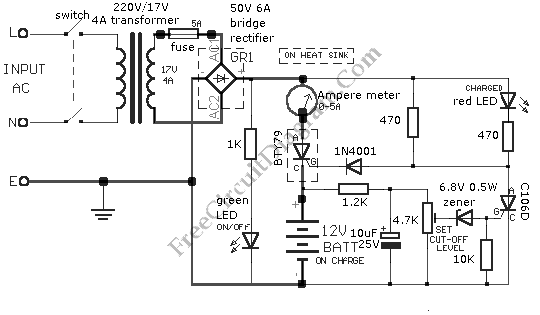
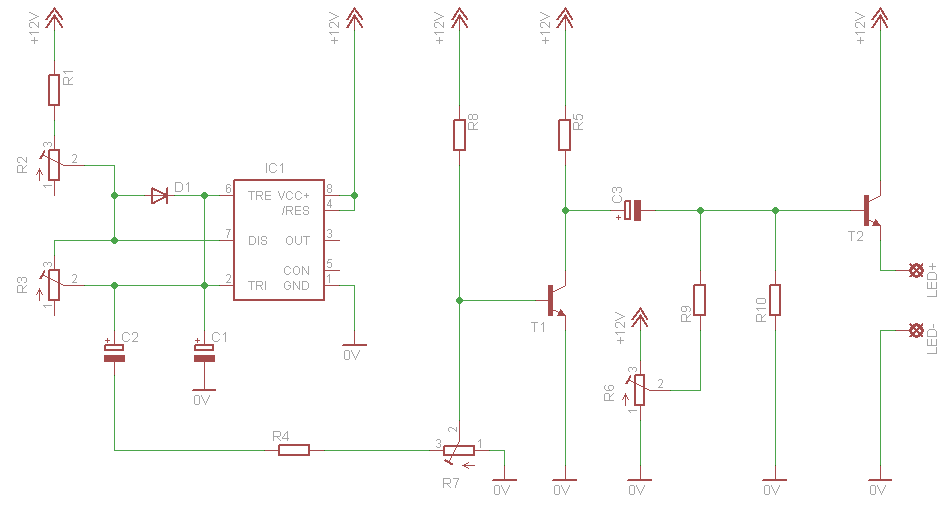
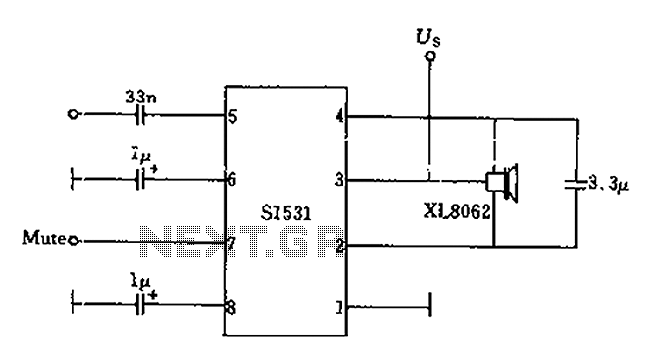
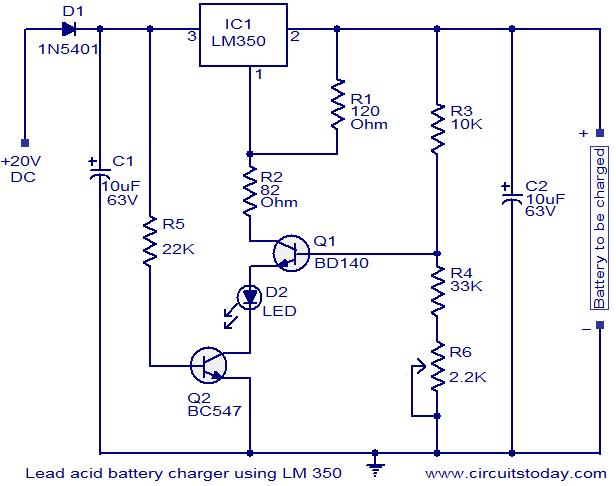
Battery Operated LED Lantern
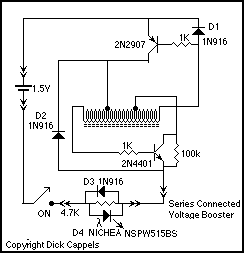
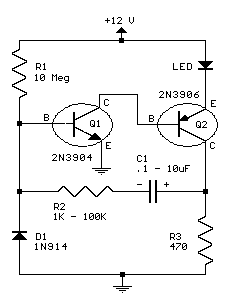
Photo. This is the test circuit -the basic driver is only two transistors, two resistors, the circuit was evaluated using a white LED, but when it was time to button it up and archive it, I replaced the expensive white LED with a cheap green one. More: When Dave and I were kicking around ideas for the best arrangement of components for white led flashlight, Dave suggested putting the voltage converter in place of the second cell in a two cell flashlight, and substitute an LED assembly for the incandescent.
