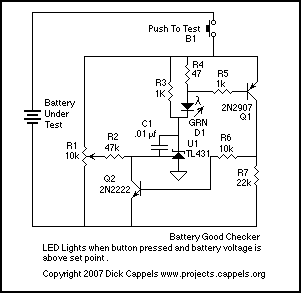
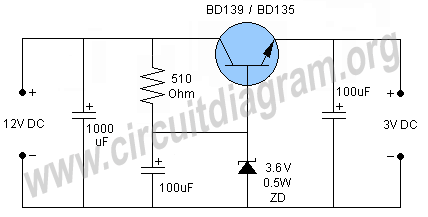
battery charger for 12v

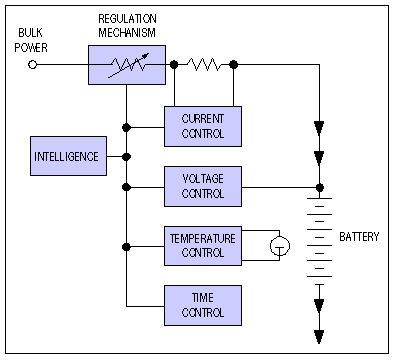
This design presents a circuit diagram for a straightforward battery charger capable of charging various types of 12V rechargeable batteries, including car batteries. The ammeter reading will indicate zero when the battery is fully charged. It is essential to connect the charger to the battery with the correct polarity to avoid any issues.
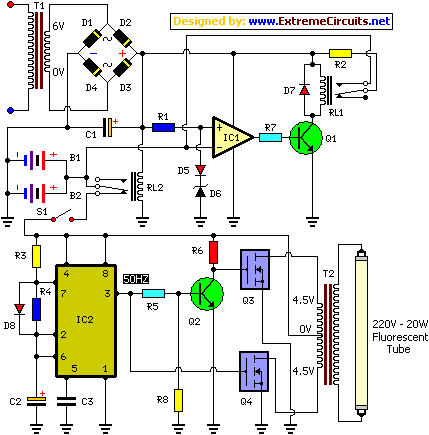
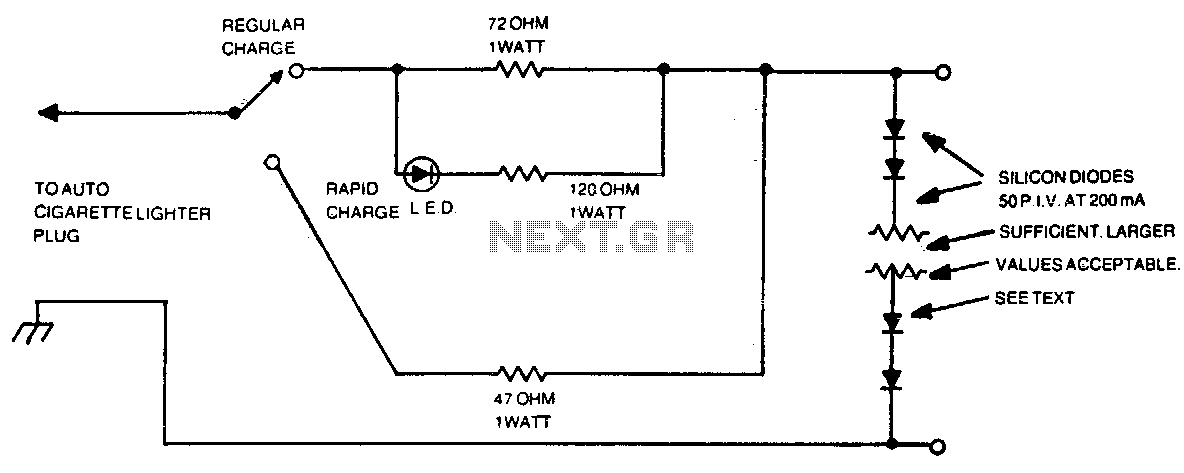
The circuit diagram for the battery charger typically includes several key components: a transformer, a rectifier, a filter capacitor, an ammeter, and a voltage regulator. The transformer steps down the AC voltage from the mains supply to a lower AC voltage suitable for charging the battery. The rectifier, often a bridge rectifier configuration, converts the AC voltage to pulsating DC voltage.
Following the rectification process, a smoothing filter capacitor is employed to reduce the ripple in the output voltage, providing a more stable DC voltage to the battery. The ammeter is connected in series with the battery to monitor the charging current. When the battery approaches full charge, the current will decrease, eventually reaching zero, indicating that the charging process is complete.
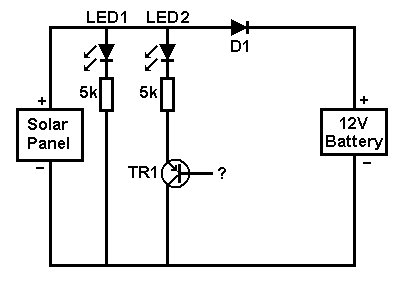
A voltage regulator may also be included in the circuit to ensure that the output voltage does not exceed the battery's rated voltage, preventing overcharging, which can damage the battery. Additionally, it is crucial to implement reverse polarity protection using a diode to safeguard against incorrect connections, which can lead to circuit failure or battery damage.
In summary, this battery charger circuit is designed with essential components to ensure efficient charging of 12V batteries while incorporating safety features to protect both the charger and the battery from potential damage due to incorrect usage. Proper attention to component selection and circuit layout is vital to achieving optimal performance and reliability.This is a design of the circuit diagram of a simple and straight forward battery charger that can be used to charge all type of 12V rechargeable batteries including car batteries. For indicate when the battery is fully charged, the ammeter reading will be zero. For attention, it is always be careful to connect the charger to the battery in correct polarity. 🔗 External reference
The circuit diagram for the battery charger typically includes several key components: a transformer, a rectifier, a filter capacitor, an ammeter, and a voltage regulator. The transformer steps down the AC voltage from the mains supply to a lower AC voltage suitable for charging the battery. The rectifier, often a bridge rectifier configuration, converts the AC voltage to pulsating DC voltage.
Following the rectification process, a smoothing filter capacitor is employed to reduce the ripple in the output voltage, providing a more stable DC voltage to the battery. The ammeter is connected in series with the battery to monitor the charging current. When the battery approaches full charge, the current will decrease, eventually reaching zero, indicating that the charging process is complete.
A voltage regulator may also be included in the circuit to ensure that the output voltage does not exceed the battery's rated voltage, preventing overcharging, which can damage the battery. Additionally, it is crucial to implement reverse polarity protection using a diode to safeguard against incorrect connections, which can lead to circuit failure or battery damage.
In summary, this battery charger circuit is designed with essential components to ensure efficient charging of 12V batteries while incorporating safety features to protect both the charger and the battery from potential damage due to incorrect usage. Proper attention to component selection and circuit layout is vital to achieving optimal performance and reliability.This is a design of the circuit diagram of a simple and straight forward battery charger that can be used to charge all type of 12V rechargeable batteries including car batteries. For indicate when the battery is fully charged, the ammeter reading will be zero. For attention, it is always be careful to connect the charger to the battery in correct polarity. 🔗 External reference