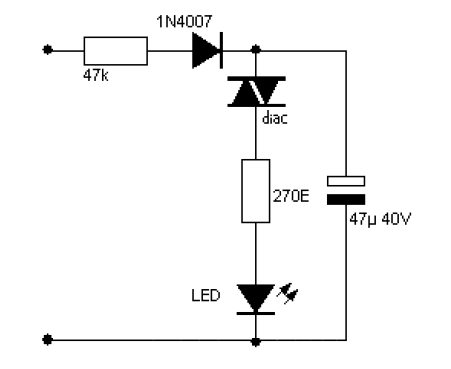
Sound Controlled Activated Triggered LED
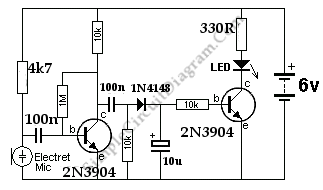
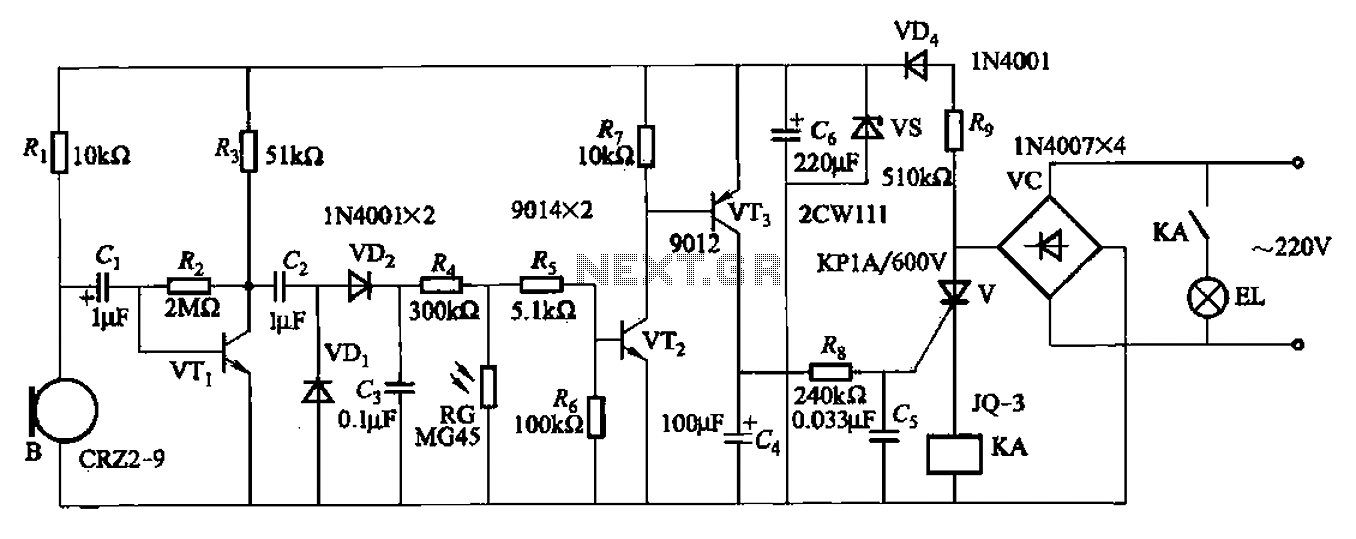
When the microphone detects a loud sound, this circuit will activate the LED. The charge pump section includes a 100nF capacitor, a 10kΩ resistor, a signal diode, and a uF capacitor.
The circuit operates by utilizing a microphone to sense sound levels. When a sound exceeds a predetermined threshold, the microphone generates a corresponding electrical signal. This signal is then processed by the charge pump section, which is designed to increase the voltage to a level sufficient to power the LED.
The charge pump consists of several critical components. The 100nF capacitor is used for energy storage, allowing the circuit to maintain a stable output voltage during operation. The 10kΩ resistor serves to limit the current flowing through the microphone and the subsequent components, ensuring that the microphone operates within its safe limits and preventing damage.
The signal diode plays a crucial role in directing the flow of current within the circuit. It allows current to flow in one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction, which helps to prevent backflow that could damage the circuit components. Additionally, the uF capacitor (the exact value should be specified for precise functionality) further stabilizes the output voltage, smoothing out any fluctuations that may occur during operation.
When the microphone detects a loud sound, the generated signal activates the charge pump, which in turn powers the LED. This visual indicator serves as an alert, signaling that a loud sound has been detected. The circuit can be applied in various applications, such as sound level monitoring systems, alarms, or audio equipment to provide visual feedback on sound levels. Proper selection of components and their values is essential to ensure responsive and reliable operation of the circuit.When the microphone detects a loud sound, this circuit will turn the LED on. The `charge-pump` section consists of the 100n, 10k, signal diode and uF.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by utilizing a microphone to sense sound levels. When a sound exceeds a predetermined threshold, the microphone generates a corresponding electrical signal. This signal is then processed by the charge pump section, which is designed to increase the voltage to a level sufficient to power the LED.
The charge pump consists of several critical components. The 100nF capacitor is used for energy storage, allowing the circuit to maintain a stable output voltage during operation. The 10kΩ resistor serves to limit the current flowing through the microphone and the subsequent components, ensuring that the microphone operates within its safe limits and preventing damage.
The signal diode plays a crucial role in directing the flow of current within the circuit. It allows current to flow in one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction, which helps to prevent backflow that could damage the circuit components. Additionally, the uF capacitor (the exact value should be specified for precise functionality) further stabilizes the output voltage, smoothing out any fluctuations that may occur during operation.
When the microphone detects a loud sound, the generated signal activates the charge pump, which in turn powers the LED. This visual indicator serves as an alert, signaling that a loud sound has been detected. The circuit can be applied in various applications, such as sound level monitoring systems, alarms, or audio equipment to provide visual feedback on sound levels. Proper selection of components and their values is essential to ensure responsive and reliable operation of the circuit.When the microphone detects a loud sound, this circuit will turn the LED on. The `charge-pump` section consists of the 100n, 10k, signal diode and uF.. 🔗 External reference