The described test circuit functions as a basic LED driver utilizing two transistors to control the current flow to the LED. The primary components include two NPN transistors, which are configured in a common emitter arrangement to amplify the input signal. The transistors are connected to a pair of resistors that set the biasing conditions and limit the base current to prevent damage to the transistors.
In this circuit, the white LED was initially used for evaluation purposes, providing a high brightness output suitable for flashlight applications. However, for practical implementation, a lower-cost green LED was substituted. The green LED operates at a different forward voltage, which may require adjustments to the resistor values to ensure optimal performance without exceeding the LED's current rating.
An additional consideration in the design is the incorporation of a voltage converter, which allows for the use of a single cell in a two-cell flashlight configuration. This converter steps up the voltage to the necessary level for the LED, enhancing efficiency and extending battery life. The LED assembly replaces traditional incandescent bulbs, offering advantages such as lower power consumption, longer lifespan, and improved durability.
The circuit layout should be carefully designed to minimize parasitic capacitance and inductance, ensuring stable operation. Proper heat dissipation measures must also be considered, especially if the circuit is to be used in high-power applications. Overall, this basic driver circuit is a practical solution for LED-based lighting applications, demonstrating the versatility and efficiency of modern electronic components.Photo. This is the test circuit -the basic driver is only two transistors, two resistors, the circuit was evaluated using a white LED, but when it was time to button it up and archive it, I replaced the expensive white LED with a cheap green one. When Dave and I were kicking around ideas for the best arrangement of components for white led flashlight, Dave suggested putting the voltage converter in place of the second cell in a two cell flashlight, and substitute an LED assembly for the incandesce 🔗 External reference
The described test circuit functions as a basic LED driver utilizing two transistors to control the current flow to the LED. The primary components include two NPN transistors, which are configured in a common emitter arrangement to amplify the input signal. The transistors are connected to a pair of resistors that set the biasing conditions and limit the base current to prevent damage to the transistors.
In this circuit, the white LED was initially used for evaluation purposes, providing a high brightness output suitable for flashlight applications. However, for practical implementation, a lower-cost green LED was substituted. The green LED operates at a different forward voltage, which may require adjustments to the resistor values to ensure optimal performance without exceeding the LED's current rating.
An additional consideration in the design is the incorporation of a voltage converter, which allows for the use of a single cell in a two-cell flashlight configuration. This converter steps up the voltage to the necessary level for the LED, enhancing efficiency and extending battery life. The LED assembly replaces traditional incandescent bulbs, offering advantages such as lower power consumption, longer lifespan, and improved durability.
The circuit layout should be carefully designed to minimize parasitic capacitance and inductance, ensuring stable operation. Proper heat dissipation measures must also be considered, especially if the circuit is to be used in high-power applications. Overall, this basic driver circuit is a practical solution for LED-based lighting applications, demonstrating the versatility and efficiency of modern electronic components.Photo. This is the test circuit -the basic driver is only two transistors, two resistors, the circuit was evaluated using a white LED, but when it was time to button it up and archive it, I replaced the expensive white LED with a cheap green one. When Dave and I were kicking around ideas for the best arrangement of components for white led flashlight, Dave suggested putting the voltage converter in place of the second cell in a two cell flashlight, and substitute an LED assembly for the incandesce 🔗 External reference