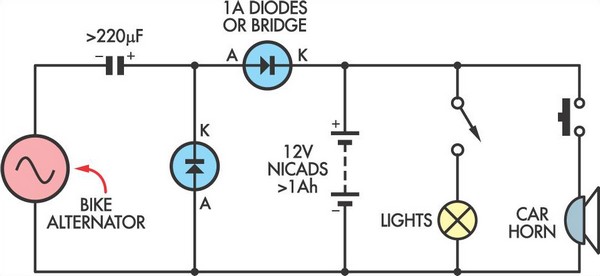
Battery charger circuit Schematic Diagram
This charger is based on a charging voltage of 2.4 volts per cell, in accordance with most manufacturers' recommendations. This circuit pulses the battery with 14.4 volts (6 cells x 2.4 volts per cell) at a rate of 120 Hz.
The charger circuit is designed to efficiently charge a battery pack consisting of six cells, each rated at 2.4 volts. The total charging voltage of 14.4 volts is derived from the multiplication of the individual cell voltage by the number of cells in series. The pulsing mechanism operates at a frequency of 120 Hz, which facilitates effective energy transfer to the battery, ensuring optimal charging performance while minimizing heat generation.
The circuit typically includes a power supply unit that converts the AC mains voltage to a suitable DC voltage, which is then regulated to provide a stable output of 14.4 volts. This regulation is crucial to prevent overcharging, which can lead to battery damage or reduced lifespan.
A control circuit, often utilizing a microcontroller or dedicated charging IC, manages the pulse width modulation (PWM) signals sent to the battery. This modulation allows for precise control over the charging current and voltage, adapting to the battery's state of charge. Additionally, safety features such as overcurrent protection, thermal shutdown, and reverse polarity protection may be integrated to enhance reliability and safety during operation.
The output stage of the charger may consist of a switching regulator or a linear regulator, depending on the design requirements, efficiency considerations, and cost constraints. Capacitors and inductors are typically employed in the output stage to filter the voltage and current, smoothing out any ripples that may arise from the pulsing action.
Overall, this battery charger circuit represents a well-engineered solution for charging multi-cell battery packs, adhering to manufacturer specifications while incorporating modern electronic design principles to ensure safety, efficiency, and performance.This cahrger based on chargeing voltage 2, 4 Volts per cell, in accordance with most manufacterers recomendation. This circuit pulses the battery under with 14. 4 Volts ( 6 cells x 2, 4 volts per cell) at a rate 120 Hz. You are reading the Circuits of Battery charger circuit And this circuit permalink url it is 🔗 External reference
The charger circuit is designed to efficiently charge a battery pack consisting of six cells, each rated at 2.4 volts. The total charging voltage of 14.4 volts is derived from the multiplication of the individual cell voltage by the number of cells in series. The pulsing mechanism operates at a frequency of 120 Hz, which facilitates effective energy transfer to the battery, ensuring optimal charging performance while minimizing heat generation.
The circuit typically includes a power supply unit that converts the AC mains voltage to a suitable DC voltage, which is then regulated to provide a stable output of 14.4 volts. This regulation is crucial to prevent overcharging, which can lead to battery damage or reduced lifespan.
A control circuit, often utilizing a microcontroller or dedicated charging IC, manages the pulse width modulation (PWM) signals sent to the battery. This modulation allows for precise control over the charging current and voltage, adapting to the battery's state of charge. Additionally, safety features such as overcurrent protection, thermal shutdown, and reverse polarity protection may be integrated to enhance reliability and safety during operation.
The output stage of the charger may consist of a switching regulator or a linear regulator, depending on the design requirements, efficiency considerations, and cost constraints. Capacitors and inductors are typically employed in the output stage to filter the voltage and current, smoothing out any ripples that may arise from the pulsing action.
Overall, this battery charger circuit represents a well-engineered solution for charging multi-cell battery packs, adhering to manufacturer specifications while incorporating modern electronic design principles to ensure safety, efficiency, and performance.This cahrger based on chargeing voltage 2, 4 Volts per cell, in accordance with most manufacterers recomendation. This circuit pulses the battery under with 14. 4 Volts ( 6 cells x 2, 4 volts per cell) at a rate 120 Hz. You are reading the Circuits of Battery charger circuit And this circuit permalink url it is 🔗 External reference