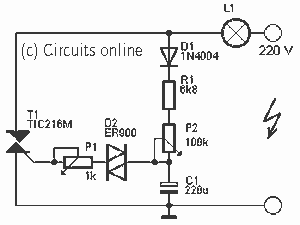
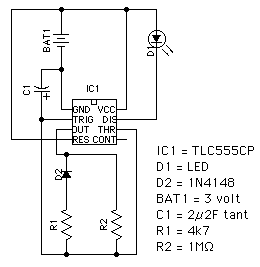
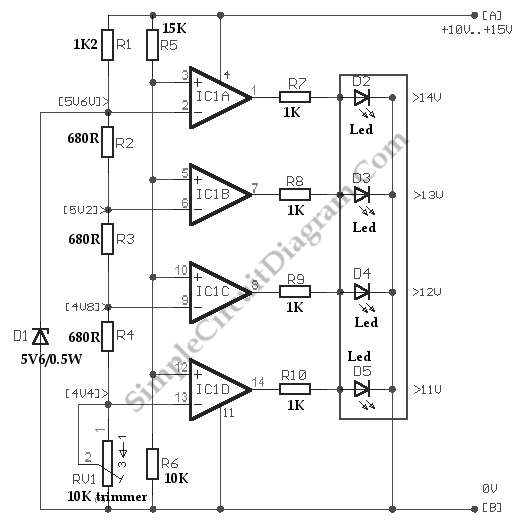
bright flash from flat battery diagram
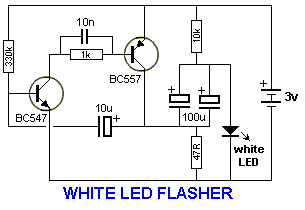
This circuit is designed to flash a white LED using a supply voltage ranging from 2V to 6V, resulting in a very bright flash. The circuit operates at approximately 2mA, allowing the use of old batteries. When powered at 6V, the two 100μF electrolytic capacitors connected in parallel enhance the flash intensity.
The circuit functions by utilizing a basic LED driver configuration that incorporates a timing mechanism to create a flashing effect. The primary components of the circuit include a white LED, a resistor to limit current, and two electrolytic capacitors that store energy to be released in a burst, resulting in the bright flash.
When the supply voltage is applied, the capacitors charge up to the supply voltage, and once they reach a certain threshold, they discharge quickly through the LED. This rapid discharge creates a high-intensity flash of light. The selected resistor value is crucial as it determines the current flowing through the LED, ensuring it operates within its safe limits.
The use of two 100μF capacitors in parallel at 6V significantly improves the flash effect due to the increased charge storage capacity, allowing for a more substantial energy release. This design not only maximizes the brightness of the LED flash but also extends the operational lifespan of the circuit by allowing the use of lower-quality or older batteries, which may not provide optimal performance under continuous load conditions.
The circuit can be further enhanced by incorporating a timer IC or a microcontroller to control the flashing frequency, providing versatility for various applications such as emergency signaling, decorative lighting, or visual alerts. Proper heat dissipation measures should also be considered to ensure reliable operation over extended periods.This circuit will flash a white LED, on a supply from 2v to 6v and produce a very bright flash. The circuit takes about 2mA and old cells can be used. The two 100u electros in parallel produce a better flash when the supply is 6v. 🔗 External reference
The circuit functions by utilizing a basic LED driver configuration that incorporates a timing mechanism to create a flashing effect. The primary components of the circuit include a white LED, a resistor to limit current, and two electrolytic capacitors that store energy to be released in a burst, resulting in the bright flash.
When the supply voltage is applied, the capacitors charge up to the supply voltage, and once they reach a certain threshold, they discharge quickly through the LED. This rapid discharge creates a high-intensity flash of light. The selected resistor value is crucial as it determines the current flowing through the LED, ensuring it operates within its safe limits.
The use of two 100μF capacitors in parallel at 6V significantly improves the flash effect due to the increased charge storage capacity, allowing for a more substantial energy release. This design not only maximizes the brightness of the LED flash but also extends the operational lifespan of the circuit by allowing the use of lower-quality or older batteries, which may not provide optimal performance under continuous load conditions.
The circuit can be further enhanced by incorporating a timer IC or a microcontroller to control the flashing frequency, providing versatility for various applications such as emergency signaling, decorative lighting, or visual alerts. Proper heat dissipation measures should also be considered to ensure reliable operation over extended periods.This circuit will flash a white LED, on a supply from 2v to 6v and produce a very bright flash. The circuit takes about 2mA and old cells can be used. The two 100u electros in parallel produce a better flash when the supply is 6v. 🔗 External reference