Automatic Headlight Brightness Switch Circuit
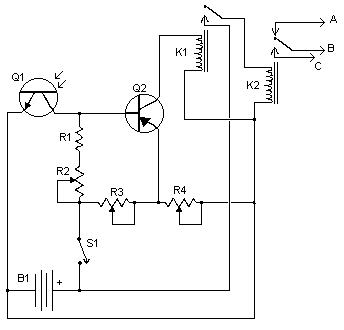
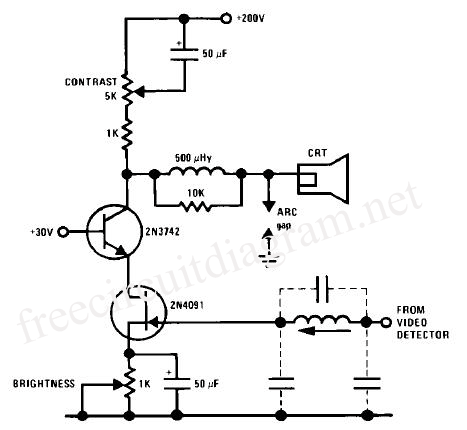
Using high-beam headlights can significantly enhance visibility while driving, but they can also pose a blinding hazard to other drivers. A simple circuit can be integrated into the headlight system to enable automatic switching between high and low beam headlights when oncoming traffic is detected. This is achieved by monitoring the lights of approaching vehicles. Consequently, drivers can safely use high beams without impairing the vision of other road users. The component Q1 should be positioned to face the front of the vehicle with an unobstructed line of sight. Ideal locations include the dashboard or the front grille.
A circuit designed for automatic switching of high-beam headlights typically involves a light sensor, often a phototransistor or photodiode, that detects the intensity of incoming light. When the sensor detects the headlights of an oncoming vehicle, it triggers a transistor switch (Q1) that toggles the headlight circuit from high beam to low beam.
The circuit can be powered by the vehicle's electrical system, typically a 12V battery. The light sensor should be calibrated to ensure it only reacts to the specific wavelengths emitted by vehicle headlights, thus preventing false triggers from other light sources.
In terms of component selection, Q1 should be a robust N-channel MOSFET capable of handling the current required by the high-beam headlights. Additionally, resistors may be included to limit the current flowing through the sensor and to set the threshold for switching. A capacitor can be added to filter out noise from the sensor signal, ensuring stable operation.
The layout of the circuit should prioritize the placement of Q1 to maintain a direct line of sight with oncoming traffic, which can be achieved by mounting it in the dashboard or front grille. Proper installation and orientation of the sensor are crucial for the effective operation of the system, ensuring that it can reliably detect oncoming headlights and switch the beams accordingly.
This automatic headlight switching circuit enhances driving safety by allowing the use of high beams in low-traffic conditions while preventing glare for other drivers.Driving the artery with your high-beam headlights can absolutely access your visibility, but can he a blinding hazard for added drivers. This simple ambit can be active into your headlight about-face to accommodate automated switching amid aerial and low axle headlights back there is advancing traffic.
It does this by analysis the lights of that t raffic. In this way, you can drive cautiously with your high-beams on after blinding added drivers. 1. Q1 should me mounted in such a way so it points toward the front of the car with a clear line of site. Suitable places are on the dashboard, in the front grill, etc. 🔗 External reference
A circuit designed for automatic switching of high-beam headlights typically involves a light sensor, often a phototransistor or photodiode, that detects the intensity of incoming light. When the sensor detects the headlights of an oncoming vehicle, it triggers a transistor switch (Q1) that toggles the headlight circuit from high beam to low beam.
The circuit can be powered by the vehicle's electrical system, typically a 12V battery. The light sensor should be calibrated to ensure it only reacts to the specific wavelengths emitted by vehicle headlights, thus preventing false triggers from other light sources.
In terms of component selection, Q1 should be a robust N-channel MOSFET capable of handling the current required by the high-beam headlights. Additionally, resistors may be included to limit the current flowing through the sensor and to set the threshold for switching. A capacitor can be added to filter out noise from the sensor signal, ensuring stable operation.
The layout of the circuit should prioritize the placement of Q1 to maintain a direct line of sight with oncoming traffic, which can be achieved by mounting it in the dashboard or front grille. Proper installation and orientation of the sensor are crucial for the effective operation of the system, ensuring that it can reliably detect oncoming headlights and switch the beams accordingly.
This automatic headlight switching circuit enhances driving safety by allowing the use of high beams in low-traffic conditions while preventing glare for other drivers.Driving the artery with your high-beam headlights can absolutely access your visibility, but can he a blinding hazard for added drivers. This simple ambit can be active into your headlight about-face to accommodate automated switching amid aerial and low axle headlights back there is advancing traffic.
It does this by analysis the lights of that t raffic. In this way, you can drive cautiously with your high-beams on after blinding added drivers. 1. Q1 should me mounted in such a way so it points toward the front of the car with a clear line of site. Suitable places are on the dashboard, in the front grill, etc. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713