bi directional motor control
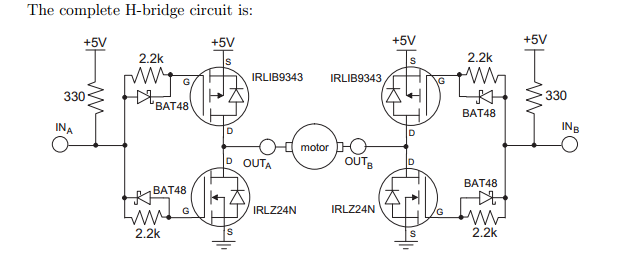
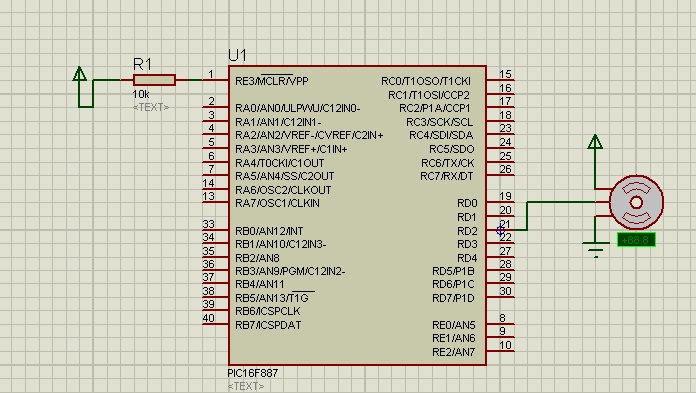
In project 2.S994, a custom "H-bridge" motor controller was developed using MOSFETs to manage motor operation. Subsequently, a commercial bi-directional motor controller was tested with the same motor. Images of the setup are available. Additional schematics and details regarding the motor controller will be provided later, believed to be a product from Pololu.
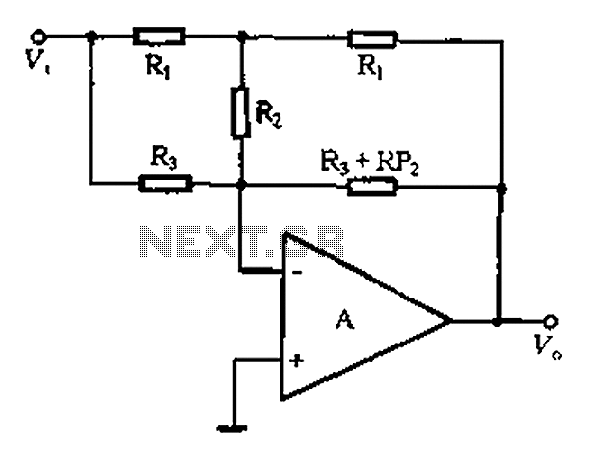
The H-bridge motor controller designed in project 2.S994 utilizes MOSFETs to enable bi-directional control of a DC motor. The configuration allows for the motor to be driven in both forward and reverse directions by switching the polarity of the voltage applied to the motor terminals. Typically, an H-bridge consists of four switches arranged in a bridge configuration, where each switch is represented by a MOSFET.
In this design, two pairs of MOSFETs are used: one pair for the forward direction and the other for reverse. When the control signals are applied, one MOSFET from each pair is turned on, allowing current to flow through the motor in the desired direction. To prevent short circuits, it is essential to ensure that only one MOSFET from each pair is activated at a time. This can be managed by using a microcontroller or a dedicated driver IC that generates the appropriate control signals based on the desired motor direction and speed.
The commercial bi-directional motor controller tested later is likely to feature similar operational principles but may include additional features such as built-in current sensing, thermal protection, and more sophisticated control algorithms for enhanced performance. The Pololu product mentioned is known for its reliability and ease of integration, making it a suitable choice for various robotic applications.
Future updates will include detailed schematics of both the custom H-bridge and the commercial controller, providing insights into the design choices, component specifications, and operational characteristics of each configuration.In 2.S994 we made our own ""h-bridge"" motor controller using MOSFETs to control a motor. We then tried out a commercial bi-directional motor controller on the same motor. Here are pictures of the setup. I will update with schematics / details on the motor controller later. I believe it was a Pololu product. Update:.. 🔗 External reference
The H-bridge motor controller designed in project 2.S994 utilizes MOSFETs to enable bi-directional control of a DC motor. The configuration allows for the motor to be driven in both forward and reverse directions by switching the polarity of the voltage applied to the motor terminals. Typically, an H-bridge consists of four switches arranged in a bridge configuration, where each switch is represented by a MOSFET.
In this design, two pairs of MOSFETs are used: one pair for the forward direction and the other for reverse. When the control signals are applied, one MOSFET from each pair is turned on, allowing current to flow through the motor in the desired direction. To prevent short circuits, it is essential to ensure that only one MOSFET from each pair is activated at a time. This can be managed by using a microcontroller or a dedicated driver IC that generates the appropriate control signals based on the desired motor direction and speed.
The commercial bi-directional motor controller tested later is likely to feature similar operational principles but may include additional features such as built-in current sensing, thermal protection, and more sophisticated control algorithms for enhanced performance. The Pololu product mentioned is known for its reliability and ease of integration, making it a suitable choice for various robotic applications.
Future updates will include detailed schematics of both the custom H-bridge and the commercial controller, providing insights into the design choices, component specifications, and operational characteristics of each configuration.In 2.S994 we made our own ""h-bridge"" motor controller using MOSFETs to control a motor. We then tried out a commercial bi-directional motor controller on the same motor. Here are pictures of the setup. I will update with schematics / details on the motor controller later. I believe it was a Pololu product. Update:.. 🔗 External reference