Motor electronic speed controller circuit diagram 7
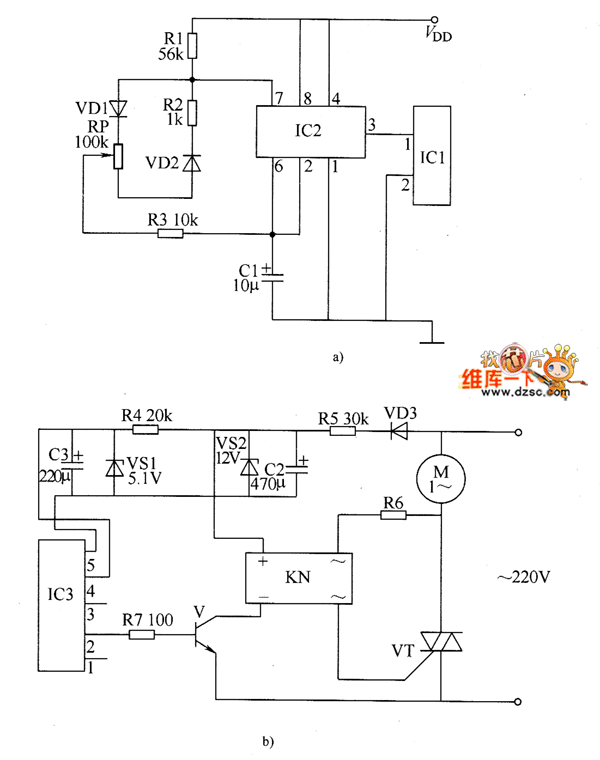
The electronic motor speed controller circuit includes a wireless remote control transmitter circuit and a wireless remote control receiver circuit, as illustrated in the accompanying chart. The wireless remote control transmitter circuit comprises a micro-power wireless remote control transmitter IC module (IC1), a time-base integrated circuit (IC2), and diodes VD1 and VD2.
The electronic motor speed controller circuit is designed to facilitate the remote control of motor speed, enhancing operational flexibility in various applications. The transmitter section utilizes a micro-power wireless remote control transmitter IC module (IC1) that generates control signals. This module is typically designed to operate at low power, ensuring longevity and efficiency in battery-operated devices.
The time-base integrated circuit (IC2) plays a critical role in generating precise timing signals, which are essential for modulating the output frequency sent to the motor. This modulation is vital for achieving varying speed levels in the motor operation. The inclusion of diodes VD1 and VD2 serves to protect the circuit from reverse polarity and voltage spikes, ensuring the integrity and longevity of the components.
The receiver circuit, which is not detailed in the initial description but is implied, would typically include a corresponding wireless receiver module that decodes the signals transmitted by the transmitter. This module would then relay the control signals to a motor driver circuit, which translates the signals into appropriate voltage and current levels to control the motor speed effectively.
Overall, the integration of these components enables a reliable and efficient wireless control system for motor speed regulation, suitable for applications ranging from remote-controlled vehicles to automated industrial processes.The electronic motor speed controller circuit consists of wireless remote control transmitter circuit, wireless remote control receiver control circuit, and it is shown as the chart. Wireless remote control transmitter circuit is composed of the micro-power wireless remote control transmitter IC module IC1, time-base integrated circuit IC2, diodes vD1, VD2,..
🔗 External reference
The electronic motor speed controller circuit is designed to facilitate the remote control of motor speed, enhancing operational flexibility in various applications. The transmitter section utilizes a micro-power wireless remote control transmitter IC module (IC1) that generates control signals. This module is typically designed to operate at low power, ensuring longevity and efficiency in battery-operated devices.
The time-base integrated circuit (IC2) plays a critical role in generating precise timing signals, which are essential for modulating the output frequency sent to the motor. This modulation is vital for achieving varying speed levels in the motor operation. The inclusion of diodes VD1 and VD2 serves to protect the circuit from reverse polarity and voltage spikes, ensuring the integrity and longevity of the components.
The receiver circuit, which is not detailed in the initial description but is implied, would typically include a corresponding wireless receiver module that decodes the signals transmitted by the transmitter. This module would then relay the control signals to a motor driver circuit, which translates the signals into appropriate voltage and current levels to control the motor speed effectively.
Overall, the integration of these components enables a reliable and efficient wireless control system for motor speed regulation, suitable for applications ranging from remote-controlled vehicles to automated industrial processes.The electronic motor speed controller circuit consists of wireless remote control transmitter circuit, wireless remote control receiver control circuit, and it is shown as the chart. Wireless remote control transmitter circuit is composed of the micro-power wireless remote control transmitter IC module IC1, time-base integrated circuit IC2, diodes vD1, VD2,..
🔗 External reference