By the actual application circuit composed of a color picture tube with TDA6103Q
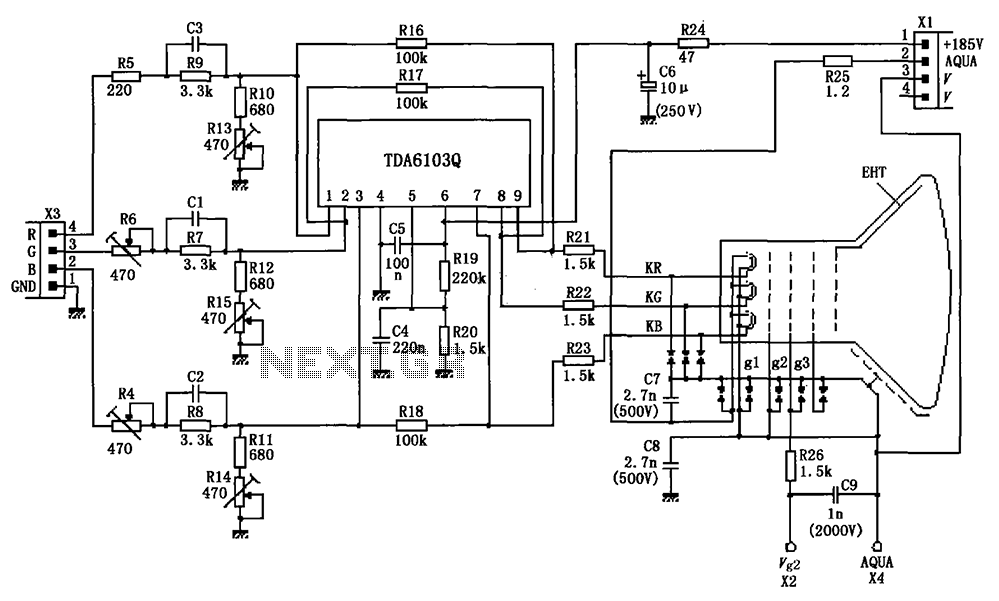
The circuit depicted in the figure integrates the TDA6103Q with a color picture tube, illustrating its practical application. The red, green, and blue (R, G, B) input signals are received from the input socket X3 and processed through a network of input resistors and capacitors before being fed into the TDA6103Q at pins 1, 2, and 3, respectively. The amplified output signals are then transmitted from pins 9, 8, and 7 through resistors R21, R22, and R23 to the three cathodes of the color picture tube: KR, KG, and KB. The emission of electrons from these cathodes generates the displayed images. The TDA6103Q is powered by a supply voltage connected to pin 1 of socket X1, providing +185V input voltage to pin 6 of the TDA6103Q. The circuit includes a network of potentiometers (R13, R6, R15, R4, R14) for white balance adjustment. Additionally, the cathodes of the color picture tube and the gate are designed with protective measures against gap discharge, ensuring that the output from the amplifier does not cause internal breakdown of the TDA6103Q during high-pressure discharges between the electrodes.
The TDA6103Q is a versatile RGB amplifier designed for driving color picture tubes. In this configuration, the input signals are conditioned through a resistor-capacitor network to ensure proper signal levels and frequency response before amplification. The output stage of the TDA6103Q provides the necessary drive currents to the cathodes of the color picture tube, where the emitted electrons interact with the phosphor coating on the inside of the tube to produce visible images.
The use of resistors R21, R22, and R23 is critical for controlling the current flowing to each cathode, allowing for precise color balance and intensity adjustments. The potentiometers included in the circuit offer a means to fine-tune the white balance, ensuring that the colors displayed on the screen are accurate and consistent. The careful selection of these components is essential for achieving optimal performance and maintaining image quality.
The protection against high-voltage discharge is a crucial aspect of this design, as it safeguards the TDA6103Q from potential damage due to electrical breakdown. This protective feature is particularly important in applications where high voltages are present, as it enhances the reliability and longevity of the circuit.
Overall, this schematic showcases a well-engineered solution for driving a color picture tube, emphasizing the importance of component selection, signal processing, and protective measures in high-voltage electronic applications. As shown in FIG grounds TDA6103Q and color picture tube composed of the actual application. R, G, B input signal from the input socket X3, through the input resistor network co nsists of capacitors into the TDA6103Q 1,2,3 feet, respectively, from the amplified signal output pin 9,8,7, through R21, R22, R23 is added to the color picture tube three cathodes KR, KG, KB, cathode emission electrons produce images. TDA6103Q supply voltage is provided by socket X1 pin 1 + 185V input voltage applied to TDA6103Q 6 feet.
Enter the network potentiometer R13, R6, R15, R4, R14 for the white balance adjustment potentiometer. Color picture tube cathode and the gate using protected forms gap discharge, the output of the amplifier to protect TDA6103Q internal breakdown will not be generated when the high pressure discharge between the electrodes.
The TDA6103Q is a versatile RGB amplifier designed for driving color picture tubes. In this configuration, the input signals are conditioned through a resistor-capacitor network to ensure proper signal levels and frequency response before amplification. The output stage of the TDA6103Q provides the necessary drive currents to the cathodes of the color picture tube, where the emitted electrons interact with the phosphor coating on the inside of the tube to produce visible images.
The use of resistors R21, R22, and R23 is critical for controlling the current flowing to each cathode, allowing for precise color balance and intensity adjustments. The potentiometers included in the circuit offer a means to fine-tune the white balance, ensuring that the colors displayed on the screen are accurate and consistent. The careful selection of these components is essential for achieving optimal performance and maintaining image quality.
The protection against high-voltage discharge is a crucial aspect of this design, as it safeguards the TDA6103Q from potential damage due to electrical breakdown. This protective feature is particularly important in applications where high voltages are present, as it enhances the reliability and longevity of the circuit.
Overall, this schematic showcases a well-engineered solution for driving a color picture tube, emphasizing the importance of component selection, signal processing, and protective measures in high-voltage electronic applications. As shown in FIG grounds TDA6103Q and color picture tube composed of the actual application. R, G, B input signal from the input socket X3, through the input resistor network co nsists of capacitors into the TDA6103Q 1,2,3 feet, respectively, from the amplified signal output pin 9,8,7, through R21, R22, R23 is added to the color picture tube three cathodes KR, KG, KB, cathode emission electrons produce images. TDA6103Q supply voltage is provided by socket X1 pin 1 + 185V input voltage applied to TDA6103Q 6 feet.
Enter the network potentiometer R13, R6, R15, R4, R14 for the white balance adjustment potentiometer. Color picture tube cathode and the gate using protected forms gap discharge, the output of the amplifier to protect TDA6103Q internal breakdown will not be generated when the high pressure discharge between the electrodes.