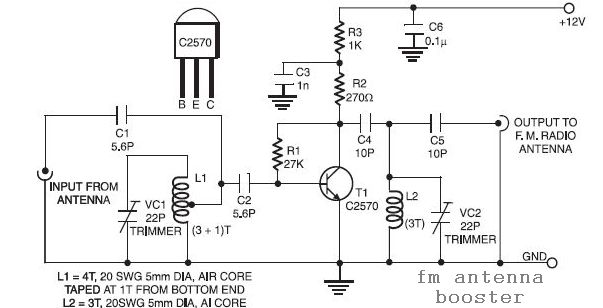
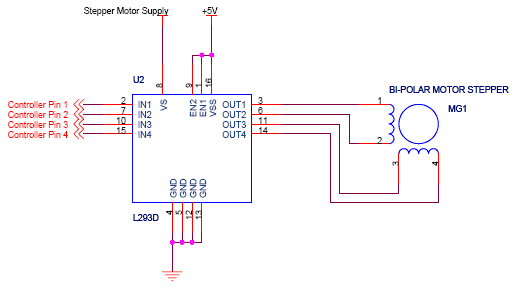
Bridge motor drive circuit

A bridge motor drive circuit is illustrated, featuring a driving stage composed of four transistors. The control circuit includes four terminals labeled A, B, C, and D, which facilitate the control of forward or reverse motor rotation. The control mode can be operated either manually or automatically.
The bridge motor drive circuit is designed to control the direction and speed of a DC motor using a H-bridge configuration. The circuit consists of four transistors arranged in a bridge formation, allowing for efficient control of the motor's operation. The transistors are typically N-channel MOSFETs or bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) capable of handling the required current and voltage levels for the motor.
The four terminals A, B, C, and D serve as inputs to the control circuit. When specific combinations of these inputs are activated, they switch the transistors on and off in a manner that determines the motor's direction. For example, activating terminals A and B may cause the motor to rotate in one direction, while activating terminals C and D would reverse the rotation. This configuration enables bidirectional control of the motor, making it suitable for applications requiring precise movement.
The control mode can be set to manual, allowing an operator to directly control the motor's direction using switches or buttons connected to the terminals. Alternatively, an automatic control mode can be implemented, where a microcontroller or other automation system manages the inputs based on pre-defined parameters or sensor feedback. This flexibility in control methods enhances the circuit's versatility for various applications, from robotics to conveyor systems.
Additionally, protective components such as diodes may be included to prevent back EMF generated by the motor from damaging the transistors. Heat sinks may also be necessary to dissipate heat generated during operation, ensuring reliable performance and longevity of the circuit. Overall, the bridge motor drive circuit provides an effective solution for controlling motor functions in a wide range of electronic and electromechanical systems. Bridge motor drive circuit Bridge motor drive circuit is shown, the driving stage of the circuit is 4 transistors. The control circuit is provided with four ends, through to A, B, C, D can control the forward or reverse rotation control. Control mode can be used manually or automatically.
The bridge motor drive circuit is designed to control the direction and speed of a DC motor using a H-bridge configuration. The circuit consists of four transistors arranged in a bridge formation, allowing for efficient control of the motor's operation. The transistors are typically N-channel MOSFETs or bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) capable of handling the required current and voltage levels for the motor.
The four terminals A, B, C, and D serve as inputs to the control circuit. When specific combinations of these inputs are activated, they switch the transistors on and off in a manner that determines the motor's direction. For example, activating terminals A and B may cause the motor to rotate in one direction, while activating terminals C and D would reverse the rotation. This configuration enables bidirectional control of the motor, making it suitable for applications requiring precise movement.
The control mode can be set to manual, allowing an operator to directly control the motor's direction using switches or buttons connected to the terminals. Alternatively, an automatic control mode can be implemented, where a microcontroller or other automation system manages the inputs based on pre-defined parameters or sensor feedback. This flexibility in control methods enhances the circuit's versatility for various applications, from robotics to conveyor systems.
Additionally, protective components such as diodes may be included to prevent back EMF generated by the motor from damaging the transistors. Heat sinks may also be necessary to dissipate heat generated during operation, ensuring reliable performance and longevity of the circuit. Overall, the bridge motor drive circuit provides an effective solution for controlling motor functions in a wide range of electronic and electromechanical systems. Bridge motor drive circuit Bridge motor drive circuit is shown, the driving stage of the circuit is 4 transistors. The control circuit is provided with four ends, through to A, B, C, D can control the forward or reverse rotation control. Control mode can be used manually or automatically.