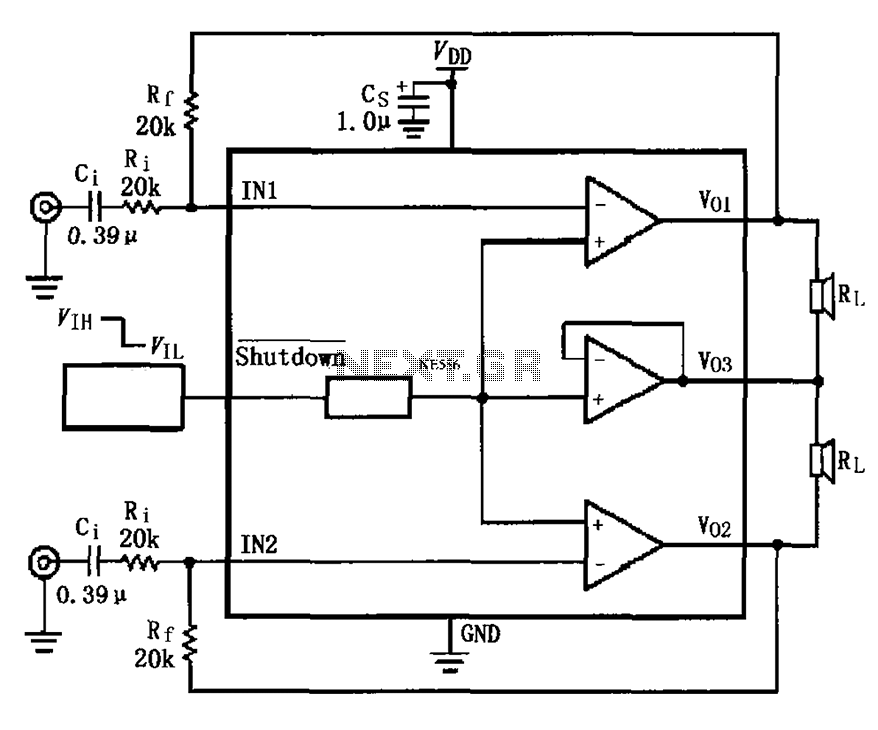
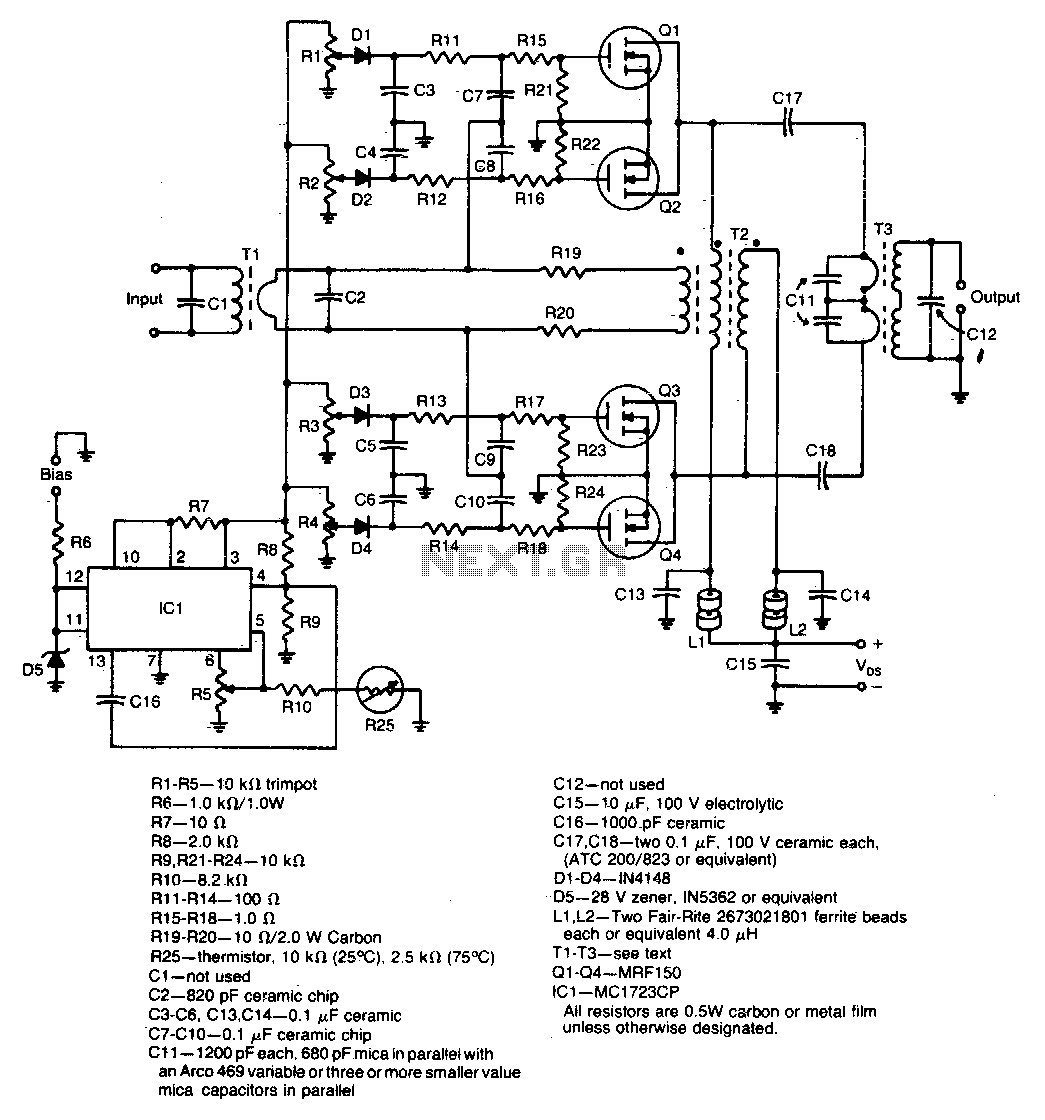
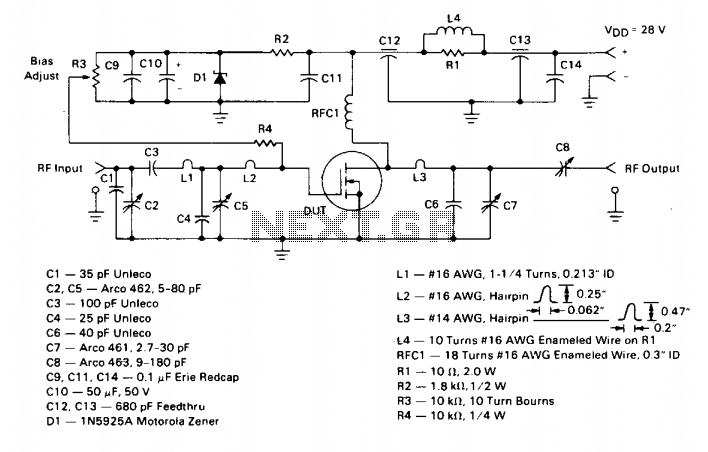
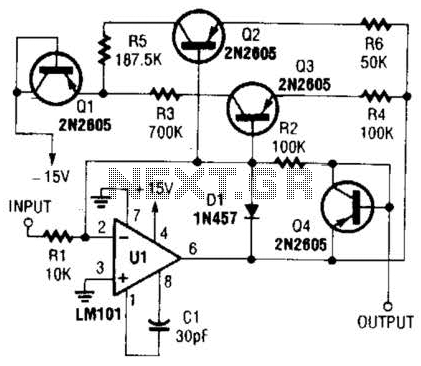
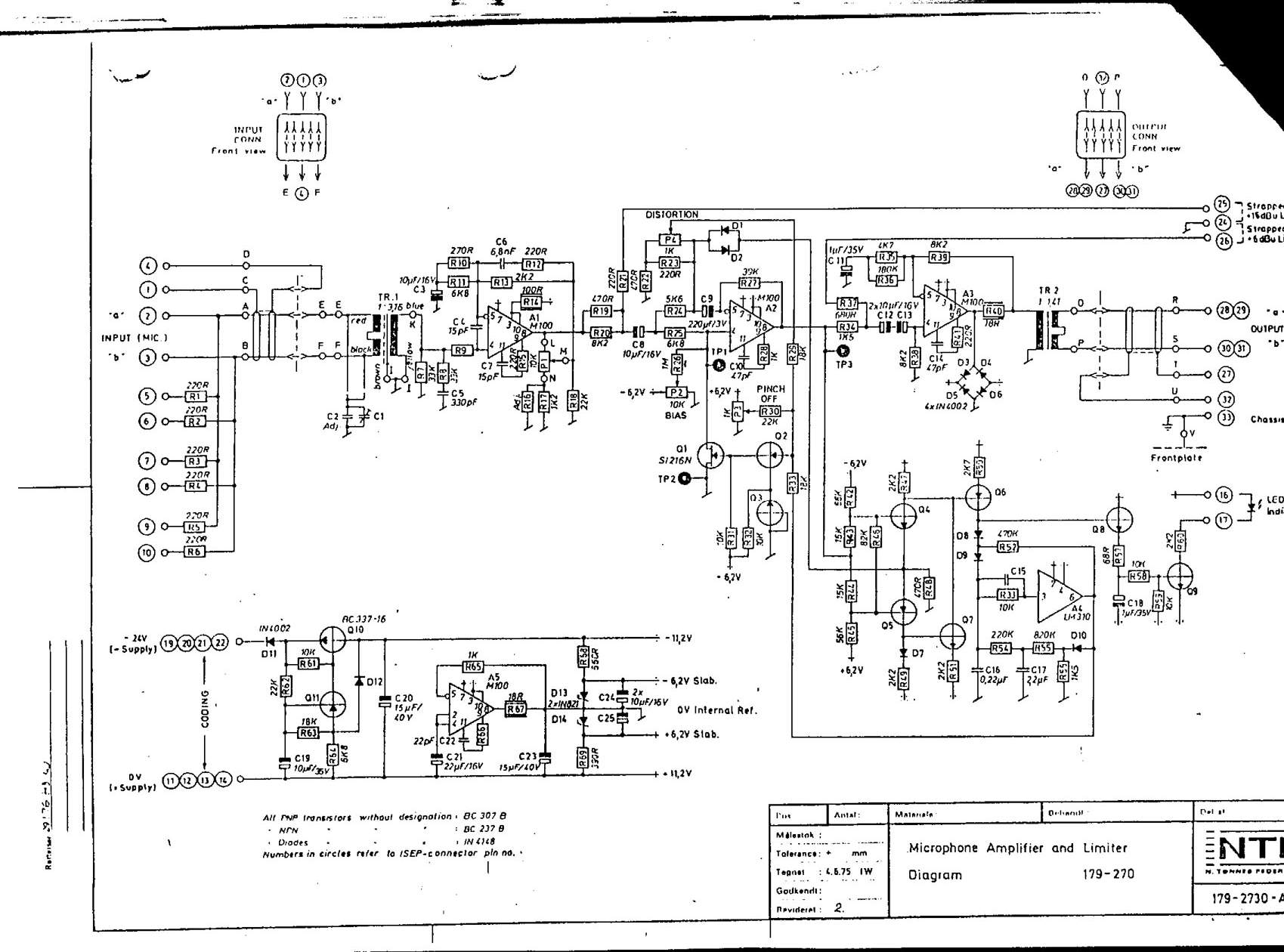
Class A-Designed Headphone Amplifier Using BC308 Transistor
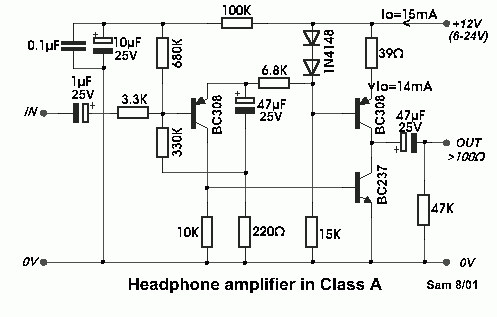
The circuit was designed based on the functionality of a Class A amplifier to create a headphone circuit. A BC308 epitaxial planar PNP transistor is utilized.
The Class A amplifier configuration is known for its linearity and low distortion, making it suitable for audio applications such as headphone amplification. In this specific circuit, the BC308 transistor serves as the primary amplifying element. This transistor is favored for its low noise characteristics and ability to handle small signal levels effectively.
The circuit typically includes a biasing network to set the operating point of the transistor in the active region, ensuring optimal performance. Resistors are used to establish the necessary biasing conditions, while capacitors may be integrated into the design to filter out unwanted high-frequency noise and provide stability.
