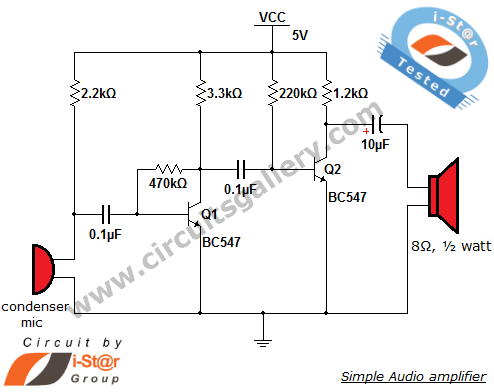
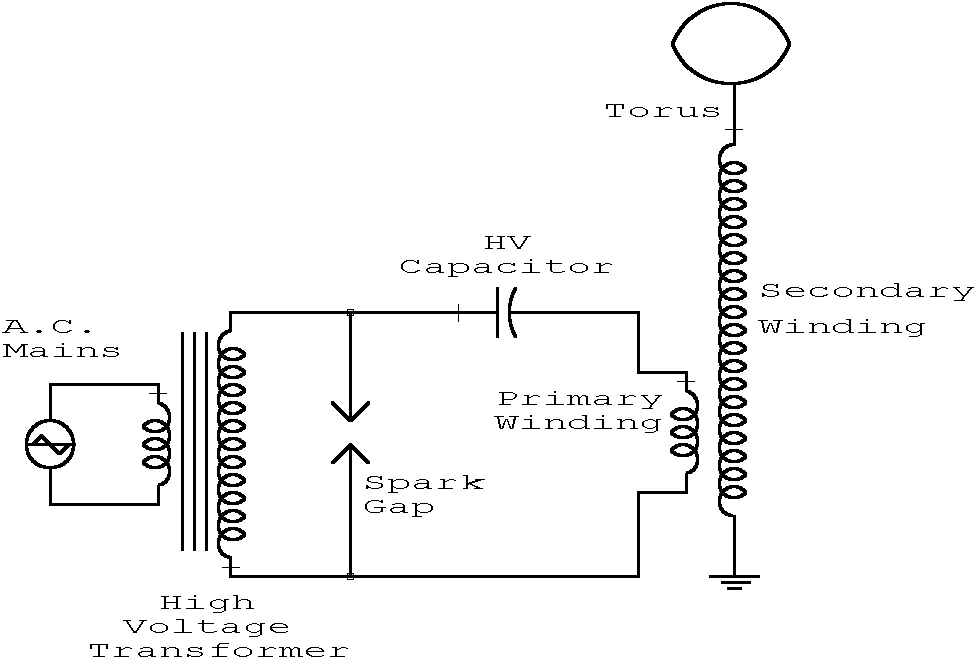
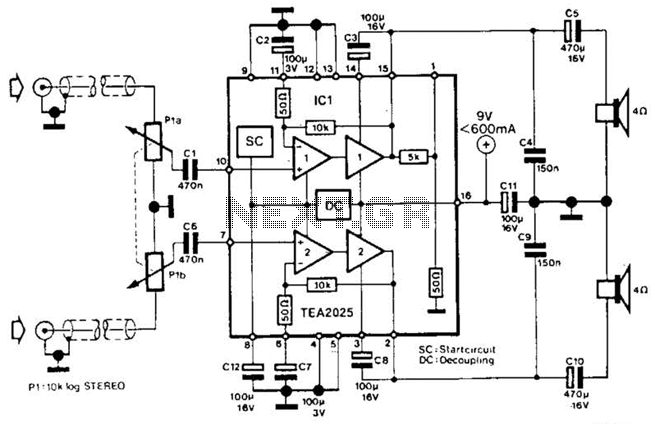
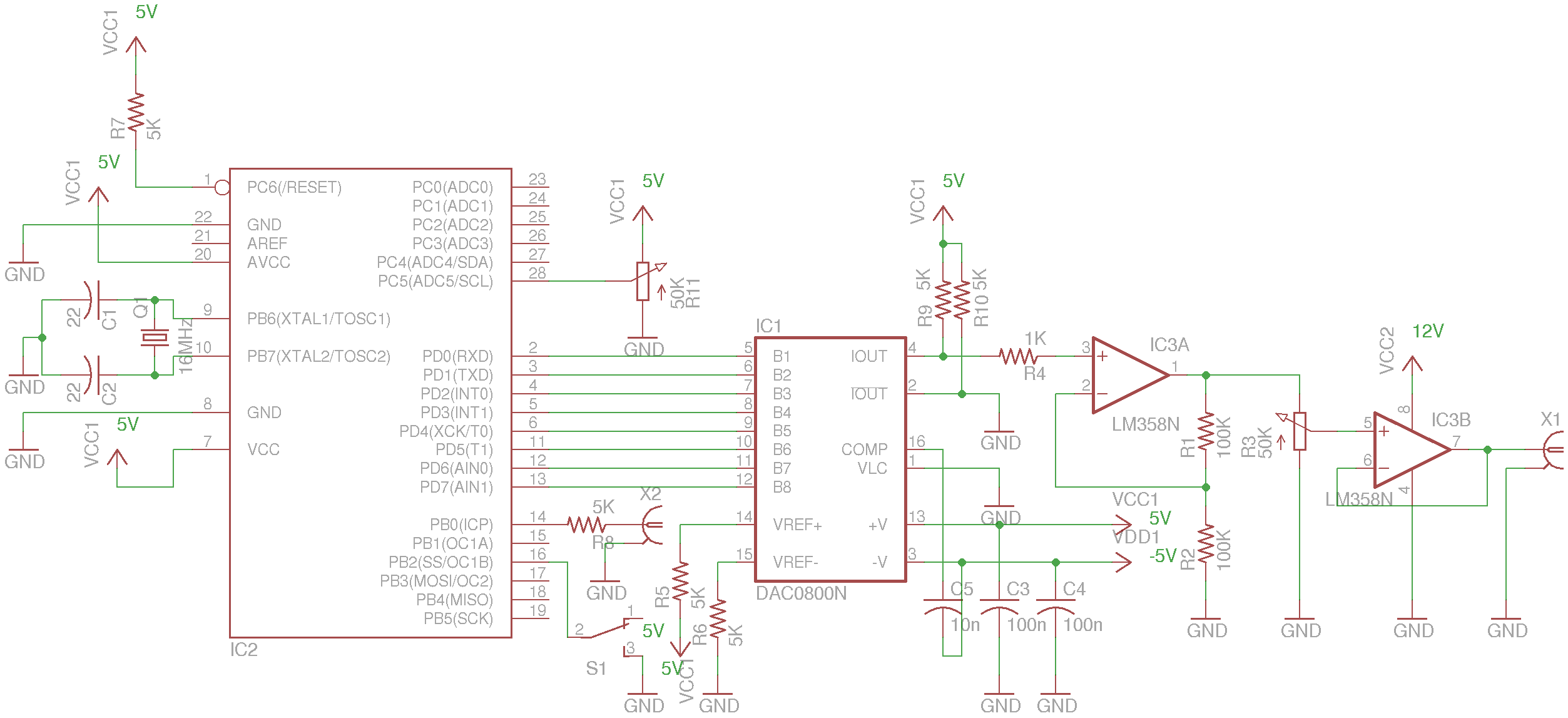
Building the poor-mans mini tesla coil
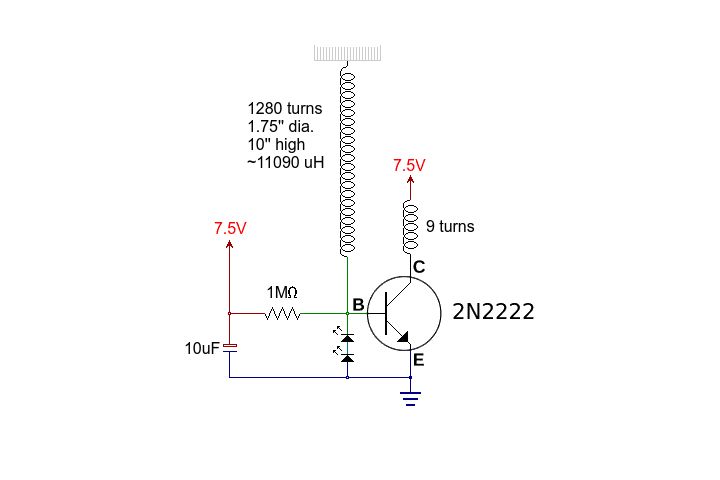
This circuit is straightforward. The accompanying graphics and images provide all necessary details. After gathering all materials, connect the transistor according to the provided schematic.
The circuit in question is a basic transistor circuit that serves as an introductory project for those learning about electronic components and their functions. The primary component, a transistor, acts as a switch or amplifier, depending on the configuration.
To construct the circuit, begin by identifying the type of transistor being used, whether it is a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) or a field-effect transistor (FET). Ensure that the transistor is oriented correctly, with the collector, base, and emitter (for BJT) or source, gate, and drain (for FET) properly aligned with the circuit schematic.
Next, gather the necessary materials, which typically include resistors, capacitors, and a power supply. Resistors may be used to limit the current flowing into the base of the transistor, while capacitors can provide stability and filtering in the circuit. The power supply should match the voltage requirements specified in the schematic to ensure proper operation.
Once all components are assembled, the wiring should follow the schematic closely, ensuring that all connections are secure and correctly positioned. It is advisable to use a breadboard for initial testing to allow for easy modifications if necessary. After wiring, double-check all connections before powering the circuit to prevent damage to components.
Upon successful assembly, the circuit can be tested by applying power and observing the behavior of the transistor. This may involve measuring voltage levels at various points or checking the output signal to confirm that the transistor is functioning as intended.
