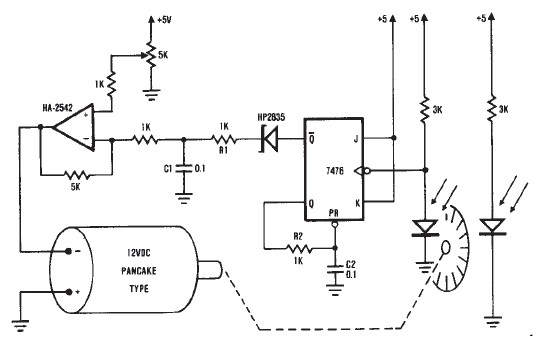
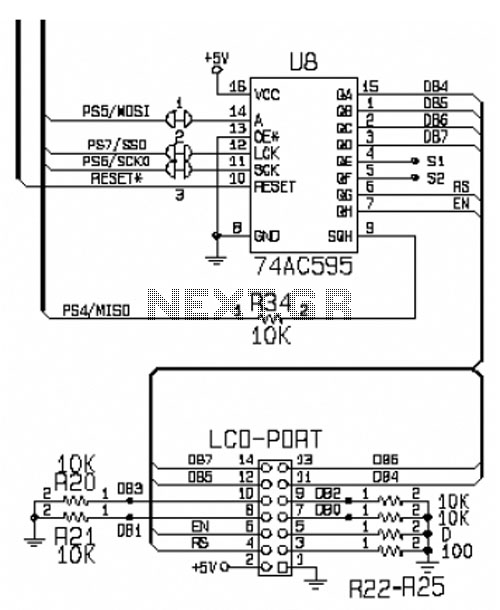
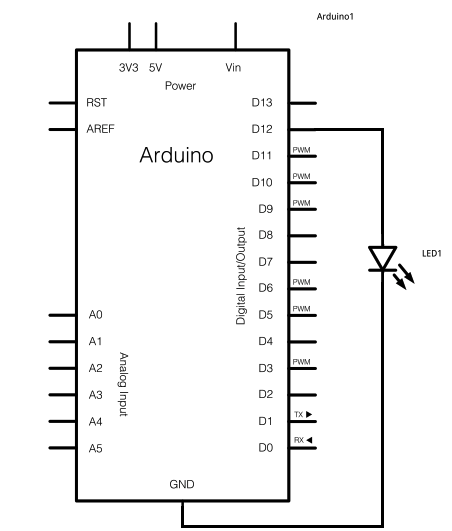
Control 7 segment LED displays with AVR
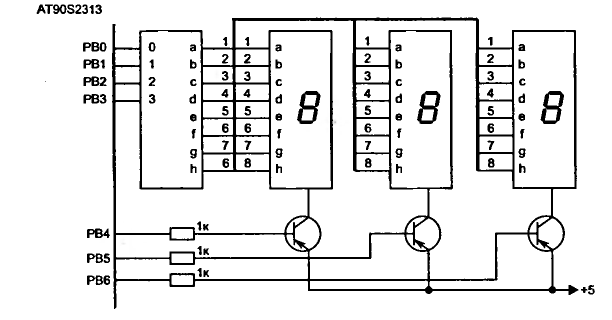
LED displays consist of arrays of Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) arranged in various shapes to convey specific information. The operation of LED displays is similar to that of standard LEDs, requiring straightforward connections when sufficient microcontroller pins are available. However, when connecting multiple displays, additional microcontroller pins may be necessary. To address this limitation, a more sophisticated circuit utilizing dynamic control is required. The fundamental principle behind this circuit is based on the human eye's inability to perceive rapid flickering. Therefore, only one display is illuminated at a time, with quick transitions between displays. Refreshing the displays at a rate of 10 to 15 times per second is typically adequate to present a clear image of all digits.
