Basic mosfet switch question
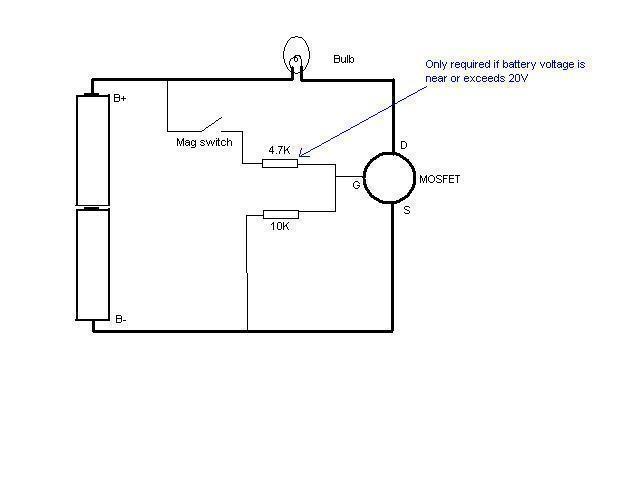
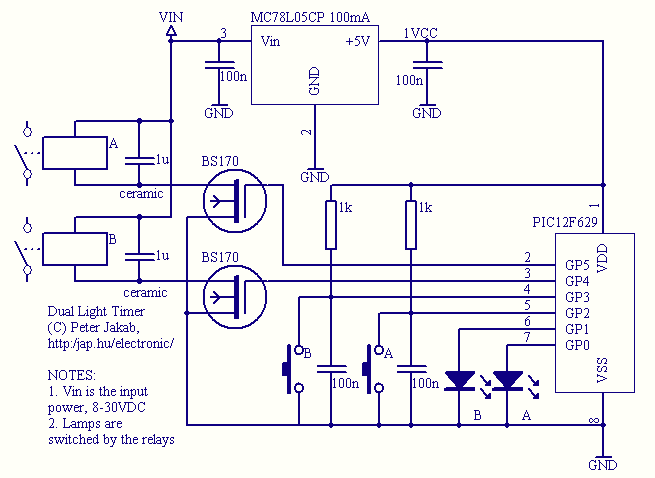
In this schematic provided by Jimmy M, will this circuit drain the batteries when the light is not in use? There is consideration for building a MOSFET circuit to be used in a compact application, where the original bulky switch is replaced with a microswitch to operate the MOSFET.
The schematic in question involves a MOSFET switch designed to control the power supply to a light source, with the aim of minimizing battery drain when the light is not active. The MOSFET is utilized for its high efficiency and low on-resistance, which allows for effective switching with minimal power loss.
In the proposed circuit, the microswitch serves as the control mechanism for the MOSFET gate. When the microswitch is activated, it applies a voltage to the gate of the MOSFET, allowing current to flow from the source to the drain, thereby powering the light. When the microswitch is released, the gate voltage drops, turning off the MOSFET and effectively cutting off power to the light. This configuration ensures that the light is only powered when needed, significantly reducing the risk of battery drainage during periods of inactivity.
It is essential to consider the MOSFET's specifications, including its threshold voltage and maximum current rating, to ensure compatibility with the light source and the power supply. Additionally, incorporating a pull-down resistor at the gate can help ensure that the MOSFET remains off when the microswitch is not engaged, preventing any unintended power leakage.
Overall, this circuit design enhances the efficiency of the light system while maintaining a compact form factor, making it suitable for applications where space is limited and battery life is critical.In this schematic, provided by Jimmy M, would this circuit drain the batteries when the light is not in use? I`m considering building a mosfet circuit like this to use in a compact M@g where I discard the original bulky switch and use a microswitch to operate the mosfet..
🔗 External reference
The schematic in question involves a MOSFET switch designed to control the power supply to a light source, with the aim of minimizing battery drain when the light is not active. The MOSFET is utilized for its high efficiency and low on-resistance, which allows for effective switching with minimal power loss.
In the proposed circuit, the microswitch serves as the control mechanism for the MOSFET gate. When the microswitch is activated, it applies a voltage to the gate of the MOSFET, allowing current to flow from the source to the drain, thereby powering the light. When the microswitch is released, the gate voltage drops, turning off the MOSFET and effectively cutting off power to the light. This configuration ensures that the light is only powered when needed, significantly reducing the risk of battery drainage during periods of inactivity.
It is essential to consider the MOSFET's specifications, including its threshold voltage and maximum current rating, to ensure compatibility with the light source and the power supply. Additionally, incorporating a pull-down resistor at the gate can help ensure that the MOSFET remains off when the microswitch is not engaged, preventing any unintended power leakage.
Overall, this circuit design enhances the efficiency of the light system while maintaining a compact form factor, making it suitable for applications where space is limited and battery life is critical.In this schematic, provided by Jimmy M, would this circuit drain the batteries when the light is not in use? I`m considering building a mosfet circuit like this to use in a compact M@g where I discard the original bulky switch and use a microswitch to operate the mosfet..
🔗 External reference