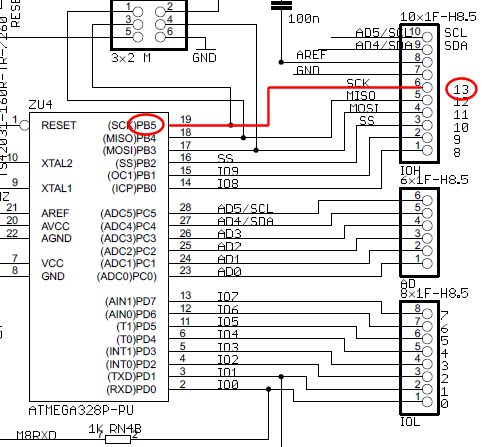
Broadband high frequency amplifying circuit
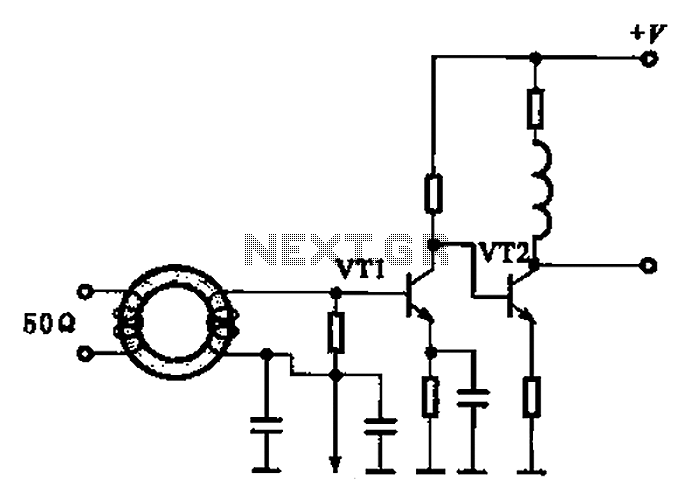
A broadband high-frequency amplifying circuit is primarily composed of a high-frequency matching transformer and an amplifying transistor. This circuit is designed to handle large high-frequency signals. The input of the amplifier circuit utilizes a matching transformer to ensure that the signal is appropriately matched to the transistor amplifier, which features high input impedance. Additionally, the circuit exhibits wide frequency band characteristics. The emitter capacitor and inductor connected to the transistor VT1 serve to compensate for high-frequency signals and optimize performance.
The broadband high-frequency amplifying circuit is engineered to amplify signals within a wide frequency range effectively. The inclusion of a high-frequency matching transformer is critical, as it provides impedance matching between the input signal and the transistor amplifier. This matching is essential for maximizing power transfer and minimizing signal reflection, which is particularly important in high-frequency applications.
The circuit typically employs a transistor, such as a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) or a field-effect transistor (FET), for amplification. The transistor's high input impedance allows it to receive signals without significantly loading the preceding stage, which is beneficial when interfacing with other circuit elements or sources.
The emitter capacitor connected to the transistor VT1 plays a dual role; it not only stabilizes the operating point of the transistor but also allows high-frequency signals to pass while blocking low-frequency signals, thus enhancing the circuit's frequency response. The inductor in conjunction with the capacitor forms a resonant circuit that can further improve the gain and bandwidth at specific frequencies.
The collector of the transistor VT2 is designed to accommodate the amplified high-frequency output. This output can be utilized in various applications, such as RF communication systems, signal processing, and other electronic devices requiring robust amplification of high-frequency signals.
Overall, this broadband high-frequency amplifying circuit is a versatile and essential component in modern electronic design, capable of delivering reliable performance across a broad spectrum of frequencies while maintaining signal integrity and minimizing distortion. Broadband high frequency amplifying circuit Shown as a broadband high frequency amplifying circuit, and is mainly composed of a high-frequency matching transformer amplifying t ransistor and the like, can be used to put a large high-frequency signals. High-frequency signal input of the amplifier circuit is to facilitate the matching transformer input signal transistor amplifier with high input impedance matching feature, but also has a wide frequency band characteristics, VT1 emitter capacitor and inductor are for the collector VT2 compensate the high frequency signal and mining take approach.
The broadband high-frequency amplifying circuit is engineered to amplify signals within a wide frequency range effectively. The inclusion of a high-frequency matching transformer is critical, as it provides impedance matching between the input signal and the transistor amplifier. This matching is essential for maximizing power transfer and minimizing signal reflection, which is particularly important in high-frequency applications.
The circuit typically employs a transistor, such as a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) or a field-effect transistor (FET), for amplification. The transistor's high input impedance allows it to receive signals without significantly loading the preceding stage, which is beneficial when interfacing with other circuit elements or sources.
The emitter capacitor connected to the transistor VT1 plays a dual role; it not only stabilizes the operating point of the transistor but also allows high-frequency signals to pass while blocking low-frequency signals, thus enhancing the circuit's frequency response. The inductor in conjunction with the capacitor forms a resonant circuit that can further improve the gain and bandwidth at specific frequencies.
The collector of the transistor VT2 is designed to accommodate the amplified high-frequency output. This output can be utilized in various applications, such as RF communication systems, signal processing, and other electronic devices requiring robust amplification of high-frequency signals.
Overall, this broadband high-frequency amplifying circuit is a versatile and essential component in modern electronic design, capable of delivering reliable performance across a broad spectrum of frequencies while maintaining signal integrity and minimizing distortion. Broadband high frequency amplifying circuit Shown as a broadband high frequency amplifying circuit, and is mainly composed of a high-frequency matching transformer amplifying t ransistor and the like, can be used to put a large high-frequency signals. High-frequency signal input of the amplifier circuit is to facilitate the matching transformer input signal transistor amplifier with high input impedance matching feature, but also has a wide frequency band characteristics, VT1 emitter capacitor and inductor are for the collector VT2 compensate the high frequency signal and mining take approach.