automatic wiper control
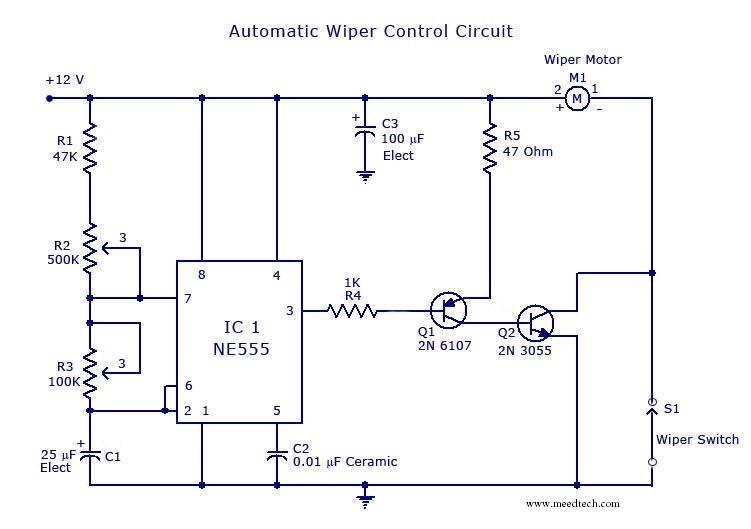
The circuit is built around an astable multivibrator using the NE555 timer. The output at pin 3 remains high for a duration determined by resistor R2 and low for a duration set by resistor R3. The low output pulse activates a transistor pair, which drives the wiper motor to complete one sweeping cycle, after which it waits for the next low pulse to initiate the subsequent sweep. The high pulse at pin 3 determines how many times the wiper should sweep within a specified time frame.
The NE555 timer in astable mode functions as a pulse generator, providing a continuous square wave output. The timing intervals for the high and low states are governed by the resistors R2 and R3, along with a timing capacitor connected to the discharge pin. The frequency of the oscillation can be calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1.44}{(R1 + 2R2) \cdot C} \]
Where:
- \( f \) is the frequency of the output waveform,
- \( R1 \) and \( R2 \) are resistance values in ohms,
- \( C \) is the capacitance in farads.
In this particular circuit, the high output pulse duration (T_high) and low output pulse duration (T_low) can be expressed as:
\[ T_{high} = 0.693 \cdot (R1 + R2) \cdot C \]
\[ T_{low} = 0.693 \cdot R2 \cdot C \]
The output from pin 3 of the NE555 timer is utilized to control a pair of transistors configured as a switch. These transistors are responsible for driving the wiper motor, which is typically a DC motor. The motor's operation is characterized by its ability to reverse direction based on the polarity of the voltage applied, which is controlled by the switching action of the transistors.
When the output at pin 3 transitions to a low state, the transistors are activated, allowing current to flow through the wiper motor, thus completing one full sweep. The circuit is designed to wait for the next low pulse from the NE555 timer to repeat the cycle. The number of sweeps executed by the wiper motor within a given period is directly influenced by the frequency of the output signal from the NE555 timer.
This configuration is commonly used in applications such as windshield wipers in vehicles, where precise timing and control of the motor's operation are essential for effective performance. Adjustments to the resistor and capacitor values allow for customization of the sweeping speed and frequency, enabling the circuit to be tailored to specific operational requirements.The circuit is build around an stable multivibrator using NE 555. Here the output at pin 3 remains high for a time period set by R2, and low for a time period set by R3. The low output pulse drives the transistor pair to drive the wiper motor to make one sweeping cycle and waits for next low pulse to arrive for next sweep.
The high going pulse at pin 3 determines how many time should wiper should sweep in a given period of time. 🔗 External reference
The NE555 timer in astable mode functions as a pulse generator, providing a continuous square wave output. The timing intervals for the high and low states are governed by the resistors R2 and R3, along with a timing capacitor connected to the discharge pin. The frequency of the oscillation can be calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1.44}{(R1 + 2R2) \cdot C} \]
Where:
- \( f \) is the frequency of the output waveform,
- \( R1 \) and \( R2 \) are resistance values in ohms,
- \( C \) is the capacitance in farads.
In this particular circuit, the high output pulse duration (T_high) and low output pulse duration (T_low) can be expressed as:
\[ T_{high} = 0.693 \cdot (R1 + R2) \cdot C \]
\[ T_{low} = 0.693 \cdot R2 \cdot C \]
The output from pin 3 of the NE555 timer is utilized to control a pair of transistors configured as a switch. These transistors are responsible for driving the wiper motor, which is typically a DC motor. The motor's operation is characterized by its ability to reverse direction based on the polarity of the voltage applied, which is controlled by the switching action of the transistors.
When the output at pin 3 transitions to a low state, the transistors are activated, allowing current to flow through the wiper motor, thus completing one full sweep. The circuit is designed to wait for the next low pulse from the NE555 timer to repeat the cycle. The number of sweeps executed by the wiper motor within a given period is directly influenced by the frequency of the output signal from the NE555 timer.
This configuration is commonly used in applications such as windshield wipers in vehicles, where precise timing and control of the motor's operation are essential for effective performance. Adjustments to the resistor and capacitor values allow for customization of the sweeping speed and frequency, enabling the circuit to be tailored to specific operational requirements.The circuit is build around an stable multivibrator using NE 555. Here the output at pin 3 remains high for a time period set by R2, and low for a time period set by R3. The low output pulse drives the transistor pair to drive the wiper motor to make one sweeping cycle and waits for next low pulse to arrive for next sweep.
The high going pulse at pin 3 determines how many time should wiper should sweep in a given period of time. 🔗 External reference