Constant Current Constant Voltage Switching Power Supply
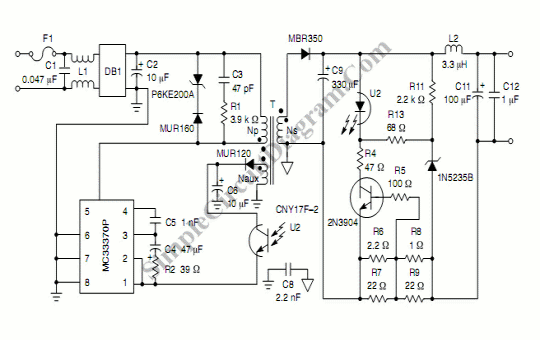
This circuit generates a constant current, constant voltage switched-mode power supply (SMPS). It is designed to efficiently charge a battery using a constant current, constant voltage approach.
The circuit operates as a constant current, constant voltage SMPS, which is crucial for battery charging applications. The design typically includes a control loop that regulates the output voltage and current to ensure that the battery is charged efficiently while preventing overcharging, which can damage the battery.
The main components of the circuit include a power switch (usually a MOSFET), an inductor, a diode, and a feedback mechanism that monitors the output voltage and current. The power switch is controlled by a pulse-width modulation (PWM) signal, which adjusts the duty cycle to maintain the desired output voltage and current levels.
During the constant current phase, the circuit limits the output current to a predetermined value, ensuring that the battery is charged safely without exceeding its maximum current rating. Once the battery voltage reaches a specified threshold, the circuit transitions to the constant voltage phase, where it maintains the output voltage at the target level while allowing the current to taper off as the battery approaches full charge.
Additional features may include protection mechanisms such as over-voltage protection (OVP), over-current protection (OCP), and thermal shutdown to enhance reliability and safety. The design may also incorporate input filtering to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and improve overall performance.
This SMPS circuit is particularly beneficial in applications requiring efficient battery charging, such as in electric vehicles, portable electronics, and renewable energy systems, where maximizing charging efficiency and battery lifespan is essential.This is a circuit that produces constant current constant voltage SMPS. To efficiently charge a battery, we can use constant current constant voltage SMPS.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates as a constant current, constant voltage SMPS, which is crucial for battery charging applications. The design typically includes a control loop that regulates the output voltage and current to ensure that the battery is charged efficiently while preventing overcharging, which can damage the battery.
The main components of the circuit include a power switch (usually a MOSFET), an inductor, a diode, and a feedback mechanism that monitors the output voltage and current. The power switch is controlled by a pulse-width modulation (PWM) signal, which adjusts the duty cycle to maintain the desired output voltage and current levels.
During the constant current phase, the circuit limits the output current to a predetermined value, ensuring that the battery is charged safely without exceeding its maximum current rating. Once the battery voltage reaches a specified threshold, the circuit transitions to the constant voltage phase, where it maintains the output voltage at the target level while allowing the current to taper off as the battery approaches full charge.
Additional features may include protection mechanisms such as over-voltage protection (OVP), over-current protection (OCP), and thermal shutdown to enhance reliability and safety. The design may also incorporate input filtering to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and improve overall performance.
This SMPS circuit is particularly beneficial in applications requiring efficient battery charging, such as in electric vehicles, portable electronics, and renewable energy systems, where maximizing charging efficiency and battery lifespan is essential.This is a circuit that produces constant current constant voltage SMPS. To efficiently charge a battery, we can use constant current constant voltage SMPS.. 🔗 External reference