LED displays are widely utilized in various applications, ranging from digital clocks and scoreboards to more complex information panels. Each LED in the display can be individually controlled, allowing for the creation of numbers, letters, and custom symbols depending on the configuration of the diodes. When designing a circuit for driving multiple LED displays, it is essential to consider the microcontroller's output capabilities, as each additional display will require more pins for control.
To implement dynamic control, a multiplexing technique is often employed. In this method, the displays are connected in such a way that only one display is activated at any given moment. A microcontroller can cycle through the displays rapidly, turning each on for a brief period while the others remain off. This rapid switching takes advantage of the persistence of vision effect, where the human eye perceives a continuous image rather than discrete flashes of light.
The circuit typically includes a microcontroller, resistors for current limiting, and transistors or MOSFETs for switching the displays on and off. The microcontroller will execute a program to control the timing and sequence of the displays, ensuring that each one is illuminated long enough for the eye to perceive the information clearly. The use of multiplexing not only conserves microcontroller pins but also reduces power consumption, as only one display is powered at a time.
In summary, LED displays are effective tools for visual communication, and their operation can be efficiently managed through dynamic control techniques such as multiplexing. This approach allows for the display of complex information while optimizing the use of available microcontroller resources.LED displays are nothing more than sets of Light Emitting Diodes. The difference is that they have different shapes in order to display specific information. So driving LED displays is the same as regular LEDs. This is simple connection when there are enough of microcontroller Pins. But if you want to connect more displays you will need more micro controller pins than it can give you. Then you need to make more advanced circuit with dynamic control. The idea of this circuit is very simple. Human eye is inertial and can`t notice fast flicker of images. Thus you need to light only one display at one time, and then switch to another and so on. Refreshing displays like 10 15 times a second should be enough to see clear image of all digits. We aim to transmit more information by carrying articles. Please send us an E-mail to wanghuali@hqew. net within 15 days if we are involved in the problems of article content, copyright or other problems. We will delete it soon. 🔗 External reference
LED displays are widely utilized in various applications, ranging from digital clocks and scoreboards to more complex information panels. Each LED in the display can be individually controlled, allowing for the creation of numbers, letters, and custom symbols depending on the configuration of the diodes. When designing a circuit for driving multiple LED displays, it is essential to consider the microcontroller's output capabilities, as each additional display will require more pins for control.
To implement dynamic control, a multiplexing technique is often employed. In this method, the displays are connected in such a way that only one display is activated at any given moment. A microcontroller can cycle through the displays rapidly, turning each on for a brief period while the others remain off. This rapid switching takes advantage of the persistence of vision effect, where the human eye perceives a continuous image rather than discrete flashes of light.
The circuit typically includes a microcontroller, resistors for current limiting, and transistors or MOSFETs for switching the displays on and off. The microcontroller will execute a program to control the timing and sequence of the displays, ensuring that each one is illuminated long enough for the eye to perceive the information clearly. The use of multiplexing not only conserves microcontroller pins but also reduces power consumption, as only one display is powered at a time.
In summary, LED displays are effective tools for visual communication, and their operation can be efficiently managed through dynamic control techniques such as multiplexing. This approach allows for the display of complex information while optimizing the use of available microcontroller resources.LED displays are nothing more than sets of Light Emitting Diodes. The difference is that they have different shapes in order to display specific information. So driving LED displays is the same as regular LEDs. This is simple connection when there are enough of microcontroller Pins. But if you want to connect more displays you will need more micro controller pins than it can give you. Then you need to make more advanced circuit with dynamic control. The idea of this circuit is very simple. Human eye is inertial and can`t notice fast flicker of images. Thus you need to light only one display at one time, and then switch to another and so on. Refreshing displays like 10 15 times a second should be enough to see clear image of all digits. We aim to transmit more information by carrying articles. Please send us an E-mail to wanghuali@hqew. net within 15 days if we are involved in the problems of article content, copyright or other problems. We will delete it soon. 🔗 External reference