Capacitors
Capacitor types, their uses, formulas for common capacitance calculations, descriptions of charge pumps, information on dielectric soakage, and how to repair.
Capacitors are essential components in electronic circuits, serving various functions depending on their type and application. The primary types of capacitors include ceramic, electrolytic, tantalum, film, and supercapacitors, each with unique characteristics. Ceramic capacitors are widely used for high-frequency applications due to their low equivalent series resistance (ESR) and stability over temperature. Electrolytic capacitors are polarized and typically used for power supply filtering due to their high capacitance values. Tantalum capacitors offer high capacitance in a small package and are known for their reliability. Film capacitors are favored for their stability and low losses, making them suitable for audio and precision applications. Supercapacitors, or ultracapacitors, provide high energy storage and are used in applications requiring rapid charge and discharge cycles.
Capacitance calculations are fundamental to circuit design, with the capacitance value (C) expressed in farads (F). Common formulas include C = Q/V, where Q is the charge stored in coulombs and V is the voltage across the capacitor. For capacitors in series, the total capacitance (C_total) is calculated using the formula 1/C_total = 1/C1 + 1/C2 + ... + 1/Cn. In parallel configurations, the total capacitance is the sum of individual capacitances: C_total = C1 + C2 + ... + Cn.
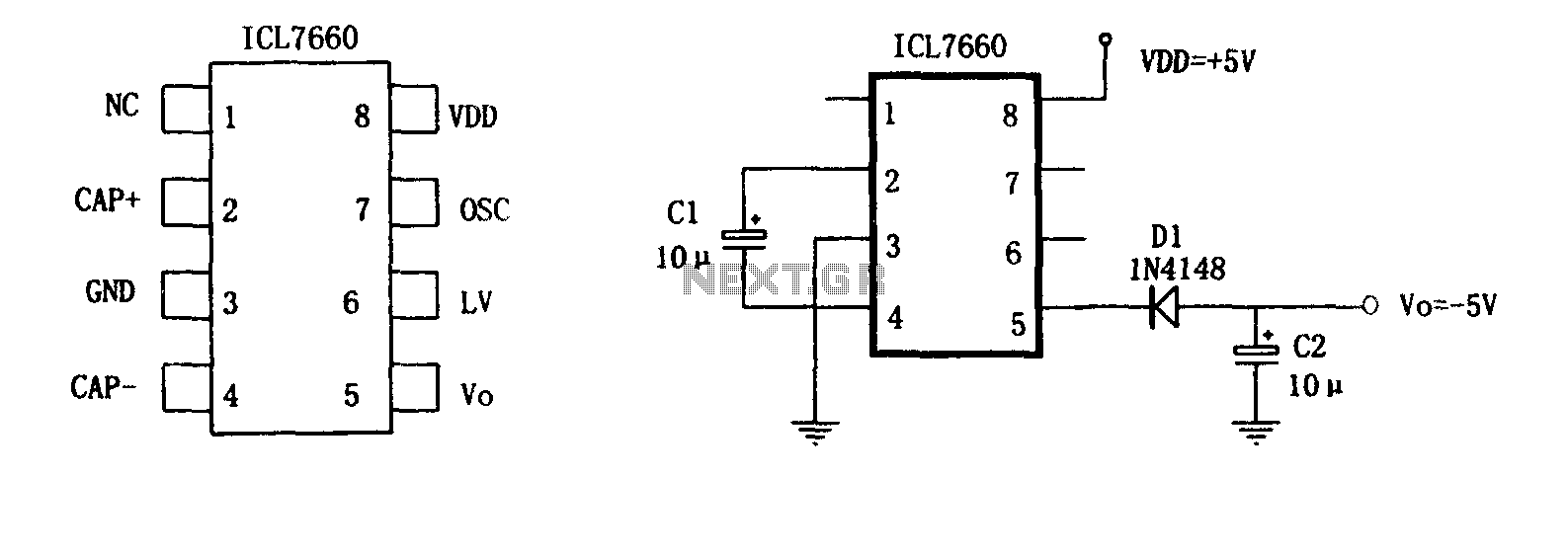
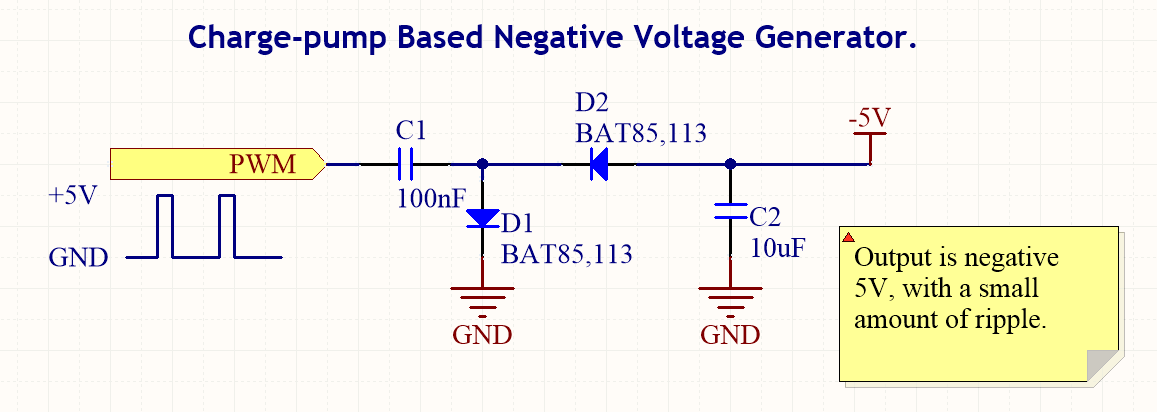
Charge pumps are specialized circuits that convert a low input voltage to a higher output voltage using capacitors as energy storage elements. They operate by alternately charging and discharging capacitors, effectively transferring charge to achieve voltage multiplication. Charge pumps are commonly used in applications such as battery-powered devices and voltage regulation circuits.
Dielectric soakage refers to the phenomenon where a capacitor's dielectric material absorbs moisture or contaminants, leading to changes in capacitance and performance. This issue can affect reliability and lifespan, particularly in high-humidity environments. Proper storage and handling of capacitors, along with selecting appropriate materials, can mitigate the effects of dielectric soakage.
Repairing capacitors typically involves assessing their condition, which may include testing for capacitance, ESR, and leakage current. If a capacitor is found to be defective, replacement with a component of equivalent specifications is necessary to restore circuit functionality. In some cases, reconditioning techniques may be employed for certain types of capacitors, although this is not always feasible or recommended.Capacitor types, their uses, formulas for common capacitance calculations, descriptions of charge pumps, info on dielectric soakage, and how to repair. 🔗 External reference
