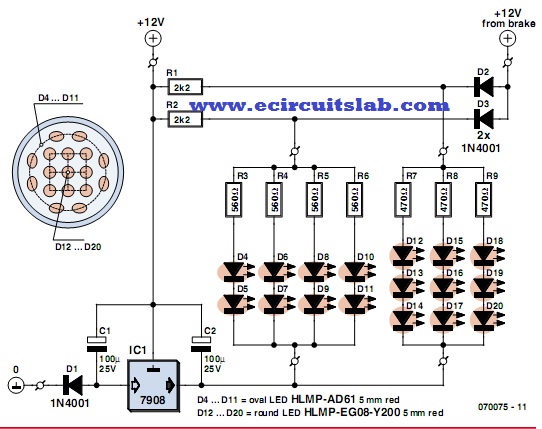
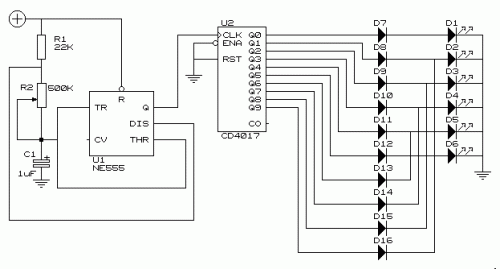
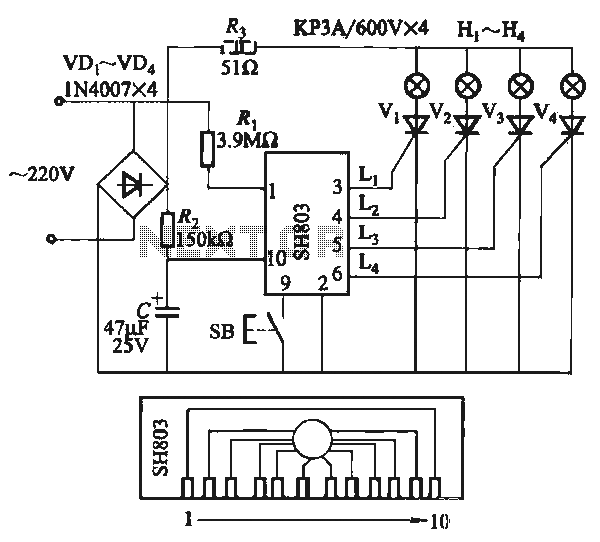
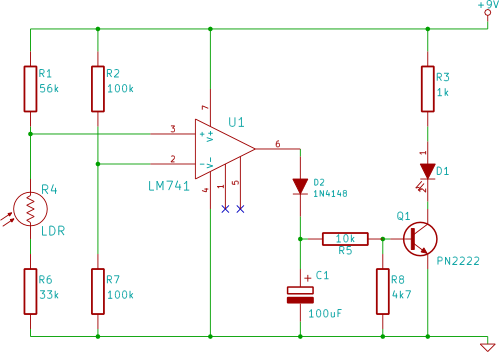
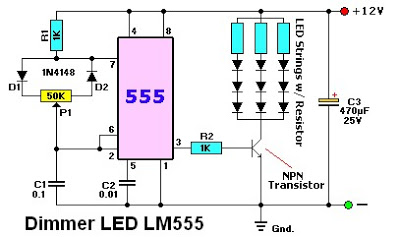
800 W soft start light dimmer
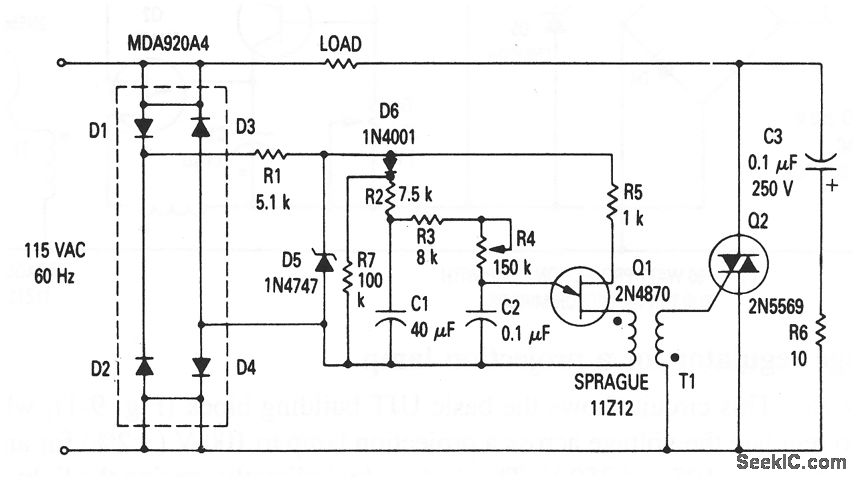
This circuit illustrates the fundamental UJT building block, utilized in a light dimmer with soft-start functionality. It gradually applies current to the light, effectively minimizing high surges (high inrush current) that typically occur in cold-filament light dimmers, which can reduce the lifespan of the lamp. The circuit ensures that the lamp is warmed slowly through a progressively increasing voltage, thereby keeping the inrush current to a minimum. Resistor R4 regulates the charging rate of capacitor C2, allowing for control over the dimming of the lamp.
