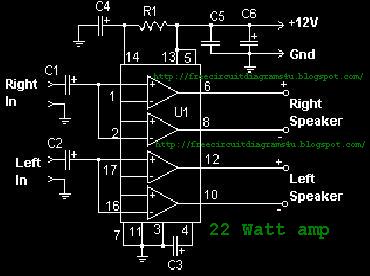
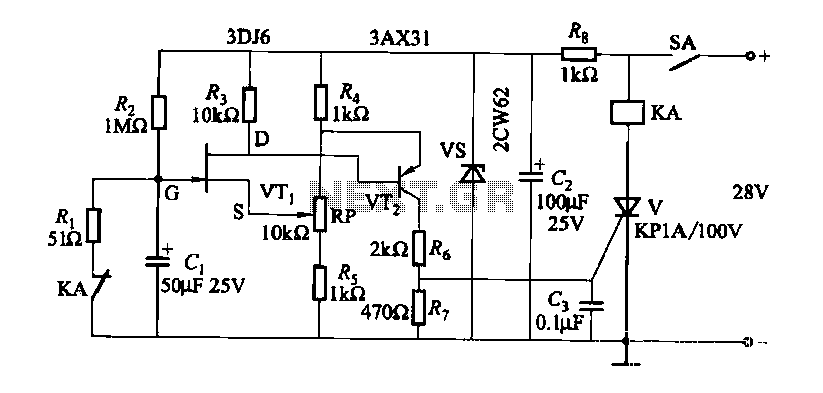
Cd Ignition System For Autos Circuit
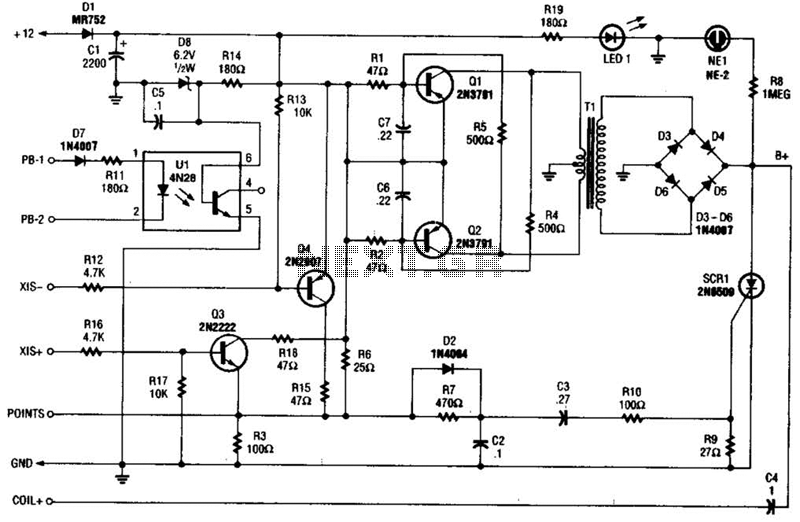
At the core of the CD4-MX is an astable multivibrator, constructed using transistors Q1 and Q2, which drives step-up transformer T1. The output from T1 is rectified by diodes D3 to D6 and utilized to charge capacitor C4. Upon the closure of the points, a small voltage is applied to the gate of SCR1, triggering it to discharge the charge stored in C4 into the vehicle's ignition coil. The circuit also features optional subcircuits to support various types of automotive ignitions. Terminals X15+ and X15- serve as alternative trigger configurations for non-point breaker ignition systems. Resistor R6 is not utilized in these configurations and should be removed. Optocoupler U1 can be employed (pin 4) in conjunction with X15- or X15+ depending on the sensor's polarity. It is important to note that the system can deliver 60 to 70 kV, thus appropriate safety precautions must be observed.
The CD4-MX circuit is designed to efficiently convert a low-frequency signal into a high-voltage output suitable for igniting an automotive ignition coil. The astable multivibrator configuration formed by Q1 and Q2 generates a continuous square wave, which drives the primary winding of transformer T1. The step-up transformer is critical as it increases the voltage to a level sufficient for ignition purposes.
