Circuit Diagram Of Slave Flash Light Control
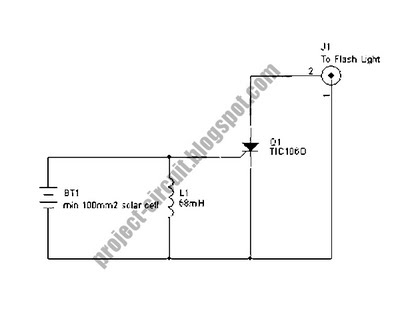
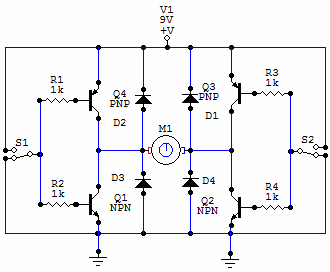
The following circuit illustrates a Slave Flash Light Control Circuit Diagram. Features include a 68 mH inductor, which provides an automatic trigger for the secondary flash light.
The Slave Flash Light Control Circuit is designed to enhance the functionality of flash lighting systems by enabling a secondary flash light to operate in conjunction with a primary flash. The circuit utilizes a 68 mH inductor, which plays a crucial role in the triggering mechanism. This inductor is responsible for storing energy and releasing it at the appropriate time to activate the secondary flash light.
The circuit typically comprises a power supply, a triggering mechanism, and the flash light components. The power supply provides the necessary voltage and current to the circuit, ensuring that both the primary and secondary flash lights function correctly. The triggering mechanism can be based on various sensors or timing circuits that detect the activation of the primary flash, subsequently sending a signal to the secondary flash light to illuminate.
The design may also incorporate additional components such as resistors, capacitors, and diodes to manage the flow of current, protect against voltage spikes, and filter signals. These elements work together to ensure a reliable and efficient operation of the slave flash light, providing enhanced lighting for photography or other applications where additional illumination is required.
Overall, the Slave Flash Light Control Circuit is an effective solution for achieving synchronized lighting, improving the versatility and performance of lighting setups.The following circuit shows about Slave Flash Light Control Circuit Diagram. Features: 68mH Inductor, give auto trigger for secondary flash light, .. 🔗 External reference
The Slave Flash Light Control Circuit is designed to enhance the functionality of flash lighting systems by enabling a secondary flash light to operate in conjunction with a primary flash. The circuit utilizes a 68 mH inductor, which plays a crucial role in the triggering mechanism. This inductor is responsible for storing energy and releasing it at the appropriate time to activate the secondary flash light.
The circuit typically comprises a power supply, a triggering mechanism, and the flash light components. The power supply provides the necessary voltage and current to the circuit, ensuring that both the primary and secondary flash lights function correctly. The triggering mechanism can be based on various sensors or timing circuits that detect the activation of the primary flash, subsequently sending a signal to the secondary flash light to illuminate.
The design may also incorporate additional components such as resistors, capacitors, and diodes to manage the flow of current, protect against voltage spikes, and filter signals. These elements work together to ensure a reliable and efficient operation of the slave flash light, providing enhanced lighting for photography or other applications where additional illumination is required.
Overall, the Slave Flash Light Control Circuit is an effective solution for achieving synchronized lighting, improving the versatility and performance of lighting setups.The following circuit shows about Slave Flash Light Control Circuit Diagram. Features: 68mH Inductor, give auto trigger for secondary flash light, .. 🔗 External reference