, which is then smoothed by a filtering stage. This filtered signal is crucial as it controls the gate of a Field Effect Transistor (FET), which acts as a variable resistor in the input path.
The FET input shunting circuit is designed to dynamically adjust the amount of input signal that is allowed to pass through to the output. As the output voltage from the op-amp increases, the control voltage at the gate of the FET also increases, leading to a greater shunting effect. This effectively reduces the amplitude of the input signal that reaches the op-amp, thereby regulating the output voltage to a desired level.
The flexibility of the circuit is highlighted by its ability to set the output level across a range from less than unity gain up to almost the full gain of the amplifier. This feature enables the circuit to be applied in various contexts, such as in automatic gain control systems, signal conditioning applications, or other scenarios where maintaining a stable output level is critical. The integration of the op-amp with the FET shunting mechanism provides a robust solution for managing signal levels in electronic systems.A portion of the op amp`s output signal is rectified by the 1N4148 diodes, then filtered and fed to the gate of the FET input shunting circuit. As the output rises, more and more input shunting takes place. That is, more of the input signal is bypassed, effectively keeping the output level constant. The output output level itself can be set from l ess than unity all the way up to nearly the gain of the amplifier, making the circuit usable in other applications as well. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit utilizes operational amplifiers (op-amps) in conjunction with 1N4148 diodes to create a feedback mechanism that stabilizes the output voltage. The rectification process performed by the diodes converts the AC component of the op-amp's output into a DC signal, which is then smoothed by a filtering stage. This filtered signal is crucial as it controls the gate of a Field Effect Transistor (FET), which acts as a variable resistor in the input path.
The FET input shunting circuit is designed to dynamically adjust the amount of input signal that is allowed to pass through to the output. As the output voltage from the op-amp increases, the control voltage at the gate of the FET also increases, leading to a greater shunting effect. This effectively reduces the amplitude of the input signal that reaches the op-amp, thereby regulating the output voltage to a desired level.
The flexibility of the circuit is highlighted by its ability to set the output level across a range from less than unity gain up to almost the full gain of the amplifier. This feature enables the circuit to be applied in various contexts, such as in automatic gain control systems, signal conditioning applications, or other scenarios where maintaining a stable output level is critical. The integration of the op-amp with the FET shunting mechanism provides a robust solution for managing signal levels in electronic systems.A portion of the op amp`s output signal is rectified by the 1N4148 diodes, then filtered and fed to the gate of the FET input shunting circuit. As the output rises, more and more input shunting takes place. That is, more of the input signal is bypassed, effectively keeping the output level constant. The output output level itself can be set from l ess than unity all the way up to nearly the gain of the amplifier, making the circuit usable in other applications as well. 🔗 External reference