This simple circuit serves as an excellent foundation for understanding more complex electronic designs and principles.There is not much to this circuit. Above are all the graphics and pictures. After you gather all your materials, take your transistor and wire it up.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit in question is a basic transistor circuit that serves as an introductory project for those learning about electronic components and their functions. The primary component, a transistor, acts as a switch or amplifier, depending on the configuration.
To construct the circuit, begin by identifying the type of transistor being used, whether it is a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) or a field-effect transistor (FET). Ensure that the transistor is oriented correctly, with the collector, base, and emitter (for BJT) or source, gate, and drain (for FET) properly aligned with the circuit schematic.
Next, gather the necessary materials, which typically include resistors, capacitors, and a power supply. Resistors may be used to limit the current flowing into the base of the transistor, while capacitors can provide stability and filtering in the circuit. The power supply should match the voltage requirements specified in the schematic to ensure proper operation.
Once all components are assembled, the wiring should follow the schematic closely, ensuring that all connections are secure and correctly positioned. It is advisable to use a breadboard for initial testing to allow for easy modifications if necessary. After wiring, double-check all connections before powering the circuit to prevent damage to components.
Upon successful assembly, the circuit can be tested by applying power and observing the behavior of the transistor. This may involve measuring voltage levels at various points or checking the output signal to confirm that the transistor is functioning as intended.
This simple circuit serves as an excellent foundation for understanding more complex electronic designs and principles.There is not much to this circuit. Above are all the graphics and pictures. After you gather all your materials, take your transistor and wire it up.. 🔗 External reference