The rectification stage, comprised of diodes D3 to D6, ensures that the alternating current output from the transformer is converted to direct current, which is then stored in capacitor C4. This storage allows for a quick release of energy upon the activation of SCR1. The firing of SCR1 is controlled by a voltage signal from the ignition points, which acts as a trigger. When the points close, the voltage applied to the gate of SCR1 allows it to conduct, effectively transferring the charge from C4 to the ignition coil, resulting in a spark necessary for engine ignition.
To accommodate different ignition systems, the circuit includes provisions for non-point breaker configurations through terminals X15+ and X15-. In such cases, the unused resistor R6 must be removed to prevent interference with the operation. The use of optocoupler U1 provides additional flexibility by allowing for isolation between the control signals and the high-voltage output, with its configuration depending on the polarity of the sensor used.
The design emphasizes safety, particularly given the potential output voltage of 60 to 70 kV. Proper safety measures, such as using insulated tools and ensuring that the circuit is not live during adjustments, are critical to prevent electrical hazards. Overall, the CD4-MX circuit is a versatile ignition system capable of adapting to various automotive applications while delivering reliable performance. At the heart of the CD4-MX is an astable multivibrator, built around Q1 and Q2, that feeds step-up transformer Tl. The output of 1 is rectified by D3 to D6 and used to charge capacitor C4. When the points close, a small voltage is fed to the gate of SCR1, causing it to fire, dumping the charge of C4 to the vehicle`s ignition coil.
The circuit also contains optional subcircuits to accommodate different types of auto ignitions.Xl5 + and X15 - are alternative trigger configurations for nonpoint breaker ignition systems. R6 is not used for these systems and must be removed. Optocoupler Ul can be used (pin 4) in conjunction withX15 - orXI5 + depending on polarity of sensor. Note that 60 to 70 kVis available from this system,,so observe suitable safety precautions.
The CD4-MX circuit is designed to efficiently convert a low-frequency signal into a high-voltage output suitable for igniting an automotive ignition coil. The astable multivibrator configuration formed by Q1 and Q2 generates a continuous square wave, which drives the primary winding of transformer T1. The step-up transformer is critical as it increases the voltage to a level sufficient for ignition purposes.
The rectification stage, comprised of diodes D3 to D6, ensures that the alternating current output from the transformer is converted to direct current, which is then stored in capacitor C4. This storage allows for a quick release of energy upon the activation of SCR1. The firing of SCR1 is controlled by a voltage signal from the ignition points, which acts as a trigger. When the points close, the voltage applied to the gate of SCR1 allows it to conduct, effectively transferring the charge from C4 to the ignition coil, resulting in a spark necessary for engine ignition.
To accommodate different ignition systems, the circuit includes provisions for non-point breaker configurations through terminals X15+ and X15-. In such cases, the unused resistor R6 must be removed to prevent interference with the operation. The use of optocoupler U1 provides additional flexibility by allowing for isolation between the control signals and the high-voltage output, with its configuration depending on the polarity of the sensor used.
The design emphasizes safety, particularly given the potential output voltage of 60 to 70 kV. Proper safety measures, such as using insulated tools and ensuring that the circuit is not live during adjustments, are critical to prevent electrical hazards. Overall, the CD4-MX circuit is a versatile ignition system capable of adapting to various automotive applications while delivering reliable performance. At the heart of the CD4-MX is an astable multivibrator, built around Q1 and Q2, that feeds step-up transformer Tl. The output of 1 is rectified by D3 to D6 and used to charge capacitor C4. When the points close, a small voltage is fed to the gate of SCR1, causing it to fire, dumping the charge of C4 to the vehicle`s ignition coil.
The circuit also contains optional subcircuits to accommodate different types of auto ignitions.Xl5 + and X15 - are alternative trigger configurations for nonpoint breaker ignition systems. R6 is not used for these systems and must be removed. Optocoupler Ul can be used (pin 4) in conjunction withX15 - orXI5 + depending on polarity of sensor. Note that 60 to 70 kVis available from this system,,so observe suitable safety precautions.