The UJT (Uni-Junction Transistor) circuit serves as a crucial component in light dimming applications, particularly where the management of inrush current is necessary to enhance lamp longevity. The soft-start feature is essential for mitigating the abrupt initial surge that can occur when power is first applied to incandescent lamps, which can lead to filament damage and reduced operational life.
In this configuration, the UJT operates in conjunction with a resistor-capacitor (RC) timing network, where R4 and C2 play pivotal roles. The charging time of C2 is determined by the resistance value of R4. As C2 charges, the voltage across it rises until it reaches the UJT's triggering threshold. At this point, the UJT turns on, allowing current to flow through the lamp. The gradual increase in voltage across the lamp results in a soft illumination that prevents the immediate, high-power draw associated with conventional dimmers.
The circuit's design ensures that the dimming effect can be finely adjusted by varying the resistance of R4, which directly influences the rate at which C2 charges. This allows for a tailored dimming experience, accommodating different lamp types and user preferences. Additionally, the UJT's characteristics provide a stable and reliable switching mechanism, ensuring consistent performance over time.
Overall, this UJT-based light dimmer circuit exemplifies effective engineering principles aimed at enhancing the functionality and lifespan of lighting solutions while providing users with a seamless dimming experience.This circuit shows the basic UJT building block (Fig. 9-1), which is used in a light dimmer with soft-start operation that applies current to the light slowly enough to eliminate high surges (high inrush current). These current surges, found in most cold-filament light dimmers, shorten lamp life. With this circuit, the lamp is heated slowly by a g radually increasing voltage so that inrush current is kept to a minimum. R4 controls the charging rate of C2 and provides the means to control or dim the lamp. 🔗 External reference
The UJT (Uni-Junction Transistor) circuit serves as a crucial component in light dimming applications, particularly where the management of inrush current is necessary to enhance lamp longevity. The soft-start feature is essential for mitigating the abrupt initial surge that can occur when power is first applied to incandescent lamps, which can lead to filament damage and reduced operational life.
In this configuration, the UJT operates in conjunction with a resistor-capacitor (RC) timing network, where R4 and C2 play pivotal roles. The charging time of C2 is determined by the resistance value of R4. As C2 charges, the voltage across it rises until it reaches the UJT's triggering threshold. At this point, the UJT turns on, allowing current to flow through the lamp. The gradual increase in voltage across the lamp results in a soft illumination that prevents the immediate, high-power draw associated with conventional dimmers.
The circuit's design ensures that the dimming effect can be finely adjusted by varying the resistance of R4, which directly influences the rate at which C2 charges. This allows for a tailored dimming experience, accommodating different lamp types and user preferences. Additionally, the UJT's characteristics provide a stable and reliable switching mechanism, ensuring consistent performance over time.
Overall, this UJT-based light dimmer circuit exemplifies effective engineering principles aimed at enhancing the functionality and lifespan of lighting solutions while providing users with a seamless dimming experience.This circuit shows the basic UJT building block (Fig. 9-1), which is used in a light dimmer with soft-start operation that applies current to the light slowly enough to eliminate high surges (high inrush current). These current surges, found in most cold-filament light dimmers, shorten lamp life. With this circuit, the lamp is heated slowly by a g radually increasing voltage so that inrush current is kept to a minimum. R4 controls the charging rate of C2 and provides the means to control or dim the lamp. 🔗 External reference