Capacitors are essential components in electronic circuits, serving various functions depending on their type and application. The primary types of capacitors include ceramic, electrolytic, tantalum, film, and supercapacitors, each with unique characteristics. Ceramic capacitors are widely used for high-frequency applications due to their low equivalent series resistance (ESR) and stability over temperature. Electrolytic capacitors are polarized and typically used for power supply filtering due to their high capacitance values. Tantalum capacitors offer high capacitance in a small package and are known for their reliability. Film capacitors are favored for their stability and low losses, making them suitable for audio and precision applications. Supercapacitors, or ultracapacitors, provide high energy storage and are used in applications requiring rapid charge and discharge cycles.
Capacitance calculations are fundamental to circuit design, with the capacitance value (C) expressed in farads (F). Common formulas include C = Q/V, where Q is the charge stored in coulombs and V is the voltage across the capacitor. For capacitors in series, the total capacitance (C_total) is calculated using the formula 1/C_total = 1/C1 + 1/C2 + ... + 1/Cn. In parallel configurations, the total capacitance is the sum of individual capacitances: C_total = C1 + C2 + ... + Cn.
Charge pumps are specialized circuits that convert a low input voltage to a higher output voltage using capacitors as energy storage elements. They operate by alternately charging and discharging capacitors, effectively transferring charge to achieve voltage multiplication. Charge pumps are commonly used in applications such as battery-powered devices and voltage regulation circuits.
Dielectric soakage refers to the phenomenon where a capacitor's dielectric material absorbs moisture or contaminants, leading to changes in capacitance and performance. This issue can affect reliability and lifespan, particularly in high-humidity environments. Proper storage and handling of capacitors, along with selecting appropriate materials, can mitigate the effects of dielectric soakage.
Repairing capacitors typically involves assessing their condition, which may include testing for capacitance, ESR, and leakage current. If a capacitor is found to be defective, replacement with a component of equivalent specifications is necessary to restore circuit functionality. In some cases, reconditioning techniques may be employed for certain types of capacitors, although this is not always feasible or recommended.Capacitor types, their uses, formulas for common capacitance calculations, descriptions of charge pumps, info on dielectric soakage, and how to repair. 🔗 External reference