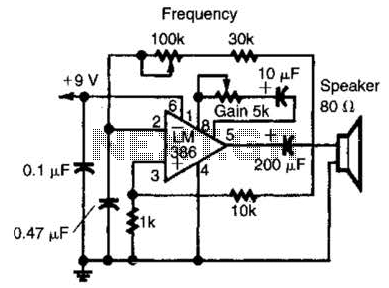
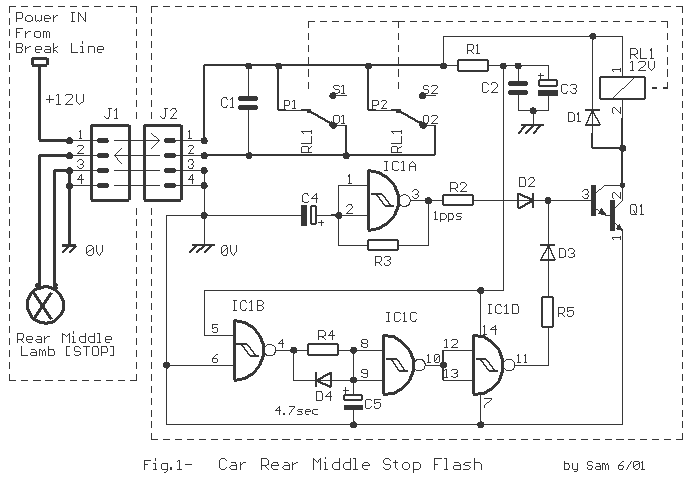
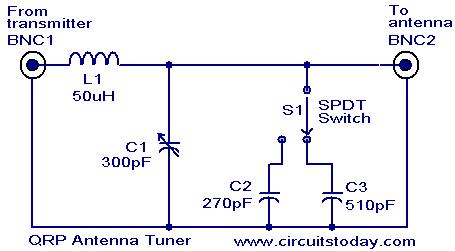
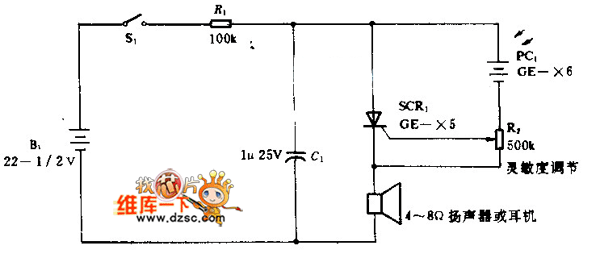
Car-Bulb Flasher circuit
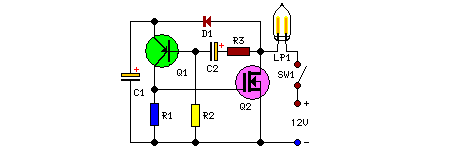
This remarkably straightforward circuit enables the operation of one or two robust 12V 21W car bulbs in a flashing mode using a power MOSFET. Such devices are especially suitable for road, traffic, and yard alerts, as well as in situations where a mains supply is unavailable but a strong flashing light is still required.
The circuit utilizes a power MOSFET to control the flashing operation of the car bulbs. The MOSFET acts as a switch that rapidly turns the bulbs on and off, creating a flashing effect. When designing this circuit, the specifications of the MOSFET must be carefully selected to ensure it can handle the voltage and current required by the 12V 21W bulbs.
To construct the circuit, the following components are necessary: a power MOSFET, resistors, capacitors, and a timer or oscillator circuit to generate the flashing frequency. The timer circuit can be built using a 555 timer IC configured in astable mode, which will provide a square wave output to the gate of the MOSFET. The duty cycle of the timer can be adjusted by varying the resistor and capacitor values, allowing for customization of the flashing rate.
The power supply for the circuit should be a 12V source capable of providing sufficient current to drive the bulbs. Proper heat sinking for the MOSFET is essential to prevent overheating during operation, especially when driving high-wattage bulbs.
In applications such as road and traffic alerts, the flashing lights can be mounted on vehicles or stationary posts to enhance visibility. The circuit's simplicity and effectiveness make it an ideal solution for various scenarios where powerful illumination is needed without access to traditional power sources.This astonishingly simple circuit allows one or two powerful 12V 21W car bulbs to be driven in flashing mode by means of a power MosFet. Devices of this kind are particularly suited for road, traffic and yard alerts and in all cases where mains supply are not available but a powerful flashing light are yet necessary..
🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes a power MOSFET to control the flashing operation of the car bulbs. The MOSFET acts as a switch that rapidly turns the bulbs on and off, creating a flashing effect. When designing this circuit, the specifications of the MOSFET must be carefully selected to ensure it can handle the voltage and current required by the 12V 21W bulbs.
To construct the circuit, the following components are necessary: a power MOSFET, resistors, capacitors, and a timer or oscillator circuit to generate the flashing frequency. The timer circuit can be built using a 555 timer IC configured in astable mode, which will provide a square wave output to the gate of the MOSFET. The duty cycle of the timer can be adjusted by varying the resistor and capacitor values, allowing for customization of the flashing rate.
The power supply for the circuit should be a 12V source capable of providing sufficient current to drive the bulbs. Proper heat sinking for the MOSFET is essential to prevent overheating during operation, especially when driving high-wattage bulbs.
In applications such as road and traffic alerts, the flashing lights can be mounted on vehicles or stationary posts to enhance visibility. The circuit's simplicity and effectiveness make it an ideal solution for various scenarios where powerful illumination is needed without access to traditional power sources.This astonishingly simple circuit allows one or two powerful 12V 21W car bulbs to be driven in flashing mode by means of a power MosFet. Devices of this kind are particularly suited for road, traffic and yard alerts and in all cases where mains supply are not available but a powerful flashing light are yet necessary..
🔗 External reference