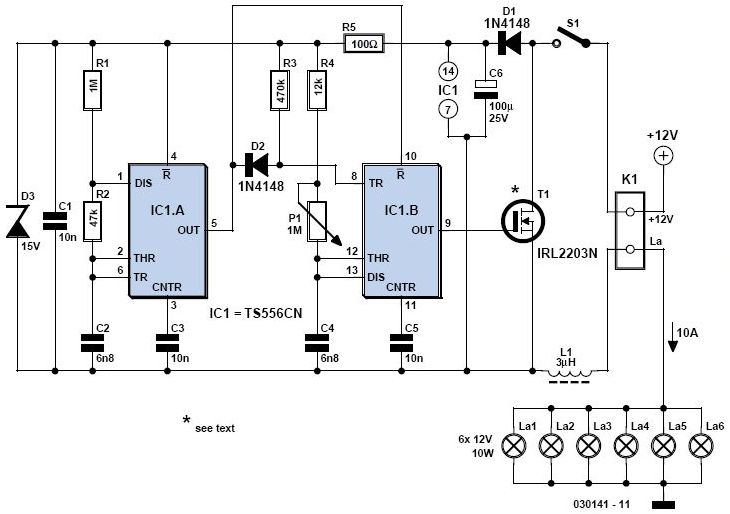
Count Down Timer Circuit
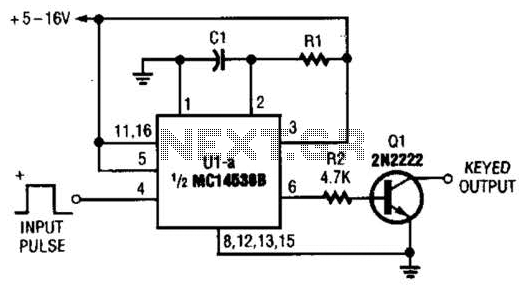
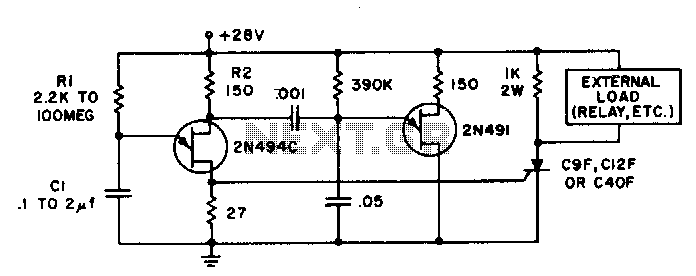
With switch SI in the off position, battery voltage is applied across timing capacitor CI, which remains charged while the rest of the circuitry is powered off. Transistor Q1, and consequently transistors Q2 through Q4, remain in an off state as long as capacitor CI maintains a sufficient charge.
In this circuit configuration, the switch SI is utilized to control the overall power supply to the system. When SI is in the off position, it allows the battery voltage to charge the timing capacitor CI. This capacitor plays a crucial role in maintaining the power state of the circuit, as it provides a temporary power source that can keep certain components inactive while preventing power from flowing to the rest of the circuitry.
Transistor Q1 serves as the main control element in this setup. When capacitor CI is charged, it ensures that Q1 remains in an off state. This state is critical, as it prevents the subsequent transistors Q2, Q3, and Q4 from turning on. These transistors are likely configured in a cascading manner, where the state of Q1 directly influences the operation of Q2 through Q4.
The design implies that the timing capacitor CI is selected based on the desired delay or timing characteristics required for the application. The charging time of CI will dictate how long the circuit remains inactive before any further action can take place. This aspect is crucial in applications where a delay is necessary before activating the main circuitry, allowing for controlled startup sequences or power management.
Overall, this circuit demonstrates a simple yet effective method for controlling power distribution within an electronic system, leveraging the properties of capacitors and transistors to achieve desired operational states without unnecessary power consumption. With switch SI in the off position, as shown, battery voltage is applied across timing-capacitor CI, which stays charged while the rest of the circuitry has no power supplied to it. Transistor Ql, and thus transistors Q2 through Q4, are kept in an off condition as long as CI has a sufficient charge.
In this circuit configuration, the switch SI is utilized to control the overall power supply to the system. When SI is in the off position, it allows the battery voltage to charge the timing capacitor CI. This capacitor plays a crucial role in maintaining the power state of the circuit, as it provides a temporary power source that can keep certain components inactive while preventing power from flowing to the rest of the circuitry.
Transistor Q1 serves as the main control element in this setup. When capacitor CI is charged, it ensures that Q1 remains in an off state. This state is critical, as it prevents the subsequent transistors Q2, Q3, and Q4 from turning on. These transistors are likely configured in a cascading manner, where the state of Q1 directly influences the operation of Q2 through Q4.
The design implies that the timing capacitor CI is selected based on the desired delay or timing characteristics required for the application. The charging time of CI will dictate how long the circuit remains inactive before any further action can take place. This aspect is crucial in applications where a delay is necessary before activating the main circuitry, allowing for controlled startup sequences or power management.
Overall, this circuit demonstrates a simple yet effective method for controlling power distribution within an electronic system, leveraging the properties of capacitors and transistors to achieve desired operational states without unnecessary power consumption. With switch SI in the off position, as shown, battery voltage is applied across timing-capacitor CI, which stays charged while the rest of the circuitry has no power supplied to it. Transistor Ql, and thus transistors Q2 through Q4, are kept in an off condition as long as CI has a sufficient charge.