Input coupling capacitors are employed to block any DC component from the audio source, allowing only the AC audio signal to pass through to the base of the transistor. The output stage is designed to drive headphones, which usually have a low impedance. Therefore, the circuit may include an output coupling capacitor to prevent any DC offset from reaching the headphones, ensuring that only the amplified audio signal is delivered.
Power supply decoupling capacitors are also essential in this design to maintain a stable voltage supply and minimize the effect of power supply fluctuations on the amplifier’s performance. Overall, this Class A headphone amplifier circuit, utilizing the BC308 transistor, is aimed at providing high-fidelity audio reproduction with minimal distortion and noise, making it suitable for high-quality headphone listening experiences.The circuit was constructed around the functionality of a Class A amplifier to create a headphone circuit. BC308 an epitaxial planar PNP transistor used.. 🔗 External reference
The Class A amplifier configuration is known for its linearity and low distortion, making it suitable for audio applications such as headphone amplification. In this specific circuit, the BC308 transistor serves as the primary amplifying element. This transistor is favored for its low noise characteristics and ability to handle small signal levels effectively.
The circuit typically includes a biasing network to set the operating point of the transistor in the active region, ensuring optimal performance. Resistors are used to establish the necessary biasing conditions, while capacitors may be integrated into the design to filter out unwanted high-frequency noise and provide stability.
Input coupling capacitors are employed to block any DC component from the audio source, allowing only the AC audio signal to pass through to the base of the transistor. The output stage is designed to drive headphones, which usually have a low impedance. Therefore, the circuit may include an output coupling capacitor to prevent any DC offset from reaching the headphones, ensuring that only the amplified audio signal is delivered.
Power supply decoupling capacitors are also essential in this design to maintain a stable voltage supply and minimize the effect of power supply fluctuations on the amplifier’s performance. Overall, this Class A headphone amplifier circuit, utilizing the BC308 transistor, is aimed at providing high-fidelity audio reproduction with minimal distortion and noise, making it suitable for high-quality headphone listening experiences.The circuit was constructed around the functionality of a Class A amplifier to create a headphone circuit. BC308 an epitaxial planar PNP transistor used.. 🔗 External reference