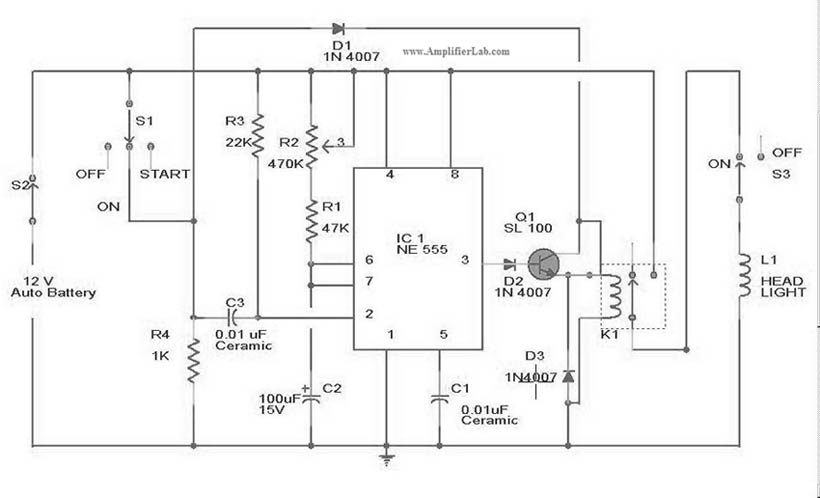
18 W MOSFET Amplifier Circuit With BC550C Transistor
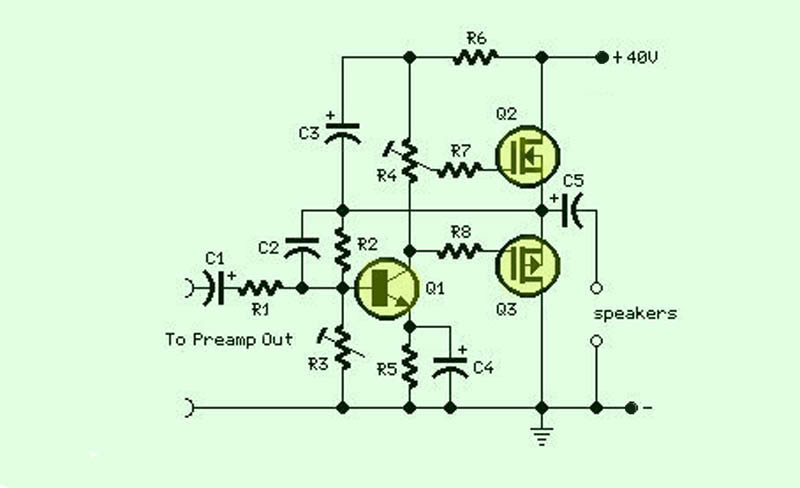
The function of this circuit is an audio amplifier capable of delivering a decent output power with a minimal number of components, with considerable efficiency.
This audio amplifier circuit is designed to enhance audio signals, providing sufficient output power while maintaining a simple and efficient design. The circuit typically consists of a few essential components, including transistors, resistors, capacitors, and a power supply, which work together to amplify the input audio signal.
The core of the amplifier is usually a class AB transistor configuration, which combines the advantages of both class A and class B amplifiers. This configuration allows the circuit to produce high-quality audio output with reduced distortion levels. The transistors are responsible for increasing the input signal's amplitude, while the accompanying resistors and capacitors help to stabilize the circuit and filter out unwanted noise.
The power supply for the amplifier is critical, as it must provide adequate voltage and current to ensure optimal performance. Typically, a dual power supply is employed, allowing the amplifier to function effectively in both positive and negative voltage swings, which is essential for audio signals.
In addition to the basic amplification function, various feedback mechanisms may be incorporated into the circuit to improve linearity and reduce distortion further. This feedback can be achieved through the use of additional resistors and capacitors strategically placed in the circuit design.
Overall, this audio amplifier circuit is an efficient and straightforward solution for amplifying audio signals, making it suitable for various applications, including personal audio systems, small public address systems, and other audio-related projects.The function for this circuit is an audio amplifier capable of delivering a decent output power with a minimum no: of parts , with considerable .. 🔗 External reference
This audio amplifier circuit is designed to enhance audio signals, providing sufficient output power while maintaining a simple and efficient design. The circuit typically consists of a few essential components, including transistors, resistors, capacitors, and a power supply, which work together to amplify the input audio signal.
The core of the amplifier is usually a class AB transistor configuration, which combines the advantages of both class A and class B amplifiers. This configuration allows the circuit to produce high-quality audio output with reduced distortion levels. The transistors are responsible for increasing the input signal's amplitude, while the accompanying resistors and capacitors help to stabilize the circuit and filter out unwanted noise.
The power supply for the amplifier is critical, as it must provide adequate voltage and current to ensure optimal performance. Typically, a dual power supply is employed, allowing the amplifier to function effectively in both positive and negative voltage swings, which is essential for audio signals.
In addition to the basic amplification function, various feedback mechanisms may be incorporated into the circuit to improve linearity and reduce distortion further. This feedback can be achieved through the use of additional resistors and capacitors strategically placed in the circuit design.
Overall, this audio amplifier circuit is an efficient and straightforward solution for amplifying audio signals, making it suitable for various applications, including personal audio systems, small public address systems, and other audio-related projects.The function for this circuit is an audio amplifier capable of delivering a decent output power with a minimum no: of parts , with considerable .. 